(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO, Aug. 27, 2024 – Kenneth M. Hargreaves, DDS, PhD, professor of endodontics at the School of Dentistry of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), has been named inaugural director of the school’s Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research.
Hargreaves, who chaired the Department of Endodontics at the school for 26 years, is a world-renowned expert in pain research and has served as principal or co-principal investigator on numerous National Institutes of Health, Department of Defense and foundation-funded projects totaling more than $139 million.
Just recently, his research proposal, “Development of non-opioid analgesics to treat chronic pain,” was approved for $1.3 million in funding over three years by the DOD’s Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs for its chronic pain management program. The project began Aug. 1.
The School of Dentistry’s new Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research represents a transformative multidisciplinary approach to decrease pain and addiction.
“There is no person more qualified to lead the School of Dentistry in this endeavor,” said Peter M. Loomer, DDS, PhD, MBA, professor and dean of the UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry. “We look forward to collaborating with Dr. Hargreaves on this exciting and significant step in the school’s path towards addressing critical health challenges in pain and addiction while continuing our ascendance to the top NIH-funded dental schools in the world.”
Non-opioid pain management
Hargreaves’ studies, including new preliminary data from his current DOD research, provide a strong scientific rationale for using omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and related metabolites to treat chronic pain, in lieu of opioids. This has application far beyond dental treatment.
While military medicine has made great strides in improving survival of personnel with traumatic burn injuries, for example, management of both acute and chronic pain is a challenge. In particular, improvised explosive devices (IEDs), or roadside bombs, often generate substantial burn injuries.
Burns comprise up to 10% of combat casualties and require considerable and sustained resources for initial treatment and subsequent rehabilitation. In addition, about 2 million burn injuries occur annually in the U.S. civilian population, with about 25% requiring medical treatment.
Hargreaves’ research proposal notes that omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and related metabolites can inhibit pain receptors such as TRPV1, a protein the provides detection and regulation of body temperature as well as a sensation of scalding heat and pain. But while those fatty acids are regarded as essential nutrients that perform important functions, the body doesn’t make enough, meaning they must come from diet.
Increased dietary intake of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids has been shown to reduce pain from migraine headaches, post-traumatic headache and several neuropathic pain conditions. They have been approved for use in humans by the Food and Drug Administration, for neonatal parenteral nutrition, greatly reducing risk of addiction in treating pain.
Foods containing omega-3s include fish and other seafood (cold-water fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring and sardines), nuts and seeds (flaxseed, chia seeds and walnuts), and plant oils (flaxseed, soybean and canola oils).
A top research dental school
In all, Hargreaves has trained 23 post-doctoral fellows and 15 PhD, DDS/PhD or MD/PhD students, and has led the nation in training endodontist/PhD clinician-scientists. He has authored more than 200 peer-reviewed publications; and is co-author of the definitive authority on endodontics, Cohen’s Pathway to the Pulp, and editor-in-chief of the prestigious Journal of Endodontics.
While a senior staff fellow at NIH, he developed the “Hargreaves test” that’s now a standard test in preclinical pain research around the world. To date, it has been cited in about 5,900 publications.
Of Hargreaves’ time as chair of the endodontics department, Loomer said, “Dr. Hargreaves’ unwavering dedication and effective leadership played a pivotal role in elevating the department to one of the most esteemed in the country and helped lay the foundation for the School of Dentistry to become one of the nation’s top research dental schools.”
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), a primary driver of San Antonio’s $44.1 billion health care and biosciences sector, is the largest academic research institution in South Texas with an annual research portfolio of $413 million. Driving substantial economic impact with its six professional schools, a diverse workforce of more than 8,500, an annual expense budget of $1.46 billion and clinical practices that provide 2.6 million patient visits each year, UT Health San Antonio plans to add more than 1,500 higher-wage jobs over the next five years to serve San Antonio, Bexar County and South Texas. To learn about the many ways “We make lives better®,” visit UTHealthSA.org.
The UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry offers 18 degrees and programs in both dentistry and dental hygiene, world-renown faculty educators, a diverse student population, state-of-the-art clinical facilities and a distinguished research enterprise. Departments include comprehensive dentistry, developmental dentistry, endodontics, periodontics, and oral and maxillofacial surgery. Scientists collaborate with clinicians and research teams worldwide, and work across multiple medical and dental disciplines to find new treatments, advancing knowledge of oral health, biomaterials, cancer, pain and more. To learn more, visit https://www.uthscsa.edu/academics/dental.
Stay connected with The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram and YouTube.
END
UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry names director of Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research
Kenneth M. Hargreaves, DDS, PhD, is a world-renowned expert in pain research
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers develop affordable, rapid blood test for brain cancer
2024-08-27
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12-18 months after diagnosis.
The crux of the diagnostic is a biochip that uses electrokinetic technology to detect biomarkers, or active Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (EGFRs), which are overexpressed in certain cancers such as glioblastoma and found in extracellular vesicles.
“Extracellular vesicles or exosomes are unique ...
