(Press-News.org) How effective medications are depends on various factors, including the time of day when they are administered. Why? Because our bodies don’t always function exactly the same. Instead, they follow the cycle set by their internal clock, otherwise known as circadian rhythm. But since each person’s circadian rhythm is different and depends on a number of different factors, it is difficult to tailor medication schedules to an individual patient’s body clock. Researchers at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have now developed a method for determining the optimum time of cancer treatment based on certain breast cancer cell lines. They describe their approach in the journal Nature Communications.*
A person’s internal clock sets the rhythm of many different bodily functions and metabolic processes, such as sleep and digestion. But the organs aren’t the only things that are more or less active depending on the time of day. Individual cells also follow a cycle set by a person’s body clock, so they respond differently to external influences at different times of the day. This is hugely important to chemotherapy administered to treat cancer. Previous studies have shown that chemotherapy is most effective when the tumor cells are dividing. But this finding has been hardly used at all in clinical treatment to date.
An interdisciplinary team at Charité headed by Dr. Adrián Enrique Granada from the Charité Comprehensive Cancer Center (CCCC) set out to close this gap. The team began looking for the optimum time to administer medication, based on the individual circadian rhythms of the tumors.
Triple-negative breast cancer as an example
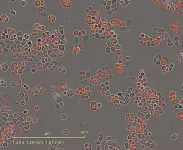
“We cultured cells from patients with triple-negative breast cancer to observe how they respond at different times of day to the medications administered,” explains Carolin Ector, a research associate in Granada’s working group. Triple-negative breast cancer is a highly aggressive form of breast cancer, with few effective treatments available. “We used live imaging, a method of continuously monitoring living cells, and complex data analysis techniques to monitor and evaluate the circadian rhythms, growth cycles, and medication responses of these cancer cells in detail.”
In this way, the researchers identified certain times of the day at which cancer cells are most responsive to medication-based treatments. For example, the chemotherapeutic drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) turned out to have peak efficacy against a certain cancer cell line between eight and ten a.m. As the study also shows, the crucial aspects here are certain cellular and genetic factors. The scientists were even able to identify which genes are key to the circadian effects of certain medications. “We call them ‘core clock genes’. They have a significant impact on how responsive cancer cells are to treatments administered at different times of day,” Granada explains.
Profiles show how cancer cell types respond to medications
This approach can be used to create detailed profiles showing how different types of cancer cells respond to different medications at various times. “This can help to identify the most effective combinations of drugs,” Granada says. “Overall, our findings indicate that personalized treatment plans based on individual circadian rhythms could substantially improve the efficacy of cancer treatment”, he concludes. Moreover, undesirable side effects could also be reduced.
For these findings to contribute to clinical practice soon, the results should be validated in studies involving larger groups of patients. “We’re also planning to study the molecular mechanisms behind the circadian influences on medication sensitivity to further optimize treatment times and identify new therapeutic targets,” Granada says.
About the study
The study was conducted at the Charité Comprehensive Cancer Center (CCCC) under the leadership of Dr. Adrián Enrique Granada (last author). He is in charge of the Granada Lab there, which focuses on systems oncology. Carolin Ector, the first author of the publication, is a research associate at the CCCC and a graduate student at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
The team worked closely with the Department of Chronobiology at Charité, led by Prof. Achim Kramer, to collect complex time series data on the cell’s biological clocks. The data analysis was created in cooperation with Prof. Hanspeter Herzel from the Institute for Theoretical Biology at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and the working group headed by Prof. Thomas Sauter at the University of Luxembourg. Sources of funding for the study included the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the German Research Foundation (DFG).
*Ector C et al. Time-of-day effects of cancer drugs revealed by high-throughput deep phenotyping. Nat Commun 15, 7205 (2024), doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51611-3
END
When is the best time of day for cancer treatment?
Researchers from Charité are developing new methods to use the internal clock inside tumor cells to optimize cancer therapies
2024-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rates of obesity-related cancer are rising sharply in young Chinese people
2024-08-23
Obesity-related cancer rates in China were rising at an alarming 3.6% every year between 2007 and 2021 while non-obesity-related cancers remained stable, according to the first comprehensive study published August 22 in the Cell Press journal Med. The increase is particularly pronounced among young people, highlighting the urgent need for better public health policies to address China’s growing overweight and obesity rates.
“If we don’t drastically change the obesity epidemic, the rates of cancer associated with obesity will inevitably continue to rise,” says Jin-Kui Yang, the paper’s corresponding author and an endocrinologist ...
