(Press-News.org) A team of Australian researchers, led by University of Melbourne has developed a genetic test that is able to predict the risk of developing Autism Spectrum Disorder, ASD.
Lead researcher Professor Stan Skafidas, Director of the Centre for Neural Engineering at the University of Melbourne said the test could be used to assess the risk for developing the disorder.
"This test could assist in the early detection of the condition in babies and children and help in the early management of those who become diagnosed," he said.
"It would be particularly relevant for families who have a history of Autism or related conditions such as Asperger's Syndrome," he said.
Autism affects around one in 150 births and is characterized by abnormal social interaction, impaired communication and repetitive behaviours.
The test correctly predicted ASD with more than 70 per cent accuracy in people of central European descent. Ongoing validation tests are continuing including the development of accurate testing for other ethnic groups.
Clinical neuropsychologist, Dr Renee Testa from the University of Melbourne and Monash University, said the test would allow clinicians to provide early interventions that may reduce behavioural and cognitive difficulties that children and adults with ASD experience.
"Early identification of risk means we can provide interventions to improve overall functioning for those affected, including families," she said.
A genetic cause has been long sought with many genes implicated in the condition, but no single gene has been adequate for determining risk.
Using US data from 3,346 individuals with ASD and 4,165 of their relatives from Autism Genetic Resource Exchange (AGRE) and Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (SFARI), the researchers identified 237 genetic markers (SNPs) in 146 genes and related cellular pathways that either contribute to or protect an individual from developing ASD.
Senior author Professor Christos Pantelis of the Melbourne Neuropsychiatry Centre at the University of Melbourne and Melbourne Health said the discovery of the combination of contributing and protective gene markers and their interaction had helped to develop a very promising predictive ASD test.
The test is based on measuring both genetic markers of risk and protection for ASD. The risk markers increase the score on the genetic test, while the protective markers decrease the score. The higher the overall score, the higher the individual risk.
"This has been a multidisciplinary team effort with expertise across fields providing new ways of investigating this complex condition," Professor Pantelis said.
The study was undertaken in collaboration with Professor Ian Everall, Cato Chair in Psychiatry and Dr Gursharan Chana from the University of Melbourne and Melbourne Health, and Dr Daniela Zantomio from Austin Health.
The next step is to further assess the accuracy of the test by monitoring children who are not yet diagnosed over an extended study.
The study has been published today in the journal Molecular Psychiatry
### END
Genetic test predicts risk for Autism
2012-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Mad Cow' blood test now on the horizon
2012-09-12
Using newly available genetic sequencing scientists discovered cells infected with prions (the infectious agent responsible for these diseases) release particles which contain easily recognized 'signature genes'.
Associate Professor Andrew Hill — from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the Bio21 Institute — said these particles travel in the blood stream, making a diagnostic blood test a possibility.
"This might provide a way to screen people who have spent time in the UK, who currently face restrictions on their ability to donate blood," he said.
"With ...
Gut microbes help the body extract more calories from food
2012-09-12
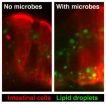
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – You may think you have your food all to yourself, but you're actually sharing it with a vast community of microbes waiting within your digestive tract. A new study from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine reveals some gut microbes increase the absorption of dietary fats, allowing the host organism to extract more calories from the same amount of food.
"This study is the first to demonstrate that microbes can promote the absorption of dietary fats in the intestine and their subsequent metabolism in the body," said senior study author ...
Age, not underlying diagnosis, key factor in weight gain in children after tonsillectomy
2012-09-12
Potentially worrisome weight gains following tonsillectomy occur mostly in children under the age of 6, not in older children, a study by Johns Hopkins experts in otolaryngology- head and neck surgery shows.
Sudden increases in body mass index, or BMI, have been routinely observed for months after some of the more than half-million surgeries performed annually in the United States to remove the sore and swollen tissues at the back of the throat.
The Johns Hopkins study, in 115 children in the Baltimore region, is believed to be the first to dispel long-held beliefs ...
A celestial witch's broom?
2012-09-12
The Pencil Nebula is pictured in a new image from ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile. This peculiar cloud of glowing gas is part of a huge ring of wreckage left over after a supernova explosion that took place about 11 000 years ago. This detailed view was produced by the Wide Field Imager on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope.
Despite the tranquil and apparently unchanging beauty of a starry night, the Universe is far from being a quiet place. Stars are being born and dying in an endless cycle, and sometimes the death of a star can create a vista of unequalled beauty as ...
Studies shed light on how to reduce the amount of toxins in plant-derived foods
2012-09-12
A number of environmental toxins pose considerable health threats to humans, and the heavy metal cadmium (Cd) ranks high on the list. Most of us are exposed to it through plant-derived foods such as grains and vegetables. Now, new research offers ways in which investigators can reduce the amount of Cd found in the food we eat, according to a review published online September 12th in the Cell Press journal Trends in Plant Science.
"Cadmium is virtually everywhere in the environment, and it is taken up into the human body and bioaccumulates for decades in the kidney," ...
Gut bacteria increase fat absorption
2012-09-12
Baltimore, MD —You may think you have dinner all to yourself, but you're actually sharing it with a vast community of microbes waiting within your digestive tract. A new study from a team including Carnegie's Steve Farber and Juliana Carten reveals that some gut microbes increase the absorption of dietary fats, allowing the host organism to extract more calories from the same amount of food.
Previous studies showed gut microbes aid in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, but their role in dietary fat metabolism remained a mystery, until now. The research is published ...
Sandia, OurEnergyPolicy.org release 'Goals of Energy Policy' poll results
2012-09-12
LIVERMORE, Calif.— U.S. energy policy should simultaneously pursue security of its energy supply, economic stability and reduced environmental impacts, says a national poll of energy professionals jointly prepared by Sandia National Laboratories and OurEnergyPolicy.org.
The findings of the national poll, "The Goals of Energy Policy," show that the vast majority — more than 85 percent — of the 884 energy professionals surveyed prefer policymaking that pursues all three goals at once.
The poll asked the experts to allocate 100 points, representing a 100 percent policymaking ...
New paper addresses causes of shattering glass cookware; Margin of safety described as 'borderline'
2012-09-12
A new paper appearing in the September 2012 edition of the Bulletin of The American Ceramic Society for the first time provides a scientific explanation of why some glass cookware sold in the United States is more susceptible than others to "explosive" shattering and the possibility of exposing consumers to injury from flying glass shards.
Clear glass baking dishes and pots are a staple in many households around the world and have been since they were first introduced in 1915 to consumers by the Corning Glass Works, which created the Pyrex brand name. The original Pyrex ...
Old deeds, witness trees offer glimpse of pre-settlement forest in West Virginia
2012-09-12
PARSONS, W. Va., September 12, 2012 – Using old deeds and witness trees, a U.S. Forest Service scientist has created a glimpse of the composition of the forests that covered today's Monongahela National Forest before settlement and logging changed the landscape.
"European Settlement-Era Vegetation of the Monongahela National Forest, West Virginia" describes how a Forest Service scientist and her West Virginia University colleague answered questions about the composition of early forests using a unique dataset. The dataset was built with original deeds, metes and bounds ...
Predicting a die throw
2012-09-12
Vegas, Monte Carlo, and Atlantic City draw people from around the world who are willing to throw the dice and take their chances. Researchers from the Technical University of Lodz, Poland, have spotted something predictable in the seemingly random throw of the dice. By applying chaos theory and some high school level mechanics, they determined that by knowing the initial conditions – such as the viscosity of the air, the acceleration of gravity, and the friction of the table – it should be possible to predict the outcome when rolling the dice.
The researchers created ...