(Press-News.org) ST. LOUIS, MO, September 25, 2024 – After an extensive search, The Academy of Science of St. Louis has named Katherine Polokonis as the next Executive Director.
“After a rigorous search, we are looking forward to Kate’s transformational leadership of The Academy of Science,” said Toni Kutchan, PhD, president of the Board of Trustees of the Academy and member emerita, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center. “Kate's comprehensive experience in STEM education and passion for social equity make her an outstanding new leader of the Academy.”
Polokonis, currently Executive Director of STEMSTL, will step down from that role into her new role as Academy Executive Director on October 14, 2024. She replaces Mary Burke, who led the Academy for the past 19 years.
Polokonis is a dynamic leader in STEM education, known for her innovative approach to fostering systemic change in the realms of education and workforce development. With a deep-rooted passion for equity and a commitment to improving educational outcomes, Polokonis leverages her extensive experience as an educator and non-profit executive to drive meaningful impact in her hometown of St. Louis.
As Executive Director of STEMSTL, St. Louis’s STEM ecosystem backbone and part of the BioSTL portfolio of programs, she has been instrumental in developing a regional strategy for career pathways in key STEM industries. Under her leadership, STEMSTL launched a Community of Practice for K12 STEM programs, established St. Louis’s STEM Celebration Week, and developed the Educator Resources Portal. Additionally, Polokonis led STEMSTL to support regional workforce development by producing a work-based learning landscape analysis, hosting the region's inaugural Work-Based Learning Summit, and becoming the new home for the Regional Youth Employment Coalition.
Polokonis's career began as a teacher in the St. Louis Public School District. Her experiences in the classroom ignited her commitment to educational equity, leading her to pursue advanced studies at The Brown School of Social Work at Washington University in St. Louis. Her graduate work, culminating in an MSW with a concentration in Domestic Social and Economic Development, focused on workforce development, an area where she has since made significant strides.
At Starkloff Disability Institute, Polokonis project-managed the expansion of the DREAM BIG program, a career-exploration camp for teens with disabilities. At Ready by 21, she supported the Regional Youth Employment Coalition and spearheaded research on short-term credentialing programs, laying the groundwork for the Blueprint4Careers online portal. As a Tomorrow Builder Fellow at WEPOWER, she led efforts to improve governance and coordination within St. Louis's early childhood education system.
“I am so honored and excited to join an institution with such an extensive history and important mission—to connect the community with science,“ said Kate Polokonis. “St. Louis is going all in on STEM industries. For our region to thrive, we have to improve educational outcomes in STEM education. Looking at the broader picture, we are at a critical point for science literacy: we’re facing large, complex problems that will require critical thinking, collaboration, and political will, which means we need a well-informed and meaningfully engaged populace that embraces the tenets of the nature of science. I look forward to leading The Academy of Science as it addresses these challenges.”
Polokonis’s work reflects her commitment to promoting racial, gender, and economic equity at the intersection of K-12 STEM education and workforce development. She is dedicated to helping St. Louis grow as national model for leveraging its ecosystem of STEM industries to create prosperity for all.
“During her tenure at STEMSTL, Kate brought a systems-change expertise that advanced the foundation for STEMSTL, driving toward collective impact in St. Louis’s STEM education and workforce ecosystem,” said Ben Johnson, Senior Vice President of Strategy and Operations, BioSTL. “After four years of partner engagement, capacity building, tool development, and celebrating St. Louis’s STEM initiatives, STEMSTL is positioned well for its mission to advance STEM learning and career opportunities that empower the growth of diverse problem solvers, innovators, and critical thinkers, enabling them to thrive in a globally connected world. BioSTL houses and helped launch STEMSTL because we recognize that the continued growth of St. Louis’s bioscience industry, along with other innovation industry clusters, requires a highly skilled, diverse, home-grown talent pool; and we are committed to continuing the important work of STEMSTL within BioSTL. We are excited for Kate and her new opportunity and for furthering our collaboration with The Academy of Science.”
Media Contact: Toni Kutchan | tmkutchan@academyofsciencestl.org
###
The Academy of Science of St. Louis’s mission is to promote the understanding and appreciation of science. Since 1856, the Academy has been a regional leader in the advancement and integration of science and technology into contemporary society. Learn more at https://academyofsciencestl.org.
END
The Academy of Science of St. Louis names Katherine Polokonis as executive director
2024-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How synchronization supports social interactions
2024-09-25
Turn-taking dynamics of social interactions are important for speech and gesture synchronization, enabling conversations to proceed efficiently, according to a study published September 25, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tifenn Fauviaux from the University of Montpellier, France, and colleagues.
Conversations encompass continuous exchanges of verbal and nonverbal information. Previous research has demonstrated that gestures and speech synchronize at the individual level. But few studies have investigated how this phenomenon ...
