(Press-News.org) Toronto, ON – A new study published this week in Child Maltreatment found that in comparison to those who had not been abused in childhood, adults who had experienced both childhood physical and sexual abuse had approximately double the odds of physical and mental health conditions, including angina, arthritis, asthma, COPD, heart attack, depression, and disability -- even after considering respondents’ age, race, income, and health behaviors, as well as obesity.
Those who had been sexually abused, but not physically abused, were 55% to 90% more likely to experience these health outcomes compared to their peers who had not experienced any abuse. Adults who were physically abused, but not sexually abused, also had significantly elevated odds of these health outcomes compared to the non-abused, but the associations were more modest (between 20% to 50%).
“People don’t typically think about the impact early adversities can have on health outcomes later in life,” says first author Shannon Halls, a Research Coordinator at University of Toronto’s Institute for Life Course and Aging. “Our research underscores the harmful associations between early adversities, such as sexual and/or physical abuse, and a wide range of health issues in adulthood.”
In exploring this association, the study also examined whether the presence of an adult in the home who made the child feel safe and protected was associated with better long-term health outcomes among children who experienced abuse.
“We found that when children experiencing abuse had a protective adult in their home, the negative impact of abuse on their health as adults was less severe,” says co-author Andie MacNeil, a doctoral student at the Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work (FIFSW).
“Though more research is needed to pinpoint the precise mechanisms, it is evident that these relationships can play a key role in supporting children and mitigating the adverse health effects of abuse.”
The presence of a protective adult was not only important for children who had experienced abuse, but important for children who had not been abused as well. Children without a protective adult in their home, irrespective of childhood abuse status, were 20% to 40% more likely to experience adverse physical health outcomes and twice as likely to suffer from depression in adulthood.
“The implication here is that lacking the safe and stable relationships with adults can be just as harmful to children’s health as being physically abused,” says senior author Esme Fuller-Thomson, a Professor at FIFSW and Director for the Institute of Life Course and Aging at the University of Toronto.
The study’s authors point to the need for future research to unpack these findings in particular.
“It will be important in future research to investigate why some adults in the home are not adequately protective of children, and to discuss potential primary prevention interventions that can help parents provide a more protective environment for children,” said co-author Philip Baiden, an Associate Professor in the School of Social Work at the University of Texas at Arlington
The study analyzed data from the 2021 and 2022 Behavioural Risk Factor Surveillance System, a large representative sample from which over 80,000 adult U.S. respondents were included.
“Our research shows the importance of positive relationships between children and the adults in their lives” says Halls. “We hope that these findings can contribute to a better understanding for creating effective programs targeted at children experiencing abuse.”
END
Adults abused as children twice as likely to develop health and mental health conditions
The presence of a protective adult in the home was associated with better outcomes in the wake of physical and sexual abuse, providing promising insights for intervention efforts
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A dive into erythritol slurry and its potential for waste heat recovery
2025-03-11
Energy efficiency is crucial for sustainability, yet vast amounts of low-temperature waste heat remain unused in industrial processes. Now, researchers from Japan have investigated erythritol slurry as a promising heat transfer medium for thermal storage and transport. By analyzing its flow behavior and non-Newtonian properties, they developed a predictive equation for its rheological characteristics. Their findings could help guide the design of industrial waste heat recovery systems, advancing energy efficiency and carbon neutrality.
Energy efficiency is one of the most important pillars of our global sustainability goals. Simply put, one of the most straightforward and effective ...
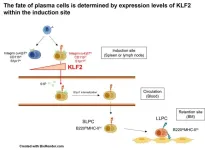
No place like home—how proteins that plasma cells express at their origin affect migration
2025-03-11
Osaka, Japan – Vaccine effectiveness relies on creating a strong antibody response that can be reactivated to fight future infections. Now, researchers from Japan report that antibody-producing cells are destined for longevity from the moment they are born.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University reveals that a key cell population involved in long-term immunity to infection is programmed early in its lifecycle to travel to protected sites in the body.
Plasma cells originate in lymphoid ...
Socioeconomic factors fuel global inequalities in Alzheimer's disease burden, study finds
2025-03-11
Ann Arbor, March 11, 2025 – An analysis of the global burden and temporal trends of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias (ADODs) reveals significant cross-country inequalities associated with a series of sociodemographic development-related risk factors, such as education, income, fertility, and health expenditure. The new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, calls for the development of targeted prevention and control strategies in different countries.
