(Press-News.org) A U.S. Army Medical Materiel Development Activity commercial partner received Emergency Use Authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the Department of Defense to use octaplasLG Powder—a potentially lifesaving treatment option for blood replacement therapies in certain operational circumstances. Notice of the EUA for this product was received by the company, Octapharma USA, on Aug. 8, 2024.
USAMMDA’s Warfighter Protection and Acute Care Project Management Office, which has a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement with Octapharma USA, manages research and development efforts for several blood products, including Freeze-Dried Plasma, for the DoD. The EUA for octaplasLG Powder is a significant milestone in WPAC’s development mission, which includes blood replacement therapies for emergent care use during military operations and training.
“The WPAC team played a vital role in assisting our commercial partner under the CRADA, helping them navigate the EUA approval request and process to give our Warfighters another tool in their aid bag in far-forward environments,” said Kendra Lawrence, Ph.D., WPAC’s program manager. “While the octaplasLG Powder is not intended to replace current FDA-approved blood replacement therapies during emergency treatment, it does give medical commands and frontline providers added capabilities when facing possible shortages of traditional blood plasma in austere locations across the world.”
The EUA authorizes U.S. military medical commands to begin procuring octaplasLG Powder (blood types A and AB) and allows military medical personnel and other authorized providers to administer the lifesaving therapy to treat hemorrhage or coagulopathy when no other FDA-approved treatments, like fresh frozen plasma, are available—or when the use of traditional plasma is not practical in a compressed time continuum during military operations.
Blood loss is a significant threat to U.S. service members during combat operations and training, and treating hemorrhage or coagulopathy is imperative to saving the lives of the wounded and injured until medevac to higher echelons of care is arranged. Logistical and supply lines during future conflicts may stretch hundreds or thousands of miles, possibly causing shortages of FDA-approved blood products at and near the point of injury. Therapies like octaplasLG Powder are designed to serve as a stopgap when whole blood, fresh frozen plasma, or liquid plasma are in short supply, according to U.S. Army Maj. Andrea Mountney, WPAC’s military deputy project manager.
“During combat operations, whether in the Arctic, the Indo-Pacific, or other regions of interest, we will be facing the dual challenges of time and distance due to the austerity of those operating environments,” said Mountney. “Each passing second after a Service member is wounded or injured increases the complications caused by combat trauma. The longer it takes to begin blood replacement therapy, the higher the chances of mortality.
The WPAC team provides solutions for capability gaps, working with stakeholders across the DoD, academia, and industry to develop treatments that are affordable, reliable, and expeditionary,” she added. “Our goal is to meet the needs of the customer—the Joint Service end-user who may one day need these life-saving treatments. Solutions like octaplasLG Powder go a long way to equip our medical providers with the tools needed to treat the Warfighter during future operations.”
USAMMDA develops, delivers, and fields critical drugs, vaccines, biologics, devices, and medical support equipment to protect and preserve the lives of Warfighters across the globe. USAMMDA Project Managers guide the development of medical products for the U.S. Army Medical Department, other U.S. military services, the Joint Staff, the Defense Health Agency, and the U.S. Special Forces community. The process takes promising technology from the Department of Defense, industry, and academia to U.S. Forces, from the testing required for U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval or licensing to fielding and sustainment of the finished product. USAMMDA Project Management Offices will transition to a Program Executive Office under the Defense Health Agency, Deputy Assistant Director for Acquisition and Sustainment.
No official endorsement of third parties or their products is made or inferred.
To read the FDA’s announcement, visit this link: eua_authorization_letter_octaplaslg_powder_final.pdf
END
USAMMDA commercial partner receives FDA emergency use authorization for plasma powder
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pennington Biomedical study to explore effects of soy on blood sugar levels
2024-08-21
Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Dr. Candida Rebello wants to know more about the intersection of blood sugar levels and a diet rich in soy. This intersection is the primary focus of her new study, “Lifestyle Intervention for Improving Metabolic and Motivational Outcomes,” or MOTIVATE, which explores how specific diets can impact blood sugar, and potentially improve mood and energy levels.
When soy seeds are cut, they produce the anti-microbial compound known as glyceollin, which has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and cognition. The cut soy seeds will be milled into flour and will be included in the diets of some of the participants. The MOTIVATE ...
Giving an antibiotic to all children under 5 in Africa saves lives
2024-08-21
When UC San Francisco research showed that routinely treating children in Sub-Saharan Africa with a common antibiotic could reduce deaths in children under five, the World Health Organization (WHO) moved quickly to recommend the treatment – but only for infants between 1 and 11 months old.
