(Press-News.org) Neuroticism may moderate the relationship between certain personality traits and self-control, and the interaction effects appear to differ by the type of self-control, according to a study published August 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fredrik Nilsen from the University of Oslo and the Norwegian Defence University, Norway, and colleagues.
Self-control is important for mental and physical health, and certain personality traits are linked to the trait. Previous studies suggest that conscientiousness and extraversion enhance self-control, whereas neuroticism hampers it. However, the link between personality and self-control has mostly been studied using a narrow conceptualization of self-control, and no previous studies examined whether and how personality traits interact with one another to increase, or reduce, self-control.
To fill this knowledge gap, Nilsen and colleagues collected data from 480 military cadets to examine the relationship between the Big Five personality traits (openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism) and self-control dimensions (general, inhibitory, and initiatory self-control). Inhibitory self-control reflects the ability to resist temptation, whereas initiatory self-control is the ability to initiate proactive actions to achieve long-term goals. The authors also investigated how neuroticism might moderate the relationship between other personality traits and self-control.
Participants scoring highly for neuroticism tended to score lower for general and inhibitory self-control, after controlling for the effect of other variables – a negative correlation. A positive correlation was seen for extraversion and conscientiousness, with participants scoring highly on these traits being more likely to also score highly on self-control dimensions. Openness and agreeableness traits did not consistently link with self-control after controlling for other variables.
The researchers found that neuroticism negatively moderated the relationship between extraversion and both general and inhibitory self-control, and the relationship between conscientiousness and both general and initiatory self-control, such that extroverted or conscientious participants scored less highly than otherwise expected for these types of self-control if they were also highly neurotic.
According to the authors, one take-home message from the study is that it is important to differentiate between the types of self-control when studying their relationship with personality traits – in particular, we should distinguish between inhibitory self-control and initiatory self-control.
The study may have practical implications, since self-control can be a valuable resource for good health, success, and proper conduct. For example, knowledge about strengths and weaknesses of personality profiles and their accompanying self-control qualities might help select individuals for professions that require high self-control. In clinical and personal growth settings, the development and training of self-control may benefit from an increased understanding of the relationship between personality profiles and self-control patterns.
The authors add: “Our research reveals a more complicated relationship between personality traits and self-control than is previously found. First, there are two different types of self-control – the ability to inhibit impulses, and the ability to initiate proactive actions – and personality traits are differently related to these two ways of exhibiting self-control. Second, the level of neuroticism can significantly alter the relationship between personality traits like conscientiousness and extraversion, and self-control. Understanding the nuanced interplay between personality and self-control can help to find more effective ways to select individuals for roles that demand high levels of self-control, and to design interventions for developing self-control.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0307871
Citation: Nilsen FA, Bang H, Røysamb E (2024) Personality traits and self-control: The moderating role of neuroticism. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0307871. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0307871
Author Countries: Norway
Funding: E.R. was supported by the Research Council of Norway, Grant 288083. https://www.forskningsradet.no/en/ The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
How personality traits might interact to affect self-control
Neuroticism may play a key role for the effects of conscientiousness and extraversion on self-control
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US Congress members’ wealth statistically linked with ancestors’ slaveholding practices
2024-08-21
Per a new study, as of April 2021, US Congress members whose ancestors enslaved 16 or more people had a net worth that was five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves. Neil Sehgal of the University of Pennsylvania, US, and Ashwini Sehgal of Case Western Reserve University, US present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 21, 2024.
Prior research has linked slavery’s intergenerational effects to contemporary inequality, poverty, education, voting behavior, and life expectancy in the US However, the extent to which past slavery in the US contributes to today’s social and economic conditions remains ...
Following a Mediterranean diet may be associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, per systematic review
2024-08-21
Following a Mediterranean diet may be associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, per systematic review, although it's unclear if the diet is also associated with reduced symptoms and severity of illness.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301564
Article Title: Relevance of Mediterranean diet as a nutritional strategy in diminishing COVID-19 risk: A systematic review
Author Countries: Indonesia
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
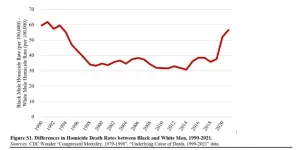
Homicide rates are a major factor in the gap between Black and White life expectancy
2024-08-21
Homicide is a major reason behind lower and more variable reduction in life expectancy for Black rather than White men in recent years, according to a new study published August 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Michael Light and Karl Vachuska of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA.
