(Press-News.org) Johns Hopkins University engineers have developed a pioneering prosthetic hand that can grip plush toys, water bottles, and other everyday objects like a human, carefully conforming and adjusting its grasp to avoid damaging or mishandling whatever it holds.
The system’s hybrid design is a first for robotic hands, which have typically been too rigid or too soft to replicate a human’s touch when handling objects of varying textures and materials. The innovation offers a promising solution for people with hand loss and could improve how robotic arms interact with their environment.
Details about the device appear today in Science Advances.
“The goal from the beginning has been to create a prosthetic hand that we model based on the human hand’s physical and sensing capabilities—a more natural prosthetic that functions and feels like a lost limb,” said Sriramana Sankar, a Johns Hopkins biomedical engineer who led the work. “We want to give people with upper-limb loss the ability to safely and freely interact with their environment, to feel and hold their loved ones without concern of hurting them.”
The device, developed by the same Neuroengineering and Biomedical Instrumentations Lab that in 2018 created the world’s first electronic “skin” with a humanlike sense of pain, features a multifinger system with rubberlike polymers and a rigid 3D-printed internal skeleton. Its three layers of tactile sensors, inspired by the layers of human skin, allow it to grasp and distinguish objects of various shapes and surface textures, rather than just detect touch. Each of its soft air-filled finger joints can be controlled with the forearm’s muscles, and machine learning algorithms focus the signals from the artificial touch receptors to create a realistic sense of touch, Sankar said. “The sensory information from its fingers is translated into the language of nerves to provide naturalistic sensory feedback through electrical nerve stimulation.”
In the lab, the hand identified and manipulated 15 everyday objects, including delicate stuffed toys, dish sponges, and cardboard boxes, as well as pineapples, metal water bottles, and other sturdier items. In the experiments, the device achieved the best performance compared with the alternatives, successfully handling objects with 99.69% accuracy and adjusting its grip as needed to prevent mishaps. The best example was when it nimbly picked up a thin, fragile plastic cup filled with water, using only three fingers without denting it.
“We’re combining the strengths of both rigid and soft robotics to mimic the human hand,” Sankar said. “The human hand isn’t completely rigid or purely soft—it’s a hybrid system, with bones, soft joints, and tissue working together. That’s what we want our prosthetic hand to achieve. This is new territory for robotics and prosthetics, which haven’t fully embraced this hybrid technology before. It’s being able to give a firm handshake or pick up a soft object without fear of crushing it.”
To help amputees regain the ability to feel objects while grasping, prostheses will need three key components: sensors to detect the environment, a system to translate that data into nerve-like signals, and a way to stimulate nerves so the person can feel the sensation, said Nitish Thakor, a Johns Hopkins biomedical engineering professor who directed the work.
The bioinspired technology allows the hand to function this way, using muscle signals from the forearm, like most hand prostheses. These signals bridge the brain and nerves, allowing the hand to flex, release, or react based on its sense of touch. The result is a robotic hand that intuitively “knows” what it’s touching, much like the nervous system does, Thakor said.
“If you’re holding a cup of coffee, how do you know you’re about to drop it? Your palm and fingertips send signals to your brain that the cup is slipping,” Thakor said. “Our system is neurally inspired—it models the hand’s touch receptors to produce nervelike messages so the prosthetics’ ‘brain,’ or its computer, understands if something is hot or cold, soft or hard, or slipping from the grip.”
While the research is an early breakthrough for hybrid robotic technology that could transform both prosthetics and robotics, more work is needed to refine the system, Thakor said. Future improvements could include stronger grip forces, additional sensors, and industrial-grade materials.
“This hybrid dexterity isn’t just essential for next-generation prostheses,” Thakor said. “It’s what the robotic hands of the future need because they won’t just be handling large, heavy objects. They’ll need to work with delicate materials such as glass, fabric, or soft toys. That’s why a hybrid robot, designed like the human hand, is so valuable—it combines soft and rigid structures, just like our skin, tissue, and bones.”
Other authors include Wen-Yu Cheng of Florida Atlantic University; Jinghua Zhang, Ariel Slepyan, Mark M. Iskarous, Rebecca J. Greene, Rene DeBrabander, and Junjun Chen of Johns Hopkins; and Arnav Gupta of the University of Illinois Chicago.
This research was funded by the grant “Neuromorphic Feedback: A Strategy to Enhance Prosthesis Embodiment and Performance” from the Department of Defense through the Orthotics and Prosthetics Outcomes Research Program (W81XWH2010842) and the National Science Foundation.
