(Press-News.org) GREENSBURG, PA—March 1, 2011— Imagine that you witness a crime. The police investigator brings you to the police station to obtain an official statement, but between the crime and your official witness statement, you are exposed to other (potentially inaccurate) information about the crime. Before administering the criminal interview, the investigator asks you a litany of mundane demographic questions in a dry and uninterested manner, then moves directly into the interview about the crime. Would you feel comfortable? Most importantly, would your report be accurate and detailed, uninfluenced by the outside information you received?
According to major investigative interviewing protocols police investigators are expected to create a comfortable environment before interviewing adult witnesses to a crime. Police often fail to spend time building rapport with adult witnesses before a criminal interview, possibly in an effort to save time. An article published in a forthcoming issue of Applied Cognitive Psychology shows that the additional time spent on building rapport (in particular using verbal techniques) may prevent inaccuracies in witness accounts and decrease the witness' susceptibility to post-event misinformation.
Lead author Dr. Jonathan P. Vallano, "When police interviewers build rapport by creating a comfortable environment with a witness, that witness is less likely to report false information than a witness that has not benefited from a comfortable environment. Our study, based on accounts from over 100 college-aged adults who viewed a videotaped mock theft crime, shows that building rapport before these adults were asked to recall the mock crime decreased the percentage of inaccurate information reported by these witnesses."
Furthermore, the researchers found that rapport-building is most beneficial when witnesses are asked open-ended questions rather than specific, or cued questions related to the crime. Vallano, "We found that when the investigator shares something about his or herself with the witness, the person being interviewed is more likely to trust the interviewer and disclose a higher percentage of accurate information in return."
The findings suggest that investigators should place a stronger emphasis on rapport-building before interviewing cooperative adult witnesses. In addition, through this research, the legal field in general, including expert witnesses, will now have important information on how rapport-building (or the lack thereof) affects witness recall, which can be used when analysing the quality of investigative interviewing techniques.
INFORMATION:
This study will be published in a forthcoming issue of Applied Cognitive Psychology. Members of the media may request a full-text version of this article by contacting scholarlynews@wiley.com.
Article: "A Comfortable Witness is a Good Witness: Rapport-Building and Susceptibility to Misinformation in an Investigative Mock-Crime Interview."; Jonathan P. Vallano, Ph.D & Nadja Schreiber Compo. Applied Cognitive Psychology.; Published Online: February 28, 2011 (DOI: 10.1002/acp.1789).
Abstract:
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/acp.1789/abstract
Jonathan P. Vallano, Ph.D. is an Assistant Professor of Psychology at the University of Pittsburgh at Greensburg. He earned his Ph.D. in experimental psychology (with an emphasis in legal psychology) at Florida International University. He uses his knowledge of psychology and law as a trial consultant, and has published and presented widely on topics of jury research and witness bias. He can be reached for questions at jov15@pitt.edu.
Applied Cognitive Psychology seeks to publish the best papers dealing with psychological analyses of memory, learning, thinking, problem solving, language, and consciousness as they occur in the real world. Professor Graham Davies is Applied Cognitive Psychology's Editor in Chief.
About Wiley-Blackwell
Wiley-Blackwell is the international scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly publishing business of John Wiley & Sons, with strengths in every major academic and professional field and partnerships with many of the world's leading societies. Wiley-Blackwell publishes nearly 1,500 peer-reviewed journals and 1,500+ new books annually in print and online, as well as databases, major reference works and laboratory protocols. For more information, please visit www.wileyblackwell.com or our new online platform, Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com), one of the world's most extensive multidisciplinary collections of online resources, covering life, health, social and physical sciences, and humanities.
END
MADISON, WI, MARCH 1, 2011 – Methane is an extremely potent greenhouse gas. Wetlands, gas hydrates, permafrost, termites, oceans, freshwater bodies, non-wetland soils, are all natural sources of atmospheric methane; however, the majority of methane presence ca n be accredited to human-related activities. These activities include: such as fossil fuel production, biomass burning, waste management and animal husbandry. The release of methane into the atmosphere by cattle and other large grazing mammals is estimated to account for 12 to 17% of the total global methane release.
