(Press-News.org) This press release is available in Spanish.
A grass fed to cattle throughout much of the tropics may become a biofuel crop that helps the nation meet its future energy needs, according to a U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist.
Napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum) is fairly drought-tolerant, grows well on marginal lands, and filters nutrients out of runoff in riparian areas, according to William Anderson, a geneticist in the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Crop Genetics and Breeding Research Unit in Tifton, Ga. ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency, and this research supports the USDA priority of developing new sources of bioenergy.
Government mandates call for production of up to 36 billion gallons of biofuel by 2022. While much of that will come from grain ethanol, 21 billion gallons is expected to be derived from other crop-based feedstocks.
As part of a nationwide search for alternatives, Anderson and his colleagues compared napiergrass with several other candidate feedstocks in a study to see how they would fare in head-to-head competition. The researchers grew energy cane, napiergrass, switchgrass and giant reed for four years and compared biomass yields and soil nutrient requirements.
Joseph Knoll, a post-doctoral researcher in Anderson's laboratory, led the research effort. The team included Timothy Strickland and Robert Hubbard, ARS scientists with the agency's Southeast Regional Watershed Research Unit in Tifton, and Ravindra Malik of Albany State University in Albany, Ga.
With sunny skies and long growing seasons, farms and forests in the Southeastern United States are expected to play a major role in providing biofuel crops. The researchers' findings, along with others, show that napiergrass could be a viable biofuel crop in the Southeast's southern tier. It is not as cold-tolerant as switchgrass, but does offer advantages, such as continuing to produce biomass until the first frost.
The researchers are continuing to study napiergrass with an eye toward improving yields, usable fiber content, and disease resistance. They are also evaluating production systems that use chicken litter, synthetic fertilizer, and winter cover crops, as well as different irrigation levels, harvest times and planting dates. Preliminary findings in those studies show yields are sufficient without irrigation, and that there is little difference in yield when poultry litter is used instead of synthetic fertilizers.
###
Read more about this and other bioenergy research in the September 2012 issue of Agricultural Research magazine.
http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/AR/archive/sep12/biofuels0912.htm
USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. To file a complaint of discrimination, write: USDA, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, Office of Adjudication, 1400 Independence Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410 or call (866) 632-9992 (Toll-free Customer Service), (800) 877-8339 (Local or Federal relay), (866) 377-8642 (Relay voice users).
Napiergrass: A potential biofuel crop for the sunny Southeast
2012-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New clues about ancient water cycles shed light on US deserts, says Texas A&M-led study
2012-09-28
The deserts of Utah and Nevada have not always been dry. Between 14,000 and 20,000 years ago, when large ice caps covered Canada during the last glacial cooling, valleys throughout the desert southwest filled with water to become large lakes, scientists have long surmised. At their maximum size, the desert lakes covered about a quarter of both Nevada and Utah. Now a team led by a Texas A&M University researcher has found a new water cycle connection between the U.S. southwest and the tropics, and understanding the processes that have brought precipitation to the western ...
Peering to the edge of a black hole
2012-09-28
Using a continent-spanning telescope, an international team of astronomers has peered to the edge of a black hole at the center of a distant galaxy. For the first time, they have measured the black hole's "point of no return" - the closest distance that matter can approach before being irretrievably pulled into the black hole.
A black hole is a region in space where the pull of gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Its boundary is known as the event horizon.
"Once objects fall through the event horizon, they're lost forever," says lead author ...
New fish species offers literal take on 'hooking up'
2012-09-28
Fishing hooks aren't the only hooks found in east-central Mexican waters.
A new species of freshwater fish described by a North Carolina State University researcher has several interesting – and perhaps cringe-inducing – characteristics, including a series of four hooks on the male genitalia.
Females of the new species – the llanos mosquitofish, or Gambusia quadruncus – also have distinguishing characteristics, including a colorful anal spot.
A paper describing the new species, which lives in a diversity hotspot and seemingly branched off from its closest relative ...
Deadly complication of stem cell transplants reduced in mice
2012-09-28
Studying leukemia in mice, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have reduced a life-threatening complication of stem cell transplants, the only curative treatment when leukemia returns.
About 50 percent of leukemia patients who receive stem cells from another person develop graft-versus-host disease, a condition where donor immune cells attack the patient's own body. The main organs affected are the skin, liver and gut. Now, the scientists have shown they can redirect donor immune cells away from these vital organs. Steering immune cells ...
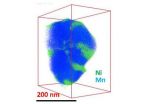
Nickelblock: An element's love-hate relationship with battery electrodes
2012-09-28
RICHLAND, Wash. -- Anyone who owns an electronic device knows that lithium ion batteries could work better and last longer. Now, scientists examining battery materials on the nano-scale reveal how nickel forms a physical barrier that impedes the shuttling of lithium ions in the electrode, reducing how fast the materials charge and discharge. Published last week in Nano Letters, the research also suggests a way to improve the materials.
The researchers, led by the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory's Chongmin Wang, created high-resolution 3D ...
Measuring the universe's 'exit door'
2012-09-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The point of no return: In astronomy, it's known as a black hole — a region in space where the pull of gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Black holes that can be billions of times more massive than our sun may reside at the heart of most galaxies. Such supermassive black holes are so powerful that activity at their boundaries can ripple throughout their host galaxies.
Now, an international team, led by researchers at MIT's Haystack Observatory, has for the first time measured the radius of a black hole at the center of a distant ...
World's first glimpse of a black hole 'launchpad'
2012-09-28
A strange thing about black holes: they shine.
The current issue of Science Express features a paper by the Event Horizon telescope team – a collaboration that includes Avery Broderick, Associate Faculty at Perimeter Institute – that may shed light on the origin of the bright jets given off by some black holes. In a world first, the team has been able to look at a distant black hole and find out where its jets are launched from: the "launchpad".
Many galaxies, including our own Milky Way, have a huge black hole lurking at their cores. In about 10 percent of such galaxies, ...
Newspaper sales suffer due to lack of stimulating content
2012-09-28
Los Angeles, CA (September 27, 2012) – Since the newspaper industry started to experience a major decrease in readership in recent years, many people have deemed the internet and other forms of new media as the culprits. However, a recent study published in the Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, a SAGE Journal, finds that sales are down because readers need more engaging and stimulating content.
Study authors Rachel Davis Mersey, Edward C. Malthouse, and Bobby J. Calder suggested that it is crucial for journalists and practitioners to focus their efforts on creating ...
Researchers investigate aggression among kindergartners
2012-09-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Not all aggressive children are aggressive for the same reasons, according to Penn State researchers, who found that some kindergartners who are aggressive show low verbal abilities while others are more easily physiologically aroused. The findings suggest that different types of treatments may be needed to help kids with different underlying causes for problem behavior.
"Aggressive responses to being frustrated are a normal part of early childhood, but children are increasingly expected to manage their emotions and control their behavior when ...
Liver cells, insulin-producing cells, thymus can be grown in lymph nodes, Pitt team finds
2012-09-28
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 27, 2012 – Lymph nodes can provide a suitable home for a variety of cells and tissues from other organs, suggesting that a cell-based alternative to whole organ transplantation might one day be feasible, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and its McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine. In a report recently published online in Nature Biotechnology, the research team showed for the first time that liver cells, thymus tissue and insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells, in an animal model, can thrive in lymph ...