How academia drives sustainability: Discover the impact of science on the SDGs
2024-10-08
(Press-News.org)
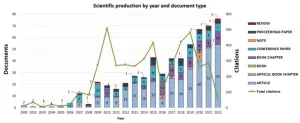
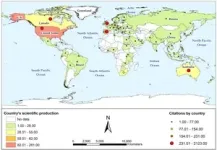
The role of universities in the fight for a fairer and more sustainable planet is increasingly significant. A team of researchers from ESPOL decided to examine how academia contributes to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by analyzing scientific publications on a global scale. Using tools such as ArcGIS, Biblioshiny, R, and VOSviewer, they conducted an in-depth review of scientific databases such as Web of Science and Scopus, tracking hundreds of articles addressing topics related to service-learning and community engagement. The results show a positive trend in scientific production on these topics, with a notable growth since 2009 and a peak in publications through 2022. Regarding the countries leading research in this field, the United States tops the list with 261 articles, followed by Spain with 64 and the United Kingdom with 40. The race for sustainability is on!.
Trending sustainability topics
Through a detailed keyword analysis, the study identified six major clusters dominating the academic conversation on sustainability in higher education. Did you know that “education for sustainable development” is the key term? Here's a quick overview of each cluster and its main lines of research:
Cluster 1: Education, Partnerships, and Health: Focuses on how universities collaborate to improve social well-being.
Cluster 2: Education for Sustainable Development, Curriculum Development, and Assessment: Everything about integrating sustainability into educational programs!
Cluster 3: Engineering Education, Interdisciplinarity, and STEM: A powerful combination to innovate in teaching.
Cluster 4: Environment, Corporate Social Responsibility, and Project-Based Learning: Knowledge put into practice in real-world projects.
Cluster 5: Social Responsibility, Social Justice, Leadership, and Transformation: Investigating how change begins in the classroom.
Cluster 6: Experiential Learning and Sustainability Competencies: Because experience is the best teacher to inspire future generations of conscious professionals.
The SDGs in Focus: The Major Contribution of Universities
After deeply analyzing 118 scientific articles, the researchers concluded that higher education is strongly committed to sustainability. Most universities have not only implemented innovative programs based on experiential learning but are also aligning their efforts with the SDGs. The most researched SDG? SDG 4: Quality Education, closely followed by SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being, and SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. Additionally, the research highlights that the main areas of expertise in which these studies are situated correspond to UNESCO fields: education, social and human sciences, and natural sciences.
Academia not only produces knowledge but creates a real impact in building a more sustainable future. And this is just the beginning!
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-08
Researchers at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science were recently awarded $2.8 million of a $5.8 million grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Climate Program Office to support a groundbreaking four-year project aimed at developing best practices for decision-ready climate projection information. This work will address increased demand by public and private sectors for reliable, long-term extreme weather climate information.
This initiative, led by the Rosenstiel School and including partners from the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Colorado State University, and Florida International ...
2024-10-08
Researchers from Western University, Stockton University, and University of Massachusetts Amherst published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines if firms benefit from adopting popular nicknames in their branding efforts.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “BMW is Powerful, Beemer is Not: Nickname Branding Impairs Brand Performance” and is authored by Zhe Zhang, Ning Ye, and Matthew Thomson.
Many brands have popular nicknames that have become a part of ...
2024-10-08
The expectations humans have of a pleasurable sensation asymmetrically shape neuronal responses and subjective experiences to hot sauce, according to a study published October 8th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Yi Luo from East China Normal University, Kenneth Kishida from Wake Forest School of Medicine, U.S., and colleagues.
Expectations shape our perception, profoundly influencing how we interpret the world. Positive expectations about sensory stimuli can alleviate distress and reduce pain through what’s ...
2024-10-08
In a rare, longitudinal study, researchers from Aalto University and the University of Oulu tracked one person’s brain and behavioral activity for five months using brain scans and data from wearable devices and smartphones.
‘We wanted to go beyond isolated events,’ says research leader Ana Triana. ‘Our behaviour and mental states are constantly shaped by our environment and experiences. Yet, we know little about the response of brain functional connectivity to environmental, physiological, and behavioral changes on different ...
2024-10-08
LA JOLLA (October 8, 2024)—The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has selected Salk Associate Professor Nicola Allen to receive a 2024 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award. The award recognizes exceptionally creative scientists pursuing highly innovative research and groundbreaking approaches to major challenges in biomedical, behavioral, or social sciences.
Allen will receive $3.5 million over five years to support her latest research, which investigates how plasticity in the adult brain could be enhanced. ...
2024-10-08
Proteins control most of the body’s functions, and their malfunction can have severe consequences, such as neurodegenerative diseases or cancer. Therefore, cells have mechanisms in place to control protein quality. In animal and human cells, chaperones of the Hsp70 class are at the heart of this control system, overseeing a wide array of biological processes. Yet, despite their crucial role, the precise molecular mechanism of Hsp70 chaperones has remained elusive for decades. Using a cutting-edge nanopore single-molecule technique, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with EPFL, has now made a significant breakthrough in determining how Hsp70 chaperones ...
2024-10-08
DataSeer and the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) are pleased to announce two new pilot programs designed to support high-quality reporting across scientific disciplines. The first will generate pre-filled MDAR reports for authors – saving them time and boosting the quality of methods reporting – for AAAS’ flagship journal Science. The second will establish an Open Science Indicators baseline dataset, quantifying how and when authors at Science share their ...
2024-10-08
Students don’t have to be friends, but they should be friendly. In other words, they should learn to be respectful of one another while sharing the same space. For Chad Rose, a nationally renowned bullying prevention expert at the University of Missouri, this idea is central to his efforts to reduce school bullying, and in turn, school violence.
Bullying is a risk factor for violence, said Rose, the director of Mizzou’s Bully Prevention Lab who has spent the past 18 years researching the subject.
“After the Safe Schools initiative was launched in 1999 by the U.S. Department of Education, we began to see that children and teens who have experienced prolonged ...
2024-10-08
Researchers at Concordia have developed a novel method of 3D printing that uses acoustic holograms. And they say it’s quicker than existing methods and capable of making more complex objects.
The process, called holographic direct sound printing (HDSP), is described in a recent article in the journal Nature Communications. It builds on a method introduced in 2022 that described how sonochemical reactions in microscopic cavitations regions — tiny bubbles — create extremely high temperatures and pressure for trillionths of a second to harden resin into complex ...
2024-10-08
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 8, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 18, 2024, entitled, “Determinants of cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy older adults.”
This research paper highlights that brain health deteriorates with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How academia drives sustainability: Discover the impact of science on the SDGs