(Press-News.org) An international team led by the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has discovered the most distant spiral galaxy candidate known to date. This ultra-massive system existed just one billion years after the Big Bang and already shows a remarkably mature structure, with a central old bulge, a large star-forming disk, and well-defined spiral arms. The discovery was made using data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and offers important insights into how galaxies can form and evolve so rapidly in the early Universe. The study is published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Large spiral galaxies like the Milky Way are expected to take several billion years to form. During the first billion years of cosmic history, galaxies are thought to be small, chaotic, and irregular in shape. However, the JWST is beginning to reveal a very different picture. Its deep infrared imaging is uncovering surprisingly massive and well-structured galaxies at much earlier times than previously expected – prompting astronomers to reassess how and when galaxies take shape in the early Universe.
A Milky Way Twin in the Early Universe
Among these new findings is Zhúlóng, the most distant spiral galaxy candidate identified to date, seen at a redshift of 5.2 – just 1 billion years after the Big Bang. Despite this early epoch, the galaxy exhibits a surprisingly mature structure: a central old bulge, a large star-forming disk, and spiral arms – features typically seen in nearby galaxies.
‘‘We named this galaxy Zhúlóng, meaning ‘Torch Dragon’ in Chinese mythology. In the myth, Zhúlóng is a powerful red solar dragon that creates day and night by opening and closing its eyes, symbolizing light and cosmic time,’’ says Dr. Mengyuan Xiao, postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Astronomy of the Faculty of Science of UNIGE and lead author of the study.
“What makes Zhúlóng stand out is just how much it resembles the Milky Way – both in shape, size, and stellar mass,” she adds. Its disk spans over 60,000 light-years, comparable to our own galaxy, and contains more than 100 billion solar masses in stars. This makes it one of the most compelling Milky Way analogues ever found at such an early time, raising new questions about how massive, well-ordered spiral galaxies could form so soon after the Big Bang.
A serendipitous discovery
Zhúlóng was discovered in deep imaging from JWST’s PANORAMIC survey (GO-2514), a wide-area extragalactic program led by Christina Williams (NOIRLab) and Pascal Oesch (UNIGE). PANORAMIC exploits JWST’s unique “pure parallel” mode – an efficient strategy to collect high-quality images while JWST’s main instrument is taking data on another target. “This allows JWST to map large areas of the sky, which is essential for discovering massive galaxies, as they are incredibly rare,” says Dr. Christina Williams, assistant astronomer at NOIRLab and principal investigator of the PANORAMIC program. “This discovery highlights the potential of pure parallel programs for uncovering rare, distant objects that stress-test galaxy formation models.”
Rewriting the Story
Spiral structures were previously thought to take billions of years to develop, and massive galaxies were not expected to exist until much later in the universe, because they typically form after smaller galaxies merged together over time. “This discovery shows how JWST is fundamentally changing our view of the early Universe,” says Prof. Pascal Oesch, associate professor in the Department of Astronomy at the Faculty of Science of UNIGE and co-principal investigator of the PANORAMIC program.
Future JWST and Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) observations will help confirm its properties and reveal more about its formation history. As new wide-area JWST surveys continue, astronomers expect to find more such galaxies – offering fresh insights into the complex processes shaping galaxies in the early Universe.
END
The most distant twin of the Milky Way ever observed
An international team led by UNIGE has discovered a massive, Milky Way-like spiral galaxy that formed just 1 billion years after the Big Bang, revealing an unexpectedly mature structure in the
2025-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New method to deliver cell therapies in critically ill patients on external lung support
2025-04-16
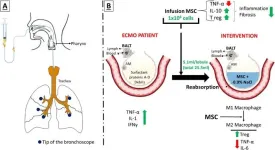
A multidisciplinary clinical team led by Professor Bernat Soria from the Institute of Bioengineering at the Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH, Spain) has developed a new method to deliver cell therapies in patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), a life support system used in cases of severe lung failure. The advance has been published in Stem Cell Research & Therapy (Springer Nature Group). The team has opted not to patent the technique in order to encourage its use in public health systems ...
Climate-related trauma can have lasting effects on decision-making, study finds
2025-04-16
A new study from University of California San Diego suggests that climate trauma — such as experiencing a devastating wildfire — can have lasting effects on cognitive function. The research, which focused on survivors of the 2018 Camp Fire in Northern California, found that individuals directly exposed to the disaster had difficulty making decisions that prioritize long-term benefits. The findings were recently published in Scientific Reports, part of the Nature portfolio of journals.
“Our previous research has shown that survivors of California’s 2018 Camp Fire experience prolonged symptoms ...
