(Press-News.org) Microplastics and the much smaller nanoplastics enter the human body in various ways, for example through food or the air we breathe. A large proportion is excreted, but a certain amount remains in organs, blood and other body fluids. In the FFG bridge project Nano-VISION, which was launched two years ago together with the start-up BRAVE Analytics, a team led by Harald Fitzek from the Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) and an ophthalmologist from Graz addressed the question of whether nanoplastics also play a role in ophthalmology. The project partners have now been able to develop a method for detecting and quantifying nanoplastics in transparent body fluids and determining their chemical composition. As an exemplary application of the method, the research team is investigating whether intraocular lenses release nanoplastics. There have been no such studies to date, and initial results have already been submitted to a scientific journal.
Scattered laser light reveals concentration and composition
Micro- and nanoplastics are detected in two steps. The sensor platform developed by BRAVE Analytics draws in the liquid to be analysed and pumps it through a glass tube. There, a weakly focused laser is shone through the liquid in or against the direction of flow. If the light hits any particles, the laser pulse accelerates or decelerates them – larger particles more strongly than smaller ones. The different velocity values allow conclusions to be drawn about the size of the particles and their concentration in the liquid. This method, called optofluidic force induction, was developed by Christian Hill from BRAVE Analytics at the Medical University of Graz.
What is new is the combination of optofluidic force induction with Raman spectroscopy. Now the spectrum of the laser light scattered by individual particles in the liquid is also analysed. A small part of the light, the so-called Raman scattering, has a different frequency to the laser itself and thus allows conclusions to be drawn about the composition of the particles. “Depending on the material of the focused particles, the frequency values are slightly different in each case and thus reveal the exact chemical composition,” says Raman spectroscopy expert Harald Fitzek. “This works particularly well with organic materials and plastics.”
Intraocular lenses: Tests on the possible presence of nanoparticles
The Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis is currently conducting further investigations into the extent to which intraocular lenses yield nanoplastics spontaneously, after mechanical stress or when exposed to laser energy. The findings from these tests are extremely important for ophthalmic surgeons and lens manufacturers and will be published in a scientific journal.
“Our method for detecting micro- and nanoplastics can be applied to clear body fluids such as urine, tear fluid or blood plasma,” says Harald Fitzek. “However, it is also suitable for the continuous monitoring of liquid flows in industry as well as drinking and waste water.”
END
New method for detecting nanoplastics in body fluids
Together with the company BRAVE Analytics, researchers at TU Graz have developed a method for detecting nanoplastics in liquids and determining their composition
2025-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Do disasters delay early cancer diagnoses?
2025-04-14
Rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnoses dropped during and shortly after Hurricanes Irma and Maria and the COVID-19 pandemic in Puerto Rico, according to a recent analysis. However, late-stage diagnoses eventually exceeded expectations, suggesting that limited access to cancer screening services due to these disasters likely hindered timely CRC diagnoses. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
During disasters, medical services may be delayed or inaccessible due to damaged infrastructure, overburdened health ...
Rise and shine: Natural light lessens morning fatigue
2025-04-14
Sleep is a necessary part of people’s daily routine, but modern lifestyles and technology have ushered in an era of decreased rest time and subsequent fatigue. Further, the bedroom environment, such as light, sound, and temperature, is important for a good night's sleep, though this is often neglected in residential architecture.
In search of a conclusive remedy, common sleep studies use artificial light that is easy to control. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers, however, believe natural light could be more effective for re-creating actual living environments.
To test this, Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology student Xiaorui Wang and Professor ...
Nature’s plan for delaying pest resistance deciphered
2025-04-14
Farmers in dozens of countries have embraced crops genetically engineered to produce proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) bacteria that kill some key pests yet are safe for people and wildlife. Although this biotech approach reduces reliance on insecticide sprays thereby providing economic and environmental benefits, resistance to Bt crops has evolved in at least 11 species of pests. Thus, effective ways to combat such pest resistance are urgently needed.
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a natural strategy for thwarting pest resistance to Bt proteins. The researchers at the University of Arizona and ...
New guidance for managing obesity in children and adolescents
2025-04-14
A new guideline to help health care providers manage obesity in children and adolescents takes a patient-centred approach, emphasizing behavioural and psychological supports that focus on outcomes valued by patients and their families.
The guidelinehttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241456, based on the latest evidence, is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
It was developed by Obesity Canada through an extensive, 4-year-long collaboration involving adolescents and caregivers with lived obesity experience, methodologists, health care providers, and more than 50 multidisciplinary ...
High blood pressure? Eat more bananas
2025-04-14
New research from the University of Waterloo suggests increasing the ratio of dietary potassium to sodium intake may be more effective for lowering blood pressure than simply reducing sodium intake.
High blood pressure affects over 30 per cent of adults globally. It's the leading cause of coronary heart disease and stroke and may also lead to other afflictions like chronic kidney disease, heart failure, irregular heartbeats, and dementia.
"Usually, when we have high blood pressure, we are advised to eat less salt," said Anita Layton, professor of Applied Mathematics, ...
Weak evidence behind how we measure pain in babies
2025-04-14
A newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration.
Despite the critical importance of accurately measuring pain in newborns, the review found that none of the available scales are backed by the high-quality evidence and methodological safeguards required to confirm their validity and reliability in clinical practice.
Neonatal pain assessment and management presents a challenge for clinical staff worldwide. Over 40 rating scales have been developed and adapted worldwide assessing ...
Novel breath test shows promise for diagnosing and monitoring bacterial infections
2025-04-13
This release has been removed upon request of the submitting institution. Please contact Luke Paskins, luke.paskins@beyondpr.com for more information. END ...
AI-guided lung ultrasound marks a major breakthrough in tuberculosis diagnosis
2025-04-13
(Monday, 14 April 2025, Vienna, Austria) A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has demonstrated that an AI-powered lung ultrasound outperforms human experts by 9% in diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis (TB).1
The ULTR-AI suite analyses images from portable, smartphone-connected ultrasound devices, offering a sputum-free, rapid, and scalable alternative for TB detection. The results exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) benchmarks for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis, marking a major opportunity for accessible and efficient TB triage.
Despite previous global declines, TB rates rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023.2 Early ...
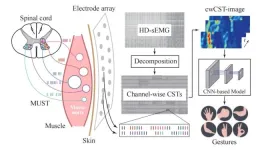
Towards hand gesture recognition using a channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model
2025-04-13
A research paper by scientists at Shanghai Jiao Tong University presented a novel channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model (cwCST-CNN) for hand gesture recognition.
The research paper, published on Mar. 21, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, leverage a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract both local and global features for classifying hand gestures, by decomposing high-density surface EMG (HD-sEMG) signals into channel-wise cumulative spike trains (cw-CSTs) ...
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
2025-04-12
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
New research has revealed that Schistosoma haematobium (S. haematobium), a parasitic infection affecting millions globally, can trigger cancer-related gene activity in the cervical lining, with changes becoming even more pronounced after treatment.1 Presented today at ESCMID Global 2025, this pivotal study sheds new light on how this often-overlooked parasitic disease may contribute to cervical cancer risk at the molecular level.
Schistosomiasis is a widespread parasitic disease, particularly prevalent in regions with poor access to clean water and sanitation.2 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New method for detecting nanoplastics in body fluidsTogether with the company BRAVE Analytics, researchers at TU Graz have developed a method for detecting nanoplastics in liquids and determining their composition