(Press-News.org) The mission of IQST is to further our understanding of nature and develop innovative technologies based on quantum science by leveraging synergies between the natural sciences, engineering, and life sciences. "Many KIT scientists already successfully support IQST with their expertise as Fellows. All the more I am pleased that the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology is now joining our interdisciplinary centre as an institution," says IQST Director Prof. Stefanie Barz. "This will strengthen networking within the academic quantum community in Baden-Württemberg," emphasizes Barz, an expert in quantum information and quantum technology from the Institute for Functional Matter and Quantum Technologies (FMQ) at the University of Stuttgart.
Focus on applications
IQST scientists collaborate on innovative research in quantum science and explore applications that will benefit society. "Although quantum technologies still require significant basic research, the focus on applications is becoming increasingly important," explains physicist Prof. Fedor Jelezko, IQST Director and Head of the Institute of Quantum Optics at the University of Ulm. "KIT joining IQST decisively strengthens this centre of excellence in quantum science in Baden-Württemberg," Jelezko continues. Among other things, quantum technologies will make sensors for manufacturing and medical technology more precise and efficient, ensure secure communication channels, and enhance high-performance computing. Promising areas of application are already emerging, particularly in sensor technology and communications.
Bundled competence in quantum research
"By joining the network, KIT scientists will become part of an established research network in quantum technologies in Baden-Württemberg," explains chemist Prof. Mario Ruben from the Institute of Quantum Materials and Technologies (IQMT) at KIT. KIT's profile in the field of quantum technologies, in particular with its focus on molecular and superconducting quantum bits, fits in very well with the activities developed by IQST over the last ten years.
Joint Cluster of Excellence initiative Chem4Quant
KIT and the Universities of Stuttgart and Ulm are also pooling their expertise in quantum research through the joint Cluster of Excellence initiative "Chem4Quant" which focuses on molecular quantum systems, a new area of quantum technologies. This rapidly developing branch of science complements the expertise developed at IQST over the past decade and is expected to further strengthen Baden-Württemberg's globally leading position in the quantum sciences.
Open to the research community and young talent
Key objectives for the growing IQST include the development of a new interdisciplinary understanding of quantum systems, the use of quantum technologies to solve major societal challenges, and the communication of these advances to the public. IQST is open to researchers from across Baden-Württemberg. In addition, the centre is dedicated to promoting young scientists through Master's, graduate and postdoctoral programmes. For example, at the beginning of 2025 eleven doctoral projects will start at the IQST Graduate School school @QuantumBW.
About the IQST and quantum technologies in Baden-Württemberg
IQST was founded in 2014 on the initiative of Prof. Wolfgang Schleich (University of Ulm) and Prof. Tilman Pfau (University of Stuttgart). In addition to the Universities of Stuttgart and Ulm, the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research (MPI-FKF) in Stuttgart is its third founding member. The centre is funded by its partner institutions, the Carl Zeiss Foundation, and the Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts Baden-Württemberg (MWK). MWK funded the entire centre from 2014 to 2019 and again from July 2024 through the IQST Graduate School @QuantumBW
As part of the Baden-Württemberg innovation campus “QuantumBW”, which aims to bring quantum technologies to market maturity, IQST connects the scientific “quantum community” and forms its academic platform. It is also part of the nationwide Quantum Alliance network.
END
State-wide center for quantum science: Karlsruhe Institute of Technology joins IQST as a new partner
2024-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cellular traffic congestion in chronic diseases suggests new therapeutic targets
2024-11-27
***Embargoed until November 27 at 11 AM EST***
Chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and inflammatory disorders have a huge impact on humanity. They are a leading cause of disease burden and deaths around the globe, are physically and economically taxing, and the number of people with such diseases is growing.
Treating chronic disease has proven difficult because there is not one simple cause, like a single gene mutation, that a treatment could target. At least, that’s how it has appeared to scientists. However, research from Whitehead Institute Member Richard Young and colleagues, published in the journal ...
Cervical cancer mortality among US women younger than age 25
2024-11-27
About The Study: This study found a steep decline in cervical cancer mortality among U.S. women younger than 25 years between 2016 and 2021. This cohort of women is the first to be widely protected against cervical cancer by human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines. The findings from this study in the context of other published research suggest that HPV vaccination affected the sequential decline in HPV infection prevalence, cervical cancer incidence, and cervical cancer mortality.
