December 25, 2012 (Press-News.org) Advances in technology can enhance the health care industry, providing various improvements and benefits. However, such developments can also create new opportunities for injury.
The Economic Cycle Research Institute, a nonprofit organization that researches the best approaches to improving patient care, recently released a report entitled "The Top 10 Health Technology Hazards for 2013." The institute intends to use the report to raise awareness of the potential dangers associated with the use of particular medical systems and devices.
The list is updated annually based upon the frequency and severity of incidents reported to the institute by health care facilities nationwide and information found in the institute's medical device reporting databases. The rankings are also based on the judgment, analysis and expertise of the organization's safety staff.
The report discusses those remedial issues that should be a part of every hospital's patient safety scheme. Health organizations can use the information to help focus and prioritize their efforts to address the dangers.
The top 10 risks on the institute's 2013 list are the following:
- Alarm hazards
- Medication administration errors -- specifically using infusion pumps
- Inadequate reprocessing of endoscopic devices and surgical instruments
- Unnecessary exposures and radiation burns from diagnostic radiology procedures
- Patient-data mismatches in electronic health records and other health IT systems
- Interoperability failures with medical devices and health IT systems
- Air embolism hazards
- Inattention to the needs of pediatric patients when using "adult" technologies
- Caregiver distractions from smartphones and other mobile devices
- Surgical fires
Every concern that made the list has clear steps that hospitals can take to reduce the risks associated with each hazard.
Additionally, every issue in the 2013 report involves one or more of the following safety concerns:
- The problem results in injury or death.
- The issue is a newsworthy, public concern.
- The concern can affect a number of individuals.
- The issue is difficult to recognize.
- The problem occurs frequently.
Hospital dangers and medical malpractice
The institute's report includes dangers and action-oriented recommendations to help address and eliminate these hospital problems. With this information, hospitals and health care providers should take the time to revamp their safety policies.
The report's warnings may help pave the way for revised medical care standards. For example, the findings might help educate physicians on proper and acceptable techniques for administering medicine using infusion pumps (one of the top five dangers).
When a health care provider fails to deliver proper treatment or departs in some way from acceptable standards of medical care, health care or safety, a patient may be entitled to financial compensation. Deviations from appropriate standards often result in surgical errors or other harm to patients.
If you believe that you are a victim of poor medical treatment or care, you should speak to a knowledgeable medical malpractice attorney today.
Article provided by Kramer & Dunleavy, LLP
Visit us at www.kramerdunleavy.com
ECRI Releases "The Top 10 Health Technology Hazards for 2013"
The ECRI recently reported on the top health technology dangers. If health care providers do not address such hazards, this could lead to serious harm among patients.
2012-12-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Oregon Prescription Drug Crimes -- When Prescription Use Violates the Law
2012-12-25
It's not unheard of for prescription drug use to get out of hand. When you are suffering from a serious medical condition, the right pills can manage a great deal of pain, suffering and discomfort; when the medical condition begins to improve, it is not always easy to stop taking the pills you have come to depend on.
But when does prescription drug use cross the line? Under Oregon and federal law, you can be found guilty of a drug crime by misusing or overusing prescription medication; and drivers of motor vehicles need to be aware that even if you are within your prescription, ...
Chinese medicine yields secrets to scientists at The Scripps Research Institute
2012-12-24
LA JOLLA, CA – December 23, 2012 – The mysterious inner workings of Chang Shan—a Chinese herbal medicine used for thousands of years to treat fevers associated with malaria—have been uncovered thanks to a high-resolution structure solved at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI).
Described in the journal Nature this week, the structure shows in atomic detail how a two-headed compound derived from the active ingredient in Chang Shan works. Scientists have known that this compound, called halofuginone (a derivative of the febrifugine), can suppress parts of the immune system—but ...
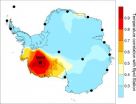
Study shows rapid warming on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet
2012-12-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio—In a discovery that raises further concerns about the future contribution of Antarctica to sea level rise, a new study finds that the western part of the ice sheet is experiencing nearly twice as much warming as previously thought.