END
Feeling is believing: Bionic hand “knows” what it’s touching, grasps like a human
2025-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $4.4 million to top young scientists
2025-03-05
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named 13 new Damon Runyon Fellows, exceptional postdoctoral scientists conducting basic and translational cancer research in the laboratories of leading senior investigators. The prestigious, four-year Fellowship encourages the nation's most promising young scientists to pursue careers in cancer research by providing them with independent funding ($300,000 total) to investigate cancer causes, mechanisms, therapies, and prevention.
The Foundation has also named ...
Over-the-counter pain relievers linked to improved recovery from concussion
2025-03-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 5, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Over-the-counter pain relievers linked to improved recovery from concussion
MINNEAPOLIS – People who take over-the-counter pain relievers after a concussion may recover faster than those who do not take pain relievers, according to a preliminary study released today, March 5, 2025, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 77th Annual Meeting taking place April 5–9, 2025, in San Diego ...
Stressed out? It may increase the risk of stroke
2025-03-05
MINNEAPOLIS — Some people living with chronic stress have a higher risk of stroke, according to a study published on March 5, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study looked at younger adults and found an association between stress and stroke, with no known cause, in female participants, but not male participants. This study does not prove that stress causes stroke; it only shows an association.
“Younger people often experience stress due to the demands and pressures associated with work, including long hours and job insecurity, as well as financial burdens,” ...
Nanoscale tweaks help alloy withstand high-speed impacts
2025-03-05
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led collaboration devised a new method for designing metals and alloys that can withstand extreme impacts, which could lead to the development of automobiles, aircraft and armor that can better endure high-speed impacts, extreme heat and stress.
The research, published in Communications Materials, introduces nanometer-scale speed bumps that suppress a fundamental transition that controls how metallic materials deform.
The project was led by Mostafa Hassani, assistant professor of mechanical ...
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
2025-03-05
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
Article URL: https://plos.io/4baFCW5
Article title: AI-determined similarity increases likability and trustworthiness of human voices
Author countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during
2025-03-05
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during the Pliocene or Miocene epochs
Article URL: https://plos.io/4gQHlB2
Article title: Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes of Theobroma cacao from northern Peru
Author countries: Perú
Funding: This study was supported by the Programa Nacional de Investigación Científica y Estudios Avanzados (PROCIENCIA) funded by the Project through the Contract N° 026-2016-FONDECYT “Círculo de Investigación ...
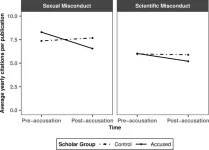
After sexual misconduct accusations, scholars’ work is cited less
2025-03-05
In a new analysis, scholars publicly accused of sexual misconduct experienced a significant decrease in the rate at which other scholars cited their published research. Giulia Maimone of the University of California, Los Angeles, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on March 5, 2025.
In academia, scholars cite other scholars’ publications as a widely agreed-upon way to reference existing research and promote scientific advancement. A scholar with a high number of citations may be considered particularly impactful in their field. Prior research ...
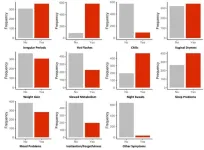
Menopause symptoms associated with future memory and neuropsychiatric problems
2025-03-05
Women who exhibit more menopausal symptoms are more likely to later have poorer cognitive function and mild behavioral impairments – both markers of dementia. That is the conclusion of a study of 896 postmenopausal females published March 5, 2025, in the open-access journal PLOS One by Zahinoor Ismail of University of Calgary, Canada, and colleagues.
Females are known to have a three-fold greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, and will be disproportionately ...
Findings may advance understanding of infertility in mothers
2025-03-05
Oxytocin, a hormone already known for its role in childbirth, milk release, and mother-infant bonding, may have a newfound purpose in mammalian reproduction. In times of maternal stress, the hormone can delay an embryo’s development for days to weeks after conception, a new study in rodents shows. According to the authors, the findings about so-called “diapause” may offer new insights into pregnancy and fertility issues faced by humans.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the study explored diapause, in which an embryo temporarily stops growing early in ...
Engineered cartilage from nasal septum cells helps treat complex knee injuries
2025-03-05
Injuries to the articular cartilage in different joints, including the knee, are painful and limit mobility. Therefore, researchers at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel are developing cartilage implants using cells from the patient’s nasal septum. A recent study shows that giving these cartilage implants more time to mature significantly improved clinical efficacy, even in patients with complex cartilage injuries. This suggests that the method could also be suitable for the treatment of degenerated cartilage in osteoarthritis.
An unlucky fall while skiing or playing ...