The COVID-19 pandemic precipitated a staggering drop in U.S. life expectancy and substantially widened Black-White disparities in lifespan. It also coincided with the largest one-year increase in the U.S. homicide rate in more than a century, with Black men bearing the brunt of these. Despite these trends, there has been limited research on the contribution ...
Human-wildlife overlap expected to increase across more than half of land on Earth by 2070
2024-08-21
ANN ARBOR—As the human population grows, more than half of Earth's land will experience an increasing overlap between humans and animals by 2070, according to a University of Michigan study.
Greater human-wildlife overlap could lead to more conflict between people and animals, say the U-M researchers. But understanding where the overlap is likely to occur—and which animals are likely to interact with humans in specific areas—will be crucial information for urban planners, conservationists and countries that have pledged international conservation commitments. Their findings ...
Freeze-frame: U of A researchers develop world's fastest microscope that can see electrons in motion
2024-08-21
Imagine owning a camera so powerful it can take freeze-frame photographs of a moving electron – an object traveling so fast it could circle the Earth many times in a matter of a second. Researchers at the University of Arizona have developed the world's fastest electron microscope that can do just that.
They believe their work will lead to groundbreaking advancements in physics, chemistry, bioengineering, materials sciences and more.
"When you get the latest version of a smartphone, it comes with a better camera," said Mohammed Hassan, associate professor of physics and optical sciences. "This transmission electron microscope is ...
Study finds highest prediction of sea-level rise unlikely
2024-08-21
In recent years, the news about Earth's climate—from raging wildfires and stronger hurricanes, to devastating floods and searing heat waves—has provided little good news.
A new Dartmouth-led study, however, reports that one of the very worst projections of how high the world's oceans might rise as the planet's polar ice sheets melt is highly unlikely—though it stresses that the accelerating loss of ice from Greenland and Antarctica is nonetheless dire.
The study challenges a new and alarming prediction in the latest high-profile report from the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on ...
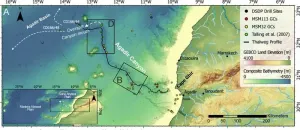
New study reveals devastating power and colossal extent of a giant underwater avalanche off the Moroccan coast
2024-08-21
New research by the University of Liverpool has revealed how an underwater avalanche grew more than 100 times in size causing a huge trail of destruction as it travelled 2000km across the Atlantic Ocean seafloor off the North West coast of Africa.
In a study publishing in the journal Science Advances (and featured on the front cover), researchers provide an unprecedented insight into the scale, force and impact of one of nature’s mysterious phenomena, underwater avalanches.
Dr Chris Stevenson, a sedimentologist from the University of Liverpool’s School of Environmental Sciences, co-led the team that for the first time has mapped a giant underwater avalanche from head ...
To kill mammoths in the Ice Age, people used planted pikes, not throwing spears, researchers say
2024-08-21
How did early humans use sharpened rocks to bring down megafauna 13,000 years ago? Did they throw spears tipped with carefully crafted, razor-sharp rocks called Clovis points? Did they surround and jab mammoths and mastadons? Or did they scavenge wounded animals, using Clovis points as a versatile tool to harvest meat and bones for food and supplies?
UC Berkeley archaeologists say the answer might be none of the above.
Instead, researchers say humans may have braced the butt of their pointed spears against the ground and angled the weapon upward in a way that would impale a charging animal. The force would have driven the spear deeper ...
Using AI to link heat waves to global warming
2024-08-21
Researchers at Stanford and Colorado State University have developed a rapid, low-cost approach for studying how individual extreme weather events have been affected by global warming. Their method, detailed in a Aug. 21 study in Science Advances, uses machine learning to determine how much global warming has contributed to heat waves in the U.S. and elsewhere in recent years. The approach proved highly accurate and could change how scientists study and predict the impact of climate change on a range of extreme weather events. The ...
The role of an energy-producing enzyme in treating Parkinson’s disease
2024-08-21
An enzyme called PGK1 has an unexpectedly critical role in the production of chemical energy in brain cells, according to a preclinical study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The investigators found that boosting its activity may help the brain resist the energy deficits that can lead to Parkinson’s disease.
The study, published Aug. 21 in Science Advances, presented evidence that PGK1 is a “rate-limiting” enzyme in energy production in the output-signaling branches, or axons, of the dopamine neurons that are affected in Parkinson’s disease. This means that even a modest boost to PGK1 activity can have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] How personality traits might interact to affect self-controlNeuroticism may play a key role for the effects of conscientiousness and extraversion on self-control