Neighborhood-level disparities in hypertension prevalence and treatment among middle-aged adults
2024-08-23
About The Study: Researchers found corresponding increases in hypertension prevalence as neighborhood disadvantage and the percentage of Black patients residing in a neighborhood increased in this cross-sectional study. A higher burden of midlife hypertension was identified in Black adults compared with other racial and ethnic groups that persisted across levels of socioeconomic disadvantage. This study also found that living in socioeconomically disadvantaged neighborhoods was associated with higher hypertension ...
Strength training activates cellular waste disposal
2024-08-23
The elimination of damaged cell components is essential for the maintenance of the body’s tissues and organs. An international research team led by the University of Bonn has made significant findings on mechanisms for the clearing of cellular wastes, showing that strength training activates such mechanisms. The findings could form the basis for new therapies for heart failure and nerve diseases, and even afford benefits for manned space missions. A corresponding article has been published in the latest issue of the journal Current Biology. EMBARGOED: Do not publish until 5 pm CEST ...
Water activation induced strong interfacial hydrogen bonding interactions for efficient oxygen reduction reaction
2024-08-23
Exploring new energy storage and conversion technologies is crucial for sustainable human development. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and metal-air batteries are particularly promising due to their high energy efficiency and environmental friendliness. A key component in these technologies is the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst. Traditionally, ORR catalysts rely on expensive platinum group metals (PGM), which are cost-prohibitive for widespread use. This has spurred interest in developing non-precious metal alternatives, such as transition metal/nitrogen-doped carbon-based materials (M–N–C). Among these, Fe–N–C ...
Temperature regulates negative supercoils to modulate meiotic crossovers and chromosome organization
2024-08-23
This study is led by Prof. Shunxin Wang (State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine and Offspring Health, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Women, Children and Reproductive Health, Shandong University) and Prof. Liangran Zhang (Advanced Medical Research Institute, Shandong University). In their study of meiosis in budding yeast, the research team found that yeast senses temperature changes by increasing the level of DNA negative supercoils to increase crossovers and modulate chromosome organization ...
Single nucleosomes tracked in live cells during cell division using super-resolution microscopy
2024-08-23
Individual cells divide through a process called mitosis, during which the cell’s copied DNA is separated between two resulting daughter cells. Despite recent advances in cell biology, the mechanism by which DNA condenses during mitosis is still poorly understood. Researchers recently tracked small stretches of DNA wound around histone proteins, called nucleosomes, to better characterize nucleosome behavior during cell division.
DNA is organized as chromatin, which are dynamic structures comprised of DNA, RNA, and proteins that regulate the accessibility of genes for expression and the overall configuration of genetic material in the cell. Histone proteins, for example, are positively ...
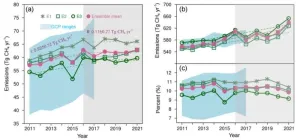
Slow down in China’s methane emission growth
2024-08-23
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas. Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric methane concentrations have nearly doubled, with its radiative forcing accounting for one-third of all greenhouse gases. As one of the world's largest methane emitters, China made a clear commitment as early as 2007 to "strive to control the growth rate of methane emissions." The country's 12th, 13th, and 14th Five-Year Plans all proposed measures to control methane emissions. In 2023, China released the "Methane Emission Control Action ...
Socioeconomics shape children’s connection to nature more than where they live
2024-08-23
The income and education levels of a child’s environment determine their relationship to nature, not whether they live in a city or the countryside. This is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at Lund University, Sweden. The results run counter to the assumption that growing up in the countryside automatically increases our connection to nature, and yet the study also shows that nature close to home increases children’s well-being.
There is a general concern that, with urbanisation, people have lost contact with nature. According to research, less contact ...
The higher the environmental stress, the lower the resistance to global change
2024-08-23
An international study led by Institute of Natural Resources and Agrobiology of Seville (IRNAS-CSIC), of the Spanish National Research Council (CISC), has shown that as the number of global change factors increases, terrestrial ecosystems become more sensitive to the impacts of global change. The results, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience, show that the resistance of our ecosystems to global change decreases significantly as the number of environmental stressors increases, especially when this stress is sustained over time.
This is the conclusion reached by the Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning ...
Intestinal parasite could hold key to scar-free wound healing, study suggests
2024-08-23
Researchers at Rutgers University in New Jersey have discovered that a protein produced by parasitic worms in the gut enhances wound healing in mice. The study, to be published August 23 in the journal Life Science Alliance (LSA), reveals that applying the protein to skin wounds speeds up wound closure, improves skin regeneration, and inhibits the formation of scar tissue. Whether the protein can be harnessed to enhance wound healing in human patients remains to be seen.
Skin wounds must be rapidly closed in order to prevent infection, but rapid wound closure can favor the development of scar tissue instead of properly regenerated skin. The balance between scarring ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
[Press-News.org] When is the best time of day for cancer treatment?Researchers from Charité are developing new methods to use the internal clock inside tumor cells to optimize cancer therapies