Recently, ...
Scientists now have a better understanding of why spider silk fibers are so incredibly strong. Recent research, published by Cell Press on February 15th in Biophysical Journal, describes the architecture of silk fibers from the atomic level up and reveals new information about the molecular structure that underlies the amazing mechanical characteristics of this fascinating natural material.
Spiders spin silk, which is remarkably strong and stretchy, to use in webs and to suspend themselves. "Silk fibers exhibit astonishing mechanical properties. They have an ultimate ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University researcher is leading an effort to create a new scientific field that will use sound as a way to understand the ecological characteristics of a landscape and to reconnect people with the importance of natural sounds.
Soundscape ecology, as it's being called, will focus on what sounds can tell people about an area. Bryan Pijanowski, an associate professor of forestry and natural resources and lead author of a paper outlining the field in the journal BioScience, said natural sound could be used like a canary in a coal mine. Sound ...
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — A review of more than 160 studies of human and animal subjects has found "clear and compelling evidence" that – all else being equal – happy people tend to live longer and experience better health than their unhappy peers.
The study, in the journal Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being, is the most comprehensive review so far of the evidence linking happiness to health outcomes. Its lead author, University of Illinois professor emeritus of psychology Ed Diener, who also is a senior scientist for the Gallup Organization, of Princeton, N.J., analyzed ...
Alcoholism is a tough addiction to kick. Eventually, most people return to drinking. But some Dutch and German psychological scientists have tested a short-term regime that promises to help alcoholics stay sober. Their study is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association of Psychological Science.
Heavy drinkers tend to behave impulsively in response to temptation. Meanwhile, their "reflective," or controlled, responses—the thoughts that would help them resist drinking—are often weak. Most therapies, including Cognitive Behavior Therapy, primarily ...
Mild heart failure patients with a particular condition that results in disorganized electrical activity throughout the heart benefit substantially from cardiac resynchronization therapy with defibrillator (CRT–D), according to a study published in the American Heart Association journal Circulation.
In patients with the condition, known as left bundle branch block or LBBB, CRT-D therapy reduced heart failure progression and the risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias, fast and potentially life-threatening heart rhythms. Heart failure patients without LBBB did not receive ...
Many people suffer from a devastating condition known as critical limb ischemia (CLI) that can lead to muscle wasting and even amputation. The disease is linked to the blockage of blood flow to the skeletal muscle and current treatment options include rehabilitative exercise and surgical bypass of blood vessels. New preclinical research suggests there may be a way to restore blood supply in skeletal muscle without traditional intervention.
Scientists at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) and the Salk Institute for Biological Studies ...
WASHINGTON, March 1—The world's largest international conference on
optical communications will take place March 6-10 at the Los Angeles Convention Center. The Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC) is the premier telecom meeting where experts from industry and academia share their results, experiences, and insights on the future of electronic and wireless communication and optical technologies. More than 10,000 attendees and an exhibit with 500 companies are expected.
CONFERENCE HIGHLIGHTS
Plenary ...
An AIDS vaccine tested in people, but found to be ineffective, influenced the genetic makeup of the virus that slipped past. The findings suggest new ideas for developing HIV vaccines.
The results were published Feb. 27 in Nature Medicine.
This is the first evidence that vaccine-induced cellular immune responses against HIV-1 infection exert selective pressure on the virus. "Selective pressure" refers to environmental demands that favor certain genetic traits over others.
The senior author of the multi-institutional study is Dr. James I. Mullins, University of Washington ...
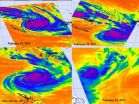
Tropical Cyclone Atu had a brief but memorable life last week, and NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a day-by-day look at its growth and death.
AIRS provides infrared images of atmospheric phenomena, oceans and land areas around the world. Basically, infrared data takes the temperature of these things. When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Atu from February 21 through the 25 it saw thunderstorm cloud tops grow colder as the clouds grew higher and thunderstorms became more powerful. When ...