NREL advances method for recyclable wind turbine blades
2024-08-27
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) see a realistic path forward to the manufacture of bio-derivable wind blades that can be chemically recycled and the components reused, ending the practice of old blades winding up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
The findings are published in the new issue of the journal Science. The new resin, which is made of materials produced using bio-derivable resources, performs on par with the current industry standard of blades made from a thermoset resin and outperforms certain thermoplastic resins intended to be recyclable.
The researchers built a prototype 9-meter blade to ...
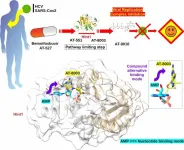
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
2024-08-27
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002743
Article Title: The activation cascade of the broad-spectrum antiviral bemnifosbuvir characterized at atomic resolution
Author Countries: France, United States, Germany
Funding: see manuscript END ...
This new technique for studying cell receptors could have sweeping implications for drug development
2024-08-27
One in every three FDA-approved drugs targets a single superfamily of receptors dotting the surfaces of human cells. From beta blockers to antihistamines, these essential, life-saving medications trigger winding biochemical pathways, via these receptors, to ultimately prevent a heart attack, or stop an allergic reaction in its tracks.
But scientists have learned that their story is much more complicated than initially believed—a number of these drugs are in fact targeting a complex composed of one receptor and one associated protein. Now, a ...
Bringing environmental justice to disadvantaged communities
2024-08-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Not all communities in the United States face the same risks for environmental problems such as air pollution, noise and wastewater. But how can federal agencies fairly identify which areas deserve the most help?
A new consensus study report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine (NASEM) offer recommendations for developing tools that can help answer that question.
“Our job was to create methods to identify disadvantaged communities that most need federal resources to address environmental justice issues,” said Harvey Miller, ...
Wiener studying learning & metacognition for the perception of time
2024-08-27
Wiener Studying Learning & Metacognition For The Perception Of Time
Martin Wiener, Associate Professor, Psychology, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding to study learning and metacognition for the perception of time.
Via this research, Wiener will conduct a series of studies that will inform metacognition and interval timing. He holds that this work will lead to a new domain of study to further understand how humans learn and adapt to temporal intervals.
By understanding how the brain measures and learns intervals of time, we can better understand ...
Dumas receives funding for study of how distinct NMDA receptor signaling domains regulate hippocampal network dynamics
2024-08-27
Dumas Receives Funding For Study Of How Distinct NMDA Receptor Signaling Domains Regulate Hippocampal Network Dynamics
Theodore Dumas, Associate Professor, Psychology, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding for the project: “Distinct NMDA receptor signaling domains regulate hippocampal network dynamics.
Dumas and his collaborators hypothesize that in wildtype mice, NMDA receptors regulate hippocampal network oscillatory activity (slow gamma frequency) in the absence of ion conductance (nonionotropic) and that enhancing GluN2B subunit-type nonionotropic signaling will increase slow gamma power and enhance spatial memory retrieval.
The researchers ...
Second genetic sensor for DNA methylation discovered
2024-08-27
DNA methylation is a process in which a methyl group is attached to the cytosine base of the DNA molecule, and a major way that DNA is epigenetically marked. Epigenetic modifications can act as on-off switches to regulate gene expression and help generate diverse cell types without changing the underlying DNA sequence. It is how the body ensures that brain-related genes don’t get turned on in heart cells, for example.
For this reason, maintenance of the DNA methylation pattern is important to ensure the correct and consistent function of each cell type. But this is no easy feat: the DNA methylation pattern can change over time, and this is linked to a variety of diseases. One ...
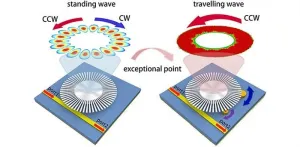
New sensor technology enhances detection of tiny particles
2024-08-27
In recent years, advances in photonics and materials science have led to remarkable developments in sensor technology, pushing the boundaries of what can be detected and measured. Among these innovations, non-Hermitian physics has emerged as a crucial area of research, offering new ways to manipulate light and enhance sensor sensitivity. A recent study published in Advanced Photonics Nexus reports a breakthrough in this field, presenting a new type of sensor that leverages exceptional points (EPs) to achieve unprecedented levels of sensitivity.
This study introduces a highly sensitive and reconfigurable sensor based on a single ...
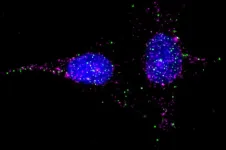
New technology ‘lights up’ bacteria in wounds for better infection prevention
2024-08-27
LOS ANGELES — Over 6.5 million Americans experience chronic wounds — wounds that do not heal after a few months. Almost all such wounds contain bacteria, which, if not detected and removed, can lead to severe infection and resulting complications, including amputation if a limb is involved.
This is especially true for patients with diabetic foot ulcers (open sores), which affects one-third of people with diabetes. Approximately 20% of those who develop a diabetic foot ulcer will require a lower-extremity amputation, according ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry names director of Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction ResearchKenneth M. Hargreaves, DDS, PhD, is a world-renowned expert in pain research