(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – A study that included more than 45,000 residents of Sweden with rheumatoid arthritis finds that individuals with this disease had an associated higher risk of venous thromboembolism (a blood clot that forms within a vein), and that this elevated risk was stable for 10 years after the time of diagnosis, according to a study in the October 3 issue of JAMA.
"Recent reports suggest that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may be a risk factor for venous thromboembolism (VTE), particularly in conjunction with hospitalization. Using hospitalization data to identify RA and VTE may identify patients when they are at elevated risk for other reasons, obscuring the incompletely understood underlying association between RA and VTE and leading to inappropriate institution or timing of interventions," according to background information in the article.
Marie E. Holmqvist, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden and colleagues conducted a study to assess the overall occurrence and relative risks of VTE in patients with RA in relation to RA onset and disease duration as well as in conjunction with hospitalization. The study included a prevalent RA group (n = 37,856), an incident RA group (n = 7,904), and matched general population comparison groups, all from Sweden, with follow-up from 1997 through 2010.
Of the patients with prevalent RA and the matched individuals in the general population comparison cohort, 838 patients (2.2 percent) and 1,866 matched individuals (1.1 percent) had a VTE event after the index date, with analysis of the data indicating that patients with prevalent RA were at greater risk of VTE than the general population. There was no statistically significant association between a history of VTE and RA by the time of RA symptom onset. Counting from RA diagnosis, an increased rate in the RA cohort vs. the comparison cohort was detected within the first year and did not increase further during the first decade. The researchers also found that although rates for VTE following hospitalization were higher, the 1-year rate of VTE was not higher in the RA cohort than in the comparison cohort after hospital discharge. The rates of VTE increased with age but were largely similar across sex and rheumatoid factor status.
"The results of this study suggest that patients with RA are at increased risk of VTE (both deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) and that the risk of VTE increases shortly after RA diagnosis and remains similarly elevated during the first decade," the authors write.
"Hospitalization is a strong risk factor for VTE in the general population and in patients with RA, but the short-term ( END
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis appear to be at increased risk for blood clots
2012-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cardiac medication may help reduce stiffness caused by certain muscle diseases
2012-10-03
CHICAGO – Preliminary research finds that for patients with nondystrophic myotonias (NDMs), rare diseases that affect the skeletal muscle and cause functionally limiting stiffness and pain, use of the anti-arrhythmic medication mexiletine resulted in improvement in patient-reported stiffness, according to a preliminary study in the October 3 issue of JAMA.
Data on treatment of NDMs are largely anecdotal, consisting of case series and a single-blind, controlled trials of several medications including mexiletine, according to background information in the article.
Jeffrey ...
The genetics of HIV-1 resistance
2012-10-03
Drug resistance is a major problem when treating infections. This problem is multiplied when the infection, like HIV-1, is chronic. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Retrovirology has examined the genetic footprint that drug resistance causes in HIV and found compensatory polymorphisms that help the resistant virus to survive.
Currently the strategy used to treat HIV-1 infection is to prevent viral replication, measured by the number of viral particles in the blood, and to repair the immune system, assessed using CD4 count. Over the past 20 ...
Balancing fertility and child survival in the developing world
2012-10-03
Children in smaller families are only slightly more likely to survive childhood in high mortality environments, according to a new study of mothers and children in sub-Saharan Africa seeking to understand why women, even in the highest fertility populations in world, rarely give birth to more than eight children.
The study by Dr David Lawson and Dr Alex Alvergne from UCL Anthropology, and Dr Mhairi Gibson from the University of Bristol, challenges the popular theory proposed by evolutionary anthropologists that natural selection sets the upper limit of high fertility to ...
State-mandated planning, higher resident wealth linked to more sustainable city transportation
2012-10-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Transportation practices tend to be more environmentally friendly in wealthier metropolitan areas located within states that mandate comprehensive planning, new research suggests.
The study involved an examination of 225 U.S. metropolitan areas between 1980 and 2008 to gauge how sustainable their transportation practices were and determine what kinds of socioeconomic factors appeared to influence those practices.
Overall, transportation has become less sustainable across the country over this period, but some communities have slowed the decline more ...
Study confirms link between indoor tanning and skin cancer risk
2012-10-03
Indoor tanning increases the risks of developing non-melanoma skin cancer (known as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma), particularly among those exposed before the age of 25, finds a study published on bmj.com today.
It follows a BMJ study published in July that showed 3,438 (5.4%) new cases of melanoma diagnosed each year in Western Europe are related to sunbed use, particularly among young adults.
Some experts are now calling for Europe to follow the example of the United States by introducing a "tan tax" on indoor tanning salons.
The researchers, ...
Doctors speak out about unnecessary care as cost put at $800 billion a year
2012-10-03
Leading doctors are calling for action to tackle unnecessary care that is estimated to account for up to $800bn in the United States every year.
In a special report for this week's BMJ, journalist Jeanne Lenzer describes how a new movement led by prominent doctors is challenging the basic assumption in US healthcare that more is better.
The report comes as an international conference 'Preventing Overdiagnosis' is announced for September 2013 in the United States, hosted by The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice, in partnership with the BMJ, ...
New firework causes severe eye injuries, warn doctors
2012-10-03
A new type of firework caused severe eye injuries and blindness in children and adults at last year's bonfire night celebrations, warn doctors in a letter to this week's BMJ.
Edward Pringle and colleagues describe how on the evening of 5 November 2011, eight patients attended the Sussex Eye Hospital, five with serious eye injuries - two were blinded and the other three have a lifelong glaucoma risk.
Police inquiries suggest the new explosive was derived from "rope banger deer scarers," which have a slow burning rope fuse that ignites several explosives along the rope. ...
Tanning beds linked to non-melanoma skin cancer
2012-10-03
Indoor tanning beds can cause non-melanoma skin cancer – and the risk is greater the earlier one starts tanning, according to a new analysis led by UCSF.
Indoor tanning is already an established risk factor for malignant melanoma, the less common but deadliest form of skin cancer. Now, the new study confirms that indoor tanning significantly increases the risk of non-melanoma skin cancers, the most common human skin cancers.
In the most extensive examination of published findings on the subject, the researchers estimate that indoor tanning is responsible for more ...
Allergy rises not down to being too clean, just losing touch with 'old friends'
2012-10-03
A new scientific report out today from the International Scientific Forum on Home Hygiene (IFH) dismantles the myth that the epidemic rise in allergies in recent years has happened because we're living in sterile homes and overdoing hygiene.
But far from saying microbial exposure is not important, the report concludes that losing touch with microbial 'old friends' may be a fundamental factor underlying rises in an even wider array of serious diseases. As well as allergies, there are numerous other 'chronic inflammatory diseases' (CIDs) such as Type 1 diabetes and multiple ...
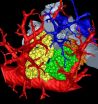
A mammal lung, in 3-D
2012-10-03
VIDEO:
The video shows the imaging of a section of a mouse lung. As the image rotates, more respiratory branches (bronchioles) are shown, along with three acini (yellow, green and orange...
Click here for more information.
Amidst the extraordinarily dense network of pathways in a mammal lung is a common destination. There, any road leads to a cul-de-sac of sorts called the pulmonary acinus. This place looks like a bunch of grapes attached to a stem (acinus means "berry" ...