(Press-News.org) A new technique pioneered at Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine (LSTM) is improving the detection and monitoring of insecticide resistance in field populations of an important malaria-carrying mosquito.
Researchers at LSTM, led by Dr Charles Wondji have developed a new technique which encourages the female Anopheles funestus mosquitoes to lay eggs which are then reared into adult mosquitoes to provide sufficient numbers to determine levels of insecticide resistance and to characterise the underlying mechanisms.
Explaining the significance, John Morgan, who designed the technique, said: "Malaria is the main cause of death in Uganda with some 12 million cases recorded annually. The Ministry of Health relies heavily on insecticide treated nets and spraying to control mosquitoes. The effectiveness of those control programmes depends on the ability to detect and monitor insecticide resistance.
"The An. funestus mosquito is difficult to collect and rear from the field and hence published studies of insecticide resistance in this species are limited. This new forced egg laying technique encourages the females to lay eggs which we were then able to rear into viable populations.
"This allowed us to study levels of resistance to particular insecticides and in doing so, we have been able to find the first documented resistance to pyrethroid/DDT insecticides in East Africa. This will enable researchers to map the distribution of this resistance and allow the Ministry of Health to modify its vector control programme, thereby increasing its effectiveness and helping to reduce the transmission of malaria."
INFORMATION:
The paper is published in PLoS ONE.
New technique uncovers hidden insecticide resistance
2010-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patients with cancer who stop hospice care boost health-care costs
2010-09-24
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that the costs of care for patients with cancer who disenrolled from hospice were nearly five times higher than for patients who remained with hospice. Patients who disenroll from hospice are far more likely to use emergency department care and be hospitalized. The results are published in the October 1 issue of the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Led by Melissa D.A. Carlson, PhD, Assistant Professor of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine, and Elizabeth H. Bradley, PhD, Professor of Public Health at Yale University, ...
Nonstick coating of a protein found in semen reduces HIV infection
2010-09-24
A non-stick coating for a substance found in semen dramatically lowers the rate of infection of immune cells by HIV a new study has found.
The new material is a potential ingredient for microbicides designed to reduce transmission of HIV, a team from the University of Rochester Medical Center and the University of California, San Diego reports in a forthcoming issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
The coating clings to fibrous strings and mats of protein called SEVI–for semen-derived enhancer of viral infection–which was first discovered just three years ago. ...
Molecular 'playbook' for halting heart failure risk factor uncovered
2010-09-24
Like a well-crafted football play designed to block the opposing team's offensive drive to the end zone, the body constantly executes complex 'plays' or sequences of events to initiate, or block, different actions or functions.
Scientists at the University of Rochester Medical Center recently discovered a potential molecular playbook for blocking cardiac hypertrophy, the unwanted enlargement of the heart and a well-known precursor of heart failure. Researchers uncovered a specific molecular chain of events that leads to the inhibition of this widespread risk factor. ...
Rensselaer researchers provide insight into the impacts of too much communication
2010-09-24
Troy, N.Y. – Individuals within a networked system coordinate their activities by communicating to each other information such as their position, speed, or intention. At first glance, it seems that more of this communication will increase the harmony and efficiency of the network. However, scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have found that this is only true if the communication and its subsequent action are immediate.
Using statistical physics and network science, the researchers were able to find something very fundamental about synchronization and coordination: ...
Study finds high rate of c-sections after pelvic fractures
2010-09-24
In research led by a Saint Louis University surgeon, investigators found that women who give birth after suffering pelvic fractures receive C-sections at more than double normal rates despite the fact that vaginal delivery after such injuries is possible. In addition, women reported lingering, yet often treatable, symptoms following their pelvic fracture injuries, from urinary complications to post-traumatic stress disorder.
The study, published in Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, retrospectively reviewed the cases of 71 women who had suffered pelvic fractures, ...
Caltech researchers design a new nanomesh material
2010-09-24
PASADENA, Calif.—Computers, light bulbs, and even people generate heat—energy that ends up being wasted. With a thermoelectric device, which converts heat to electricity and vice versa, you can harness that otherwise wasted energy. Thermoelectric devices are touted for use in new and efficient refrigerators, and other cooling or heating machines. But present-day designs are not efficient enough for widespread commercial use or are made from rare materials that are expensive and harmful to the environment.
Researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) ...
University of Nevada, Reno, demonstrates successful sludge-to-power research
2010-09-24
RENO, Nev. – Like the little engine that could, the University of Nevada, Reno experiment to transform wastewater sludge to electrical power is chugging along, dwarfed by the million-gallon tanks, pipes and pumps at the Truckee Meadows Water Reclamation Facility where, ultimately, the plant's electrical power could be supplied on-site by the process University researchers are developing.
"We are very pleased with the results of the demonstration testing of our research," Chuck Coronella, principle investigator for the research project and an associate professor of chemical ...
Groundwater depletion rate accelerating worldwide
2010-09-24
WASHINGTON– In recent decades, the rate at which humans worldwide are pumping dry the vast underground stores of water that billions depend on has more than doubled, say scientists who have conducted an unusual, global assessment of groundwater use.
These fast-shrinking subterranean reservoirs are essential to daily life and agriculture in many regions, while also sustaining streams, wetlands, and ecosystems and resisting land subsidence and salt water intrusion into fresh water supplies. Today, people are drawing so much water from below that they are adding enough ...
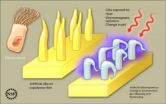
Cilia revolution
2010-09-24
University of Southern Mississippi scientists recently imitated Mother Nature by developing, for the first time, a new, skinny-molecule-based material that resembles cilia, the tiny, hair-like structures through which organisms derive smell, vision, hearing and fluid flow.
While the new material isn't exactly like cilia, it responds to thermal, chemical, and electromagnetic stimulation, allowing researchers to control it and opening unlimited possibilities for future use.
This finding is published in today's edition of the journal Advanced Functional Materials. The ...
Taking a new look at old digs: Trampling animals may alter Stone Age sites
2010-09-24
Archaeologists who interpret Stone Age culture from discoveries of ancient tools and artifacts may need to reanalyze some of their conclusions.
That's the finding suggested by a new study that for the first time looked at the impact of water buffalo and goats trampling artifacts into mud.
In seeking to understand how much artifacts can be disturbed, the new study documented how animal trampling in a water-saturated area can result in an alarming amount of disturbance, says archaeologist Metin I. Eren, a graduate student at Southern Methodist University, Dallas, and ...