(Press-News.org) Whether it’s a sore arm or a fear of injections, how a child is treated when they present with pain could significantly affect how they respond to and manage pain later in life.
In a new study from the University of South Australia, researchers say that parents and doctors should be mindful of how they talk to and treat children experiencing pain – no matter how big or small the injury – knowing that these foundational experiences can be carried forward into adulthood.
Drawing from diverse research across developmental psychology, child mental health, and pain sciences, researchers say that it may be important to validate children’s pain by demonstrating that their pain-related experiences, emotions, or behaviours are acceptable, understood, and legitimate.
By validating a child’s pain, the child feels heard and believed, which reinforces their trust and connection with their parent, or with a treating doctor.
UniSA researcher Dr Sarah Wallwork says social relationships play a critical role in shaping how health is experienced throughout the lifespan.
“When a parent or doctor validates a child’s experiences in a way that matches their expressed vulnerability, it helps the child to feel accepted, builds connection and trust, and may help the child to develop critical skills in regulating their emotions,” Dr Wallwork says.
“For example, when a doctor is attentive, and responds to a child’s emotional and behavioural cues, particularly about seeking help, the clinician is telling the child their pain is real and concurrently reinforcing helpful pain management behaviours, such as attending the clinic.
“However, if these cues are missed, or the doctor questions the validity of their pain, this can have negative consequences for the child. Not only can it affect the clinician-patient relationship and trust but it can also impact future attendance at appointments and adherence to a pain management plan.
“Pain and emotion are inextricably linked, with emotion dysregulation commonly co-occurring with chronic pain.
“By validating children’s experiences of pain, they are likely to hold fewer negatively biased memories of pain and be in better position to seek help in the future, when then need it.”
In Australia, as many as one in four children experience chronic pain. The economic burden of chronic pain in Australia is more than $139 billion, mostly through reduced quality of life and productivity losses.
Dr Wallwork says that setting children up for success should cover all aspects of life, including pain management.
“Our research highlights an underemphasised element of child and youth pain treatment, especially for children in minoritised groups, who are systematically undertreated for pain,” Dr Wallwork says.
“People with chronic pain often report that their pain-related experiences are met with disbelief or dismissal. This can have significant consequences, including poor mental health and reduced quality of life.
“Given the significant burden of chronic pain, and the clear intersection with the rising child mental health crisis, it’s important that we better manage pain earlier on, rather than waiting until it is too late.”
Dr Wallwork says this review provides a building block for future empirical research.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Media contacts: Annabel Mansfield M: +61 479 182 489 E: Annabel.Mansfield@unisa.edu.au
Jack Trehearne E: Jack.Trehearne@unisa.edu.au
Researcher: Dr Sarah Wallwork E: Sarah.Wallwork@unisa.edu.au
END
When a child hurts, validating their pain may be the best first aid
2024-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Single-dose gene therapy is potentially life-changing for adults with hemophilia B
2024-09-25
PHILADELPHIA – Adults with hemophilia B saw their number of bleeding episodes drop by an average of 71 percent after a single infusion of gene therapy, according to the results of an international Phase III clinical trial published today in the New England Journal of Medicine by researchers from the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and a multicenter group of investigators.
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that limits the blood’s ability to clot and affects around 30,000 people in the United States, ...
NEJM: Results from targeted therapy for ulcerative colitis study
2024-09-25
An international placebo-controlled study led by Cedars-Sinai suggests that a targeted drug therapy that was developed by researchers at Cedars-Sinai is safe and effective at helping people with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis reach clinical remission.
Results from the multicenter Phase II study, ARTEMIS-UC, were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that damages the digestive tract, causing stomach cramping, diarrhea, weight loss and rectal bleeding. ...
Study finds certain MS therapies may not slow disability progression
2024-09-25
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 25, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – In people with primary progressive multiple sclerosis (MS), a new study has found no difference in the amount of time before disability worsened between people taking certain medications and those not receiving treatment. The study is published in the September 25, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
With MS, the body’s immune system attacks myelin, the fatty, white substance that insulates and protects the nerves. People with ...
Are gender and sexual identity linked to brain health?
2024-09-25
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 25, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – LGBTQ+ people may be more likely to have negative brain health outcomes, including a higher risk of dementia and late-life depression, than people who are cisgender and straight, according to a study published in the September 25, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. These results do not prove that sexual or gender diversity causes neurological diseases, they only show an association.
LGBTQ+ refers to people who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, ...
The Academy of Science of St. Louis names Katherine Polokonis as executive director
2024-09-25
ST. LOUIS, MO, September 25, 2024 – After an extensive search, The Academy of Science of St. Louis has named Katherine Polokonis as the next Executive Director.
“After a rigorous search, we are looking forward to Kate’s transformational leadership of The Academy of Science,” said Toni Kutchan, PhD, president of the Board of Trustees of the Academy and member emerita, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center. “Kate's comprehensive experience in STEM education and passion for social equity make her ...
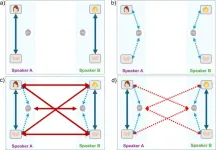
How synchronization supports social interactions
2024-09-25
Turn-taking dynamics of social interactions are important for speech and gesture synchronization, enabling conversations to proceed efficiently, according to a study published September 25, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tifenn Fauviaux from the University of Montpellier, France, and colleagues.
Conversations encompass continuous exchanges of verbal and nonverbal information. Previous research has demonstrated that gestures and speech synchronize at the individual level. But few studies have investigated how this phenomenon ...
Dogs trained to detect explosives may perform worse in extreme temperature and humidity, taking longer to identify substances and with lower sensitivity
2024-09-25
Dogs trained to detect explosives may perform worse in extreme temperature and humidity, taking longer to identify substances and with lower sensitivity
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306817
Article Title: Environmental effects on explosive detection threshold of domestic dogs
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This research was made possible through funding provided by the DoD Army Research Office under Contract No. W911NF2120124. https://www.arl.army.mil/who-we-are/aro/. SAK’s work was supported by the National Science Foundation ...
Digital biomarkers shedding light on seasonality in mood disorders
2024-09-25
Wrist-based activity sensors worn by individuals with depression and those without over the course of two weeks provided evidence for the relationship between daily sunlight exposure and physical activity, according to a study published September 25, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS Mental Health by Oleg Kovtun and Sandra Rosenthal from Vanderbilt University, U.S.
Mood disorders are the leading cause of ‘disability’ worldwide. Up to 30 percent of individuals with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder display a seasonal pattern of symptoms. This phenomenon is now recognized in official diagnostic manuals. Yet very little ...
US politicians support climate action when linked to certain other issues
2024-09-25
The US House of Representatives is more likely to vote on climate action when it is linked with certain other environmental issues, according to a study published September 25, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Kayla Morton of the University of Washington, Seattle and colleagues.
Climate change is a very polarizing issue in US politics. While Congress has not passed many climate-related bills over the past two decades, the House of Representatives has voted on many bills and resolutions related to climate issues, thus providing an opportunity to examine the factors that motivate ...
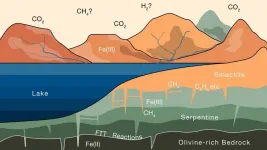
Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight
2024-09-25
Mars wasn’t always the cold desert we see today. There’s increasing evidence that water once flowed on the Red Planet’s surface, billions of years ago. And if there was water, there must also have been a thick atmosphere to keep that water from freezing. But sometime around 3.5 billion years ago, the water dried up, and the air, once heavy with carbon dioxide, dramatically thinned, leaving only the wisp of an atmosphere that clings to the planet today.
Where exactly did Mars’ ...