The temperature record from Byrd Station, a scientific outpost in the center of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS), demonstrates a marked increase of 4.3 degrees Fahrenheit (2.4 degrees Celsius) in average annual temperature since 1958—that is, three times faster than the average temperature rise around the globe.
This temperature ...
Fat influences decisions taken by brain cells for production and survival
2012-12-24
Scientists at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified two molecules that play an important role in the survival and production of nerve cells in the brain, including nerve cells that produce dopamine. The discovery, which is published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology, may be significant in the long term for the treatment of several diseases, such as Parkinson's disease.
The same scientists have previously shown that receptors known as "liver X receptors" or LXR, are necessary for the production of different types of nerve cells, or neurons, in the developing ...
Understanding cell organization to tackle cancer
2012-12-24
Scientists at The University of Manchester have identified how cells know which way up they need to be. The discovery could help in the fight against cancer because in the early stages of the disease the cells become disorganised.
Professor Charles Streuli and Dr Nasreen Akhtar of the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell-Matrix Research have conducted new research that leads to a better understanding of cell polarity. Properly organised tissues are vital to maintaining functional organs and a healthy body. Part of being organised includes cells being in the correct position ...
Research sheds new light on mechanisms of T-ALL, a form of leukemia that primarily affects children
2012-12-24
Acute lymphatic leukemia (ALL) is the most common cancer in children under the age of 14 years. With optimum treatment, approximately 75 % of children are currently cured, but the treatment consists of severe chemotherapy with many side effects. In collaboration with international research teams, scientists at VIB, KU Leuven and UZ Leuven have identified new genetic mutations that lead to T-ALL, a variant of ALL. They have unmasked the ribosome – the molecular machine in the cell that is involved in the production of proteins – as a weak spot in leukemia cells. Their research ...
Neuroscientists find excessive protein synthesis linked to autistic-like behaviors
2012-12-24
Autistic-like behaviors can be partially remedied by normalizing excessive levels of protein synthesis in the brain, a team of researchers has found in a study of laboratory mice. The findings, which appear in the latest issue of Nature, provide a pathway to the creation of pharmaceuticals aimed at treating autism spectrum disorders (ASD) that are associated with diminished social interaction skills, impaired communication ability, and repetitive behaviors.
"The creation of a drug to address ASD will be difficult, but these findings offer a potential route to get there," ...
3 new genetic links to colorectal cancer
2012-12-24
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center investigators have identified three new genetic "hotspots" linked to colorectal cancer.
These variants, reported Dec. 23 in an Advanced Online Publication in Nature Genetics, provide new insight into the biology of colorectal cancer – and could represent new therapeutic targets for the disease.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide – and rates are particularly high in the United States and other developed countries. Genetics plays an important role in both sporadic and familial (inherited) forms of ...
OpGen announces sequence assembly and finishing of first reference genome of domestic goat
2012-12-24
Gaithersburg, Md.—December 23, 2012— OpGen, Inc. today announced its ARGUS® Whole Genome Mapping System technology was used in combination with next-generation sequencing (NGS) to produce the first, high-quality reference genome of the domestic goat. The study, which was led by BGI-Shenzhen and Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences was published online today in Nature Biotechnology. The paper, titled Sequencing and automated whole-genome optical mapping of the genome of a domestic goat (Capra hircus), demonstrates the value, efficiency and cost effectiveness ...
Study turns parasite invasion theory on its head
2012-12-24
Current thinking on how the Toxoplasma gondii parasite invades its host is incorrect, according to a study published today in Nature Methods describing a new technique to knock out genes. The findings could have implications for other parasites from the same family, including malaria, and suggest that drugs that are currently being developed to block this invasion pathway may be unsuccessful.
Toxoplasma gondii is a parasite that commonly infects cats but is also carried by other warm-blooded animals, including humans. Up to a third of the UK population are chronically ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] ECRI Releases "The Top 10 Health Technology Hazards for 2013"The ECRI recently reported on the top health technology dangers. If health care providers do not address such hazards, this could lead to serious harm among patients.