The burden of ADODs has risen globally over the past three decades. The authors of this first systematic and comprehensive global study analyzing ...
Foraging footballers suggest how we come together to act as one
2025-03-11
What do albatrosses searching for food, stock market fluctuations, and the dispersal patterns of seeds in the wind have in common?
They all exhibit a type of movement pattern called Lévy walk, which is characterized by a flurry of short, localized movements interspersed with occasional, long leaps. For living organisms, this is an optimal strategy for balancing the exploitation of nearby resources with the exploration of new opportunities when the distribution of resources is sparse and unknown.
Originally described in the context of particles drifting through liquid, Lévy walk has been found to accurately describe a very wide range of phenomena, from cold atom dynamics to ...
SSA: Semantic Structure Aware Inference for Weakly Pixel-Wise Dense Predictions without Cost
2025-03-11
CAM is proposed to highlight the class-related activation regions for an image classification network, where feature positions related to the specific object class are activated and have higher scores while other regions are suppressed and have lower scores. For specific visual tasks, CAM can be used to infer the object bounding boxes in weakly-supervised object location(WSOL) and generate pseudo-masks of training images in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS). Therefore, obtaining the high-quality CAM is very important to improve the recognition performance of weakly supervised pixel-wise ...
New test helps doctors predict a dangerous side effect of cancer treatment
2025-03-11
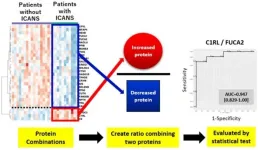
Fukuoka, Japan — Medical researchers in Japan have discovered a way to predict a potentially life-threatening side effect of cancer immunotherapy before it occurs. By analyzing cerebrospinal fluid collected pre-treatment, researchers at Kyushu University identified specific proteins associated with a damaging immune response that can affect the central nervous system after therapy. Their findings, published in Leukemia on 11 March, 2025, could make immunotherapy cancer treatment safer by helping doctors identify high-risk patients in advance, ...
UC Study: Long sentences for juveniles make reentry into society more difficult
2025-03-11
Juveniles grow up hearing a multitude of adages about life, such as: “True friends are forever,” “Fake it ’til you make it,” and “Change is a good thing.”
However, these adages — and other life advice about behavior in society — are difficult to process for juveniles who were incarcerated at a young age and served long sentences, says J.Z. Bennett, a criminologist at the University of Cincinnati whose research focuses on prison reform.
“Spending decades in prison removes individuals from social structures and sources of informal social control, such as education, employment, marriage and parenting,” he writes ...
Death by feral cat: DNA shows cats to be culprits in killing of native animals
2025-03-11
Conservation scientists from UNSW Sydney have used DNA technology to identify feral cats as the primary predators responsible for the deaths of reintroduced native animals at two conservation sites in South Australia.
The finding fits in with research data that suggests feral cats have killed more native animals than any other feral predators in Australia, and are believed to be responsible for two thirds of mammal extinctions since European settlement.
But in a study published recently in the ...
Plant Physiology is Searching for its Next Editor-in-Chief
2025-03-10
After taking the helm of Plant Physiology 2022, Yunde Zhao's celebrated term as Editor-in-Chief of the journal, during which he introduced changes that saw the journal flourish, will come to a close on December 31, 2026. The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is seeking a prominent plant scientist to assume the duties and responsibilities of Editor-in-Chief of Plant Physiology effective January 1, 2027. ASPB’s EIC Search Committee is charged with evaluating candidates for the position and invites members of the plant science community to participate in the process by nominating someone who they ...
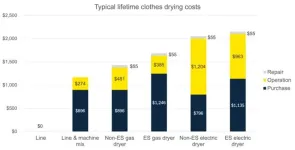
Clothes dryers and the bottom line: Switching to air drying can save hundreds
2025-03-10
Researchers from the University of Michigan are hoping their new study will inspire some Americans to rethink their relationship with laundry. Because, no matter how you spin it, clothes dryers use a lot of comparatively costly energy when air works for free.
Household dryers in the U.S. consume about 3% of our residential energy budget, about six times that used by washing machines. Collectively, dryers cost more than $7 billion to power each year in this country, and generating that energy emits the equivalent of more than ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Adults abused as children twice as likely to develop health and mental health conditionsThe presence of a protective adult in the home was associated with better outcomes in the wake of physical and sexual abuse, providing promising insights for intervention efforts