Your cells can hear
2025-04-16
Kyoto, Japan -- There's a sensation that you experience -- near a plane taking off or a speaker bank at a concert -- from a sound so total that you feel it in your very being. When this happens, not only do your brain and ears perceive it, but your cells may also.
Technically speaking, sound is a simple phenomenon, consisting of compressional mechanical waves transmitted through substances, which exists universally in the non-equilibrated material world. Sound is also a vital source of environmental information for living beings, while its capacity to induce physiological responses at the cell ...
Farm robot autonomously navigates, harvests among raised beds
2025-04-16
Strawberry fields forever will exist for the in-demand fruit, but the laborers who do the backbreaking work of harvesting them might continue to dwindle. While raised, high-bed cultivation somewhat eases the manual labor, the need for robots to help harvest strawberries, tomatoes, and other such produce is apparent.
As a first step, Osaka Metropolitan University Assistant Professor Takuya Fujinaga has developed an algorithm for robots to autonomously drive in two modes: moving to a pre-designated destination and moving alongside ...
The bear in the (court)room: who decides on removing grizzly bears from the endangered species list?
2025-04-16
By Dr Kelly Dunning
The Endangered Species Act (ESA), now 50 years old, was once a rare beacon of bipartisan unity, signed into law by President Richard Nixon with near-unanimous political support. Its purpose was clear: protect imperiled species and enable their recovery using the best available science to do so. Yet, as our case study on the grizzly bear in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem reveals, wildlife management under the ESA has changed, becoming a political battleground where science is increasingly drowned out by partisan ideology, bureaucratic delays, power struggles, and competing political interests. ...
First study reveals neurotoxic potential of rose-scented citronellol at high exposure levels
2025-04-16
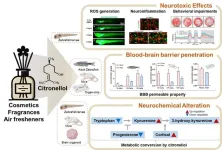
Citronellol, a rose-scented compound commonly found in cosmetics and household products, has long been considered safe. However, a Korean research team has, for the first time, identified its potential to cause neurotoxicity when excessively exposed.
A collaborative research team led by Dr. Myung Ae Bae at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) and Professors Hae-Chul Park and Suhyun Kim at Korea University has discovered that high concentrations of citronellol can trigger neurological and behavioral toxicity. The study, published in the Journal ...
For a while, crocodile
2025-04-16
Most people think of crocodylians as living fossils— stubbornly unchanged, prehistoric relics that have ruled the world’s swampiest corners for millions of years. But their evolutionary history tells a different story, according to new research led by the University of Central Oklahoma (UCO) and the University of Utah.
Crocodylians are surviving members of a 230-million-year lineage called crocodylomorphs, a group that includes living crocodylians (i.e. crocodiles, alligators and gharials) and their many extinct ...
Scientists find evidence that overturns theories of the origin of water on Earth
2025-04-16
Images available via link in the notes section
University of Oxford researchers have helped overturn the popular theory that water on Earth originated from asteroids bombarding its surface;
Scientists have analysed a meteorite analogous to the early Earth to understand the origin of hydrogen on our planet.
The research team demonstrated that the material which built our planet was far richer in hydrogen than previously thought.
The findings, which support the theory that the formation of habitable conditions on Earth did not rely on asteroids ...
Foraging on the wing: How can ecologically similar birds live together?
2025-04-16
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A spat between birds at your backyard birdfeeder highlights the sometimes fierce competition for resources that animals face in the natural world, but some ecologically similar species appear to coexist peacefully. A classic study in songbirds by Robert MacArthur, one of the founders of modern ecology, suggested that similar wood warblers — insect-eating, colorful forest songbirds — can live in the same trees because they actually occupy slightly different locations in the tree and presumably eat different insects. Now, a new study is using modern techniques to revisit MacArthur’s ...
Little birds’ personalities shine through their song – and may help find a mate
2025-04-16
In birds, singing behaviours play a critical role in mating and territory defence.
Although birdsong can signal individual quality and personality, very few studies have explored the relationship between individual personality and song complexity, and none has investigated this in females, say Flinders University animal behaviour experts.
They have examined the relationships between song complexity and two personality traits (exploration and aggressiveness) in wild superb fairy-wrens (Malurus cyaneus) in Australia, a species in which both sexes learn to produce complex songs.
“Regardless of their sex ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] The most distant twin of the Milky Way ever observedAn international team led by UNIGE has discovered a massive, Milky Way-like spiral galaxy that formed just 1 billion years after the Big Bang, revealing an unexpectedly mature structure in the