Dogs trained to detect explosives may perform worse in extreme temperature and humidity, taking longer to identify substances and with lower sensitivity
2024-09-25
Dogs trained to detect explosives may perform worse in extreme temperature and humidity, taking longer to identify substances and with lower sensitivity
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306817
Article Title: Environmental effects on explosive detection threshold of domestic dogs
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This research was made possible through funding provided by the DoD Army Research Office under Contract No. W911NF2120124. https://www.arl.army.mil/who-we-are/aro/. SAK’s work was supported by the National Science Foundation ...
Digital biomarkers shedding light on seasonality in mood disorders
2024-09-25
Wrist-based activity sensors worn by individuals with depression and those without over the course of two weeks provided evidence for the relationship between daily sunlight exposure and physical activity, according to a study published September 25, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS Mental Health by Oleg Kovtun and Sandra Rosenthal from Vanderbilt University, U.S.
Mood disorders are the leading cause of ‘disability’ worldwide. Up to 30 percent of individuals with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder display a seasonal pattern of symptoms. This phenomenon is now recognized in official diagnostic manuals. Yet very little ...
US politicians support climate action when linked to certain other issues
2024-09-25
The US House of Representatives is more likely to vote on climate action when it is linked with certain other environmental issues, according to a study published September 25, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Kayla Morton of the University of Washington, Seattle and colleagues.
Climate change is a very polarizing issue in US politics. While Congress has not passed many climate-related bills over the past two decades, the House of Representatives has voted on many bills and resolutions related to climate issues, thus providing an opportunity to examine the factors that motivate ...
Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight
2024-09-25
Mars wasn’t always the cold desert we see today. There’s increasing evidence that water once flowed on the Red Planet’s surface, billions of years ago. And if there was water, there must also have been a thick atmosphere to keep that water from freezing. But sometime around 3.5 billion years ago, the water dried up, and the air, once heavy with carbon dioxide, dramatically thinned, leaving only the wisp of an atmosphere that clings to the planet today.
Where exactly did Mars’ ...
Pitt study identifies potential new treatment for liver fibrosis
2024-09-25
New research from the University of Pittsburgh School of Pharmacy sheds light on the processes that lead to liver fibrosis and suggests a novel treatment approach for this common and serious condition.
Led by senior author Wen Xie, M.D., Ph.D., professor and Joseph Koslow endowed chair of the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and co-first authors Hung-Chun Tung, graduate student, and Jong-Won Kim, Ph.D., postdoctoral fellow, the study published today in Science Translational Medicine.
In this Q&A, Xie elaborates ...
Hardest hit by heat
2024-09-25
Each passing year, climate change drives summer temperatures to new extremes, with heat records being shattered one after another. In a new study, scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) have examined how extreme temperatures in the US affect the mortality of people from different racial groups. Risto Conte Keivabu, Ugofilippo Basellini, and Emilio Zagheni (director of MPIDR) analyzed data from 1993 to 2005 and examined racial differences in temperature-related deaths. The study found that both extreme cold (temperatures in the coldest 5%) and extreme heat (temperatures in the hottest 5%) increase mortality rates, with heat disproportionate impacting ...
Pigs may be transmission route of rat hepatitis E to humans
2024-09-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that pigs may function as a transmission vehicle for a strain of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) common in rats that has recently been found to infect humans.
The Rocahepevirus ratti strain is called “rat HEV” because rats are the primary reservoir of the virus. Since the first human case was reported in a person with a suppressed immune system in Hong Kong in 2018, at least 20 total human cases have been reported – including in people with normal immune function.
People infected with rat HEV did not report exposure to rats, leaving the cause of infection undefined. ...
The Foundation of Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (FCMSC) receives $100,000 gift for the June Halper MS Nursing Scholarship Fund
2024-09-25
(Hackensack, NJ, September 2024) The Foundation of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (FCMSC) recently received a generous donation of $100,000 from EMD Serono Inc., in honor of June Halper, MSN, APN-C, FAAN, MSCN. Ms. Halper a longtime pioneer in the comprehensive care movement for multiple sclerosis (MS), and leading nurse practitioner and MS advocate, passed away on July 24, 2024, at the age of 86, working until her final days as CEO of the CMSC, FCMSC and IOMSN (International Organization of MS Nurses).
Since 1978, Ms. ...
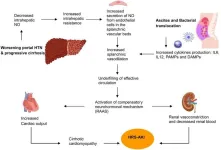
Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on renal and pulmonary function in hepatic decompensation with and without hepatorenal and hepatopulmonary syndromes
2024-09-25
Cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of mortality from non-communicable diseases, with complications arising as liver function deteriorates. HRS and HPS represent the most severe outcomes of cirrhosis, associated with systemic vasodilation driven by elevated levels of vasodilators like nitric oxide (NO). These complications significantly impair renal and pulmonary functions, leading to high mortality rates. TIPS, by shunting blood from the portal to systemic circulation, can potentially improve renal function by increasing systemic blood volume. However, the diversion of NO through TIPS could exacerbate systemic hypotension, posing a risk to renal ...