Corresponding ...
Fossil dung reveals clues to dinosaur success story
2024-11-27
In an international collaboration, researchers at Uppsala University have been able to identify undigested food remains, plants and prey in the fossilised faeces of dinosaurs. These analyses of hundreds of samples provide clues about the role dinosaurs played in the ecosystem around 200 million years ago. The findings have been published in the journal Nature.
“Piecing together ‘who ate whom’ in the past is true detective work,” says Martin Qvarnström, researcher at the Department of Organismal Biology and lead author of the study. “Being able to examine what animals ate and how they interacted with their environment helps us understand what enabled ...
New research points way to more reliable brain studies
2024-11-27
Brain-wide association studies, which use magnetic resonance imaging to identify relationships between brain structure or function and human behavior or health, have faced criticism for producing results that often cannot be replicated by other researchers.
A new study published in Nature demonstrates that careful attention to study design can substantially improve the reliability of this type of research. For the study, Kaidi Kang, a biostatistics PhD student, Simon Vandekar, PhD, associate professor of Biostatistics, and colleagues analyzed data from more than 77,000 brain scans across 63 studies.
The ...
‘Alzheimer’s in dish’ model shows promise for accelerating drug discovery
2024-11-27
A decade ago, researchers introduced a new model for studying Alzheimer’s disease. Known as “Alzheimer’s in a dish,” the model uses cultures of mature brain cells suspended in a gel to recapitulate what takes place in the human brain over 10 to 13 years in just six weeks. But does the model truly produce the same changes that take place in patients? In a new study, researchers from Mass General Brigham, in collaboration with colleagues at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), created an algorithm to assess, in an unbiased manner, how well models of Alzheimer’s disease ...
Ultraprocessed food intake and psoriasis
2024-11-27
About The Study: The results of this study showed an association between high ultraprocessed food intake and active psoriasis status. After adjustments for age, body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, and comorbidities, the results remained significant, suggesting that ultraprocessed food intake has a proinflammatory action separate from high BMI.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Emilie Sbidian, MD, PhD, email emilie.sbidian@aphp.fr.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Race and ethnicity, gender, and promotion of physicians in academic medicine
2024-11-27
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that preferential promotion of white men within academic medicine continues to persist in the new millennium, with racially and ethnically diverse women experiencing greater underpromotion. To achieve a workforce that reflects the diversity of the U.S. population, this study suggests that academic medicine needs to transform its culture and practices surrounding faculty appointments and promotions.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lauren Clark, MS, email lclark5@kumc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Testing and masking policies and hospital-onset respiratory viral infections
2024-11-27
About The Study: In this study, stopping universal masking and SARS-CoV-2 testing was associated with a significant increase in hospital-onset respiratory viral infections relative to community infections. Restarting the masking of health care workers was associated with a significant decrease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Theodore R. Pak, MD, PhD, email tpak@mgh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.48063)
Editor’s ...
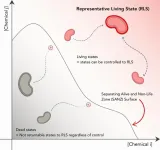
A matter of life and death
2024-11-27
Cellular death is a fundamental concept in the biological sciences. Given its significance though, its definition depends on the context in which it takes place, and lacks a general mathematical definition. Researchers from the University of Tokyo propose a new mathematical definition of death based on whether a potentially dead cell can return to a predefined “representative state of living,” which are the states of being that we can confidently call “alive.” The researchers’ work could be useful for biological researchers and future medical research.
While it’s ...
Huge cost savings from more efficient use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer reported in SONIA study
2024-11-27
On November 27, the prestigious journal Nature will publish the results of an innovative breast cancer research project from the Netherlands. This study, the SONIA trial, showed that delaying and shortening the duration of a specific anti-cancer therapy (CDK4/6 inhibitors) in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer leads to similar survival outcomes, while reducing toxicity and achieving substantial cost reductions: over 45 million euros per year in the Netherlands and over 5 billion dollars in the United States. This is the first time an efficiency study like this has been conducted in collaboration with Dutch health ...