Chinese herbal medicine’s potential in preventing dementia
Model mice given extracts and powders show restoration of cognitive and motor functions
2024-11-06
(Press-News.org)
Attempts to discover a breakthrough dementia drug might be drawing attention these days, but traditional medicinal products can offer hints for preventive medicine.
A research group led by Specially Appointed Professor Takami Tomiyama of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine has found that administering the dried seeds of a type of jujube called Ziziphus jujuba Miller var. spinosa, used as a medicinal herb in traditional Chinese medicine, holds promise in restoring cognitive and motor function in model mice.
By administering hot water extracts of Zizyphi spinosi semen to model mice with Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia with Lewy bodies, the team found that cognitive and motor functions were restored.
Furthermore, when the seeds were simply crushed into powder and administered to the model mice, the team discovered that the cognitive function of the model mice recovered to a level above that of control mice. In addition, the powders apparently suppressed cellular aging in older mice and improved their cognitive function to a similar level as younger mice.
Previously, members of the research team reported separately that the pathology of dementia in model mice improved with cognitive and motor functions restored after using the Hawaiian herb mamaki and the Chinese herb Acorus gramineus.
“The results of our research will hopefully make it possible to develop dementia prevention products that middle-aged and elderly people can take at their own discretion,” Professor Tomiyama suggested.
The findings are currently available as a reviewed preprint in eLife.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-06
[Vienna, November 6, 2024] — “Tell me how you read and I’ll tell you who you are.” By analyzing online reading behavior across millions of firms worldwide, a new study out of the Complexity Science Hub (CSH) connects how much information companies consume and how the consumption relates to their size.
"The way companies consume information is reminiscent of biological organisms. They take in, transmit, and transform information to make decisions. As with organisms, there are important size differences. Larger firms tend to consume information more efficiently ...
2024-11-06
A tightly tied waist cord of the underskirt (petticoat) traditionally worn under a saree, particularly in rural parts of India, may lead to what has been dubbed ‘petticoat cancer,’ warn doctors in the journal BMJ Case Reports after treating two women with this type of malignancy.
The continued pressure and friction on the skin can cause chronic inflammation, leading to ulceration, and, in some cases, progression to skin cancer, say the authors.
This phenomenon has previously been described as “saree cancer,” but it is the tightness of the waist cord that’s to blame, ...
2024-11-06
EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:30 PM EST Tuesday, November 5, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
10% of Children in High-Burden Tuberculosis Settings May Develop the Disease by Age 10
New findings also indicate that children who live in settings with a high burden of TB have a consistently high annual risk of developing TB infection throughout childhood.
An estimated 1.2 million children develop tuberculosis disease (TB) and 200,000 kids die from TB worldwide each year, but the risk of developing TB infection and disease throughout childhood remains under-studied. Furthermore, the majority of studies on the pediatric burden of TB are informed by data ...
2024-11-06
The Biden administration’s recently announced plan to replace all lead pipes in the U.S. is a reminder that the toxic metal remains a threat, even in a country that has largely banned its use. The smallest levels of lead exposure can cause a range of health damages over time, especially to children’s brain development. Stanford researchers Stephen Luby and Jenna Forsyth have spent years examining the widespread presence of lead in low-income countries, including in some commonly consumed products. They led a perspective published Nov. 5 in The Lancet Public Health that tallies lead’s global ...
2024-11-05
The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and defense technology company Lockheed Martin announced the signing of a new five-year master research agreement Oct. 31, reinforcing a longstanding partnership that helps UT take its research capabilities from the lab to the field.
“This partnership allows UT researchers to conduct true translational research,” said James Andes, director of national security research initiatives for UT. “Our research concepts are matured by working with technical champions at Lockheed Martin, and as a ...
2024-11-05
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The “RNA world” hypothesis proposes that the earliest life on Earth may have been based on RNA — a single-stranded molecule similar in many ways to DNA — like some modern viruses. This is because, like DNA, RNA can carry genetic information, but, like a protein, it can also act as an enzyme, initiating or accelerating reactions. While the activity of a few RNA enzymes — called ribozymes — have been tested on a case-by-case basis, there are thousands more that have been computationally predicted to exist in organisms ranging from bacteria to plants and animals. Now, ...
2024-11-05
At the end of the last global ice age, the deep-frozen Earth reached a built-in limit of climate change and thawed into a slushy planet.
Results from a Virginia Tech-led study provide the first direct geochemical evidence of the slushy planet — otherwise known as the “plumeworld ocean” era — when sky-high carbon dioxide levels forced the frozen Earth into a massive, rapid melting period.
“Our results have important implications for understanding how Earth's climate and ocean chemistry changed after the extreme conditions of the last global ...
2024-11-05
International survey of more than 1600 biomedical researchers on the perceived causes of irreproducibility of research results
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002870
Article Title: Biomedical researchers’ perspectives on the reproducibility of research
Author Countries: Canada, Australia, United States
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
2024-11-05
Integrating data from different experimental approaches into one model is challenging – this study presents a community-based, full-scale in silico model of the rat hippocampal CA1 region that integrates diverse experimental data from synapse to network
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002861
Article Title: Community-based reconstruction ...
2024-11-05
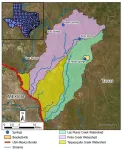
SAN ANTONIO — November 5, 2024 — Hydrologists at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will begin a 12-month targeted water-sampling campaign of the Las Moras Springs system near Brackettville, Texas. The project will analyze and characterize the system of springs and their relationship to the Pinto Creek watershed to improve water management and conservation efforts.
“Las Moras, like many other Texas spring systems, are at-risk and prone to going dry. It is important to clear up uncertainties about their source and relationship with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Chinese herbal medicine’s potential in preventing dementia
Model mice given extracts and powders show restoration of cognitive and motor functions