Brigham-led study estimates 1 in 7 Medicare beneficiaries with high body mass index may qualify for anti-obesity drug
If Medicare Part D narrowly defines cardiovascular disease, majority of patients would remain ineligible while new federal spending could still exceed $10 billion
2024-08-26
(Press-News.org) If Medicare Part D narrowly defines cardiovascular disease, majority of patients would remain ineligible while new federal spending could still exceed $10 billion
Current federal regulation restricts Medicare from covering drugs prescribed solely for weight loss. However, in March 2024, Medicare announced it would extend coverage to semaglutide (Wegovy), a popular glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), for patients with elevated body mass index (BMI) who also had established cardiovascular disease (CVD). This means that the definition of “established CVD,” which has not been formally codified, will have outsized impacts on both public health and Medicare costs. A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, estimates that 3.6 million Medicare beneficiaries are most likely to become eligible for semaglutide. The study also estimates eligibility and associated maximum costs if different definitions of cardiovascular risk were to be considered. Findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The research team analyzed data from respondents over 65 or who were on Medicare and who took part in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) between 2011 and 2020. They found that if all patients with elevated BMI and history of heart attack, stroke, coronary artery disease, or angina were treated with semaglutide, maximum annual costs to Medicare could be as high as $34.3 billion after rebates.
“When established cardiovascular disease is narrowly defined, only 1 in 7 Medicare beneficiaries with elevated BMI are likely to be eligible to receive semaglutide, but costs to Medicare could still exceed $10 billion per year,” said lead author Alexander Chaitoff, MD, MPH, of the Center for Healthcare Delivery Sciences in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology at BWH. “In this conservative coverage scenario, that means most beneficiaries with elevated BMI and cardiovascular risk would remain ineligible for semaglutide, yet the medication could still potentially become one of the costliest drugs to Medicare.”
Authorship: In addition to Chaitoff, BWH authors include Liam Bendicksen, William Feldman and Hussain Lalani. Additional authors include Alexander Zheutlin.
Disclosures: Unrelated to the current work, Alexander Chaitoff and William Feldman disclose consulting for Alosa Health, an academic detailing non-profit organization that works on topics related to the health of older adults. Dr. Lalani is a medical officer at the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation. The views presented herein do not represent those of the Federal government.
Funding: None
Paper cited: Chaitoff, A et al. “Estimating New Eligibility and Maximum Costs of Expanded Medicare Coverage of Semaglutide for Cardiovascular Risk Prevention” Annals of Internal Medicine DOI: 10.7326/ANNALS-24-00308
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-26
With a grand vision of investing $66 million over 10 years in groundbreaking medical innovations, WEHI’s first strategic investment fund, 66ten, is the largest internal pre-seed and seed fund created by an Australian medical research institute.
Managed by WEHI Ventures, 66ten serves the sole purpose of bridging the gap between scientific discoveries and commercial viability, ultimately creating both positive outcomes for patients and healthcare systems globally as well as financial returns to investors.
Since its foundation a year ago, 66ten has ...
2024-08-26
LA JOLLA, CA—Fighting cancer effectively often involves stopping cancer cells from multiplying, which requires understanding proteins that the cells rely on to survive. Protein profiling plays a critical role in this process by helping researchers identify proteins—and their specific parts—that future drugs should target. But when used on their own, past approaches haven’t been detailed enough to spotlight all potential protein targets, leading to some being missed.
Now, by combining two methods of protein analysis, a team of chemists at Scripps Research has mapped more than 300 small molecule-reactive ...
2024-08-26
Simulating particles is a relatively simple task when those particles are spherical. In the real world, however, most particles are not perfect spheres but take on irregular and varying shapes and sizes. Simulating these particles becomes a much more challenging and time-consuming task.
The ability to simulate particles is critical to understanding how they behave. For example, microplastics are a new form of pollution as plastic waste has increased drastically and uncontrollably decays in the environment ...
2024-08-26
New Orleans, LA. – Ochsner Digital Medicine has teamed up with AmeriHealth Caritas Louisiana to offer digital medicine services to the health plan’s members. Utilizing remote patient management (RPM), Ochsner Digital Medicine and AmeriHealth Caritas Louisiana will work together to help members with certain chronic conditions better manage their health and improve their quality of life.
AmeriHealth Caritas Louisiana, part of the AmeriHealth Caritas Family of Companies, is a Healthy Louisiana managed Medicaid health plan covering ...
2024-08-26
New methods to shape RNA molecules into circles could lead to more effective and long-lasting therapies, shows a study by researchers at the University of California San Diego. The advance holds promise for a range of diseases, offering a more enduring alternative to existing RNA therapies, which often suffer from short-lived effectiveness in the body.
The work was published Aug. 26 in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
RNA molecules have emerged as powerful tools in modern medicine. They can silence ...
2024-08-26
As electronic devices continue to get smaller and smaller, physical size limitations are beginning to disrupt the trend of doubling transistor density on silicon-based microchips approximately every two years according to Moore’s law. Molecular electronics—the use of single molecules as the building blocks for electronic components—offers a potential pathway for the continued miniaturization of small-scale electronic devices. Devices that utilize molecular electronics require precise control over the flow of electrical current. However, the dynamic nature of these single molecule components affects device performance and impacts ...
2024-08-26
Over 12,000 feet below the surface of the sea, in a region of the Pacific Ocean known as the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), million-year-old rocks cover the seafloor. These rocks may seem lifeless, but nestled between the nooks and crannies on their surfaces, tiny sea creatures and microbes make their home, many uniquely adapted to life in the dark.
These deep-sea rocks, called polymetallic nodules, don’t only host a surprising number of sea critters. A team of scientists that includes Boston University experts has discovered they ...
2024-08-26
At the end of the Paleocene and beginning of the Eocene epochs, between 59 to 51 million years ago, Earth experienced dramatic warming periods, both gradual periods stretching millions of years and sudden warming events known as hyperthermals.
Driving this planetary heat up were massive emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, but other factors like tectonic activity may have also been at play.
New research led by University of Utah geoscientists pairs sea surface temperatures with levels ...
2024-08-26
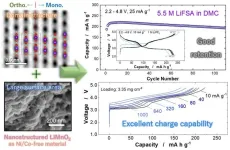
Lithium-ion (or Li-ion) batteries are heavy hitters when it comes to the world of rechargeable batteries. As electric vehicles become more common in the world, a high-energy, low-cost battery utilizing the abundance of manganese (Mn) can be a sustainable option to become commercially available and utilized in the automobile industry. Currently, batteries used for powering electric vehicles (EVs) are nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co)-based, which can be expensive and unsustainable for a society with a growing desire for EVs. By switching the positive electrode ...
2024-08-26
The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (TLI) announced updates to its Board of Directors today. TLI welcomes one new distinguished member and thanks the two outgoing members for their invaluable contributions.
“On behalf of the Board, I am delighted that Dr. Bill Dorfman, a global leader in cosmetic dentistry, has joined the TLI Board. Dr. Dorfman's extensive expertise and commitment to philanthropy make him an invaluable addition to our leadership,” said Mitchel Sayare, PhD, TLI Board ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Brigham-led study estimates 1 in 7 Medicare beneficiaries with high body mass index may qualify for anti-obesity drug
If Medicare Part D narrowly defines cardiovascular disease, majority of patients would remain ineligible while new federal spending could still exceed $10 billion