Now, UCSF researchers have shown that treating babies is not enough. The antibiotic must be given to all children up to 5 years old to realize its full benefit, which is considerable: It lowers child mortality ...
Pivotal study supports belzutifan approval for patients with advanced kidney cancer
2024-08-21
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Belzutifan Versus Everolimus for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
Publication: New England Journal of Medicine, August 22, 2024
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute authors: Toni K. Choueiri, MD
Summary: The LITESPARK-005 phase 3 clinical enrolled 746 patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) who had progressed after treatment with both an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) and an anti-angiogenic therapy. Patients were randomized to receive treatment with either belzutifan, a HIF-2α inhibitor, or everolimus. Overabundant HIF-2α is associated with increased cancer-driving activity. At the second interim analysis of this study, ...
Next time you beat a virus, thank your microbial ancestors
2024-08-21
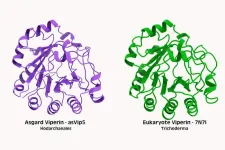
When you get infected with a virus, some of the first weapons your body deploys to fight it were passed down to us from our microbial ancestors billions of years ago. According to new research from The University of Texas at Austin, two key elements of our innate immune system came from a group of microbes called Asgard archaea.
Specifically, viperins and argonautes, two proteins that are known to play important roles in the immune systems of all complex life — from insects to plants to humans — came from the Asgard archaea. Versions of these defense proteins are also present in bacteria, but the versions in complex life forms are ...
Two UCSB professors selected by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to be Experimental Physics Investigators
2024-08-21
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — UC Santa Barbara professors Andrew Jayich and Jon Schuller have been selected by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to be part of the 2024 cohort of Experimental Physics Investigators. They join 17 other mid-career researchers from around the country, each receiving a five-year, $1.25 million grant to pursue research goals.
“This initiative is designed to support novel and potentially high-payoff projects that will advance the field of physics but might be hard to fund through traditional funding sources,” said Theodore ...
Study of pythons could lead to new therapies for heart disease, other illnesses
2024-08-21
In the first 24 hours after a python devours its massive prey, its heart grows 25%, its cardiac tissue softens dramatically, and the organ squeezes harder and harder to more than double its pulse. Meanwhile, a vast collection of specialized genes kicks into action to help boost the snake’s metabolism fortyfold. Two weeks later, after its feast has been digested, all systems return to normal—its heart remaining just slightly larger, and even stronger, than before.
This extraordinary process, described by CU Boulder researchers this week in the journal PNAS, could ultimately inspire novel treatments for a common human heart condition called cardiac fibrosis, in which ...
Study finds no link between migraine and Parkinson’s disease
2024-08-21
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, AUGUST 21, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Contrary to previous research, a new study of female participants finds no link between migraine and the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. The study is published in the August 21, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These results are reassuring for women who have migraine, which itself causes many burdens, that they don’t have to worry about an increased risk ...
How personality traits might interact to affect self-control
2024-08-21
Neuroticism may moderate the relationship between certain personality traits and self-control, and the interaction effects appear to differ by the type of self-control, according to a study published August 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fredrik Nilsen from the University of Oslo and the Norwegian Defence University, Norway, and colleagues.
Self-control is important for mental and physical health, and certain personality traits are linked to the trait. Previous studies suggest that conscientiousness and extraversion enhance self-control, whereas neuroticism hampers it. However, the link between personality ...
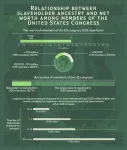
US Congress members’ wealth statistically linked with ancestors’ slaveholding practices
2024-08-21
Per a new study, as of April 2021, US Congress members whose ancestors enslaved 16 or more people had a net worth that was five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves. Neil Sehgal of the University of Pennsylvania, US, and Ashwini Sehgal of Case Western Reserve University, US present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 21, 2024.
Prior research has linked slavery’s intergenerational effects to contemporary inequality, poverty, education, voting behavior, and life expectancy in the US However, the extent to which past slavery in the US contributes to today’s social and economic conditions remains ...
Following a Mediterranean diet may be associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, per systematic review
2024-08-21
Following a Mediterranean diet may be associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, per systematic review, although it's unclear if the diet is also associated with reduced symptoms and severity of illness.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301564
Article Title: Relevance of Mediterranean diet as a nutritional strategy in diminishing COVID-19 risk: A systematic review
Author Countries: Indonesia
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...