(Press-News.org) This press release is available in Spanish.
Poultry producers can reduce bacterial cross-contamination in poultry cages by treating the cages with forced air that's been heated to 122 degrees Fahrenheit, according to a study by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists.
While being transported in coops on trucks, poultry that have bacteria such as Campylobacter can contaminate, through their feces, other poultry that are free of pathogens. Those disease-causing bacteria can then be passed on to the next group of birds during the next trip, and so forth, unless the cycle is broken.
Campylobacter is a food-borne pathogen that can be present in raw or undercooked poultry. Since the bacteria are commonly found in the digestive tracts of poultry, they're readily deposited onto coops and trucks when contaminated animals are transported to processing plants.
In the study, Agricultural Research Service (ARS) microbiologists Mark Berrang and Richard Meinersmann collaborated with researcher Charles Hofacre of the University of Georgia at Athens. Berrang and Meinersmann work in the ARS Bacterial Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Research Unit in Athens. ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency, and this research supports the USDA priority of promoting food safety.
The researchers tested the use of hot flowing air to speed the process of drying soiled or washed cages to lower or eliminate detectable Campylobacter on cage flooring.
When the hot flowing air was applied to fecally soiled transport cage flooring samples for 15 minutes after a water-spray wash treatment, Campylobacter levels declined to an undetectable level. Static heat at similar temperatures was not nearly as effective, and unheated flowing air was moderately effective, but less so than hot flowing air.
### Read more about this research in the January 2013 issue of Agricultural Research magazine.
http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/AR/archive/jan13/bacteria0113.htm
USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. To file a complaint of discrimination, write: USDA, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, Office of Adjudication, 1400 Independence Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410 or call (866) 632-9992 (Toll-free Customer Service), (800) 877-8339 (Local or Federal relay), (866) 377-8642 (Relay voice users).
With hot air treatment, bacteria fly the coop
2013-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Islet transplant may slow progression of atherosclerosis
2013-01-28
Minimally invasive islet transplantation for patients with type 1 diabetes achieves insulin independence and reverses the progression of atherosclerosis in the first few years after transplant, according to a University of Illinois at Chicago study.
The research is published in the February issue of the journal Diabetes Care and is available online.
Patients with diabetes, particularly women, have a substantial increased risk of dying from ischemic heart disease, according to previous research. However, future cardiac events may be prevented with intensive glycemic ...
Central Valley irrigation intensifies rainfall, storms across the Southwest
2013-01-28
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 28, 2013 – Agricultural irrigation in California's Central Valley doubles the amount of water vapor pumped into the atmosphere, ratcheting up rainfall and powerful monsoons across the interior Southwest, according to a new study by UC Irvine scientists.
Moisture on the vast farm fields evaporates, is blown over the Sierra Nevada and dumps 15 percent more than average summer rain in numerous other states. Runoff to the Colorado River increases by 28 percent, and the Four Corners region experiences a 56 percent boost in runoff. While the additional ...
Safeguards needed for tissue donors
2013-01-28
Donors to biobanks – vast collections of human tissue samples that scientists hope will lead to new treatments for diseases – have a right to basic information about how their donations may be used, a Michigan State University ethicist argues in a new paper.
The idea behind biobanks is that a repository with hundreds of thousands of samples, each linked to medical records and other health information, can yield discoveries smaller data sets can't match. Once samples are collected, researchers in many fields can use the data repeatedly.
"More and larger biobanks are ...
New LGBT Health journal launching in 2013
2013-01-28
New Rochelle, NY, January 28, 2013—Over 4 million adults in the United States identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual and approximately 700,000 identify as transgender. An NIH-sponsored investigation by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) concluded that the health status and healthcare needs of this sizable population are poorly understood and likely inadequately met. A journal is urgently needed to support, promote, and address the unique healthcare needs of each population that comprises the LGBT community, in the United States and worldwide. LGBT Health, a new peer-reviewed ...
Best friends influence when teenagers have first drink
2013-01-28
Chances are the only thing you remember about your first swig of alcohol is how bad the stuff tasted. What you didn't know is the person who gave you that first drink and when you had it says a lot about your predisposition to imbibe later in life.
A national study by a University of Iowa-led team has found that adolescents who get their first drink from a friend are more likely to drink sooner in life, which past studies show makes them more prone to abusing alcohol when they get older. The finding is designed to help specialists predict when adolescents are likely to ...
Patients' own skin cells are transformed into heart cells to create 'disease in a dish'
2013-01-28
LA JOLLA, Calif., January 27, 2013 – Most patients with an inherited heart condition known as arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) don't know they have a problem until they're in their early 20s. The lack of symptoms at younger ages makes it very difficult for researchers to study how ARVD/C evolves or to develop treatments. A new stem cell-based technology created by 2012 Nobel Prize winner Shinya Yamanaka, M.D., Ph.D., helps solve this problem. With this technology, researchers can generate heart muscle cells from a patient's own skin cells. ...
Demagnetization by rapid spin transport
2013-01-28
For purposes of their research, the scientists irradiated two separate layered systems with ultrashort laser pulses on the order of just one hundred femtoseconds (10-15 s). One sample consisted essentially of a single thin layer of ferromagnetic nickel. By contrast, a second sample of this same nickel material was coated with a non-magnetic layer of gold. Only a mere 30 nanometers (10-9 m) thick, the gold layer swallowed up the lion's share of the laser light so that barely any light ended up reaching the nickel layer. In spite of this, the nickel layer's magnetization ...
Accelerating neutral atoms on a table top
2013-01-28
Charged particle accelerators have become crucially important to modern day life, be it in health care for cancer treatment or for answering important fundamental scientific questions like the existence of the HIGGS boson, the so called 'God particle'. In a simple picture, charged particles like electrons and protons are accelerated between two end plates across which an electrical voltage is applied. High energies need high voltages (millions and billions of volts) and long acceleration paths in giant sized machines – for instance the trillion volt machine called the 'large ...
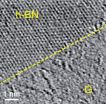
Rice technique points toward 2-D devices
2013-01-28
HOUSTON – (Jan. 28, 2013) – Rice University scientists have taken an important step toward the creation of two-dimensional electronics with a process to make patterns in atom-thick layers that combine a conductor and an insulator.
The materials at play – graphene and hexagonal boron nitride – have been merged into sheets and built into a variety of patterns at nanoscale dimensions.
Rice introduced a technique to stitch the identically structured materials together nearly three years ago. Since then, the idea has received a lot of attention from researchers interested ...
Cities affect temperatures for thousands of miles
2013-01-28
BOULDER – Even if you live more than 1,000 miles from the nearest large city, it could be affecting your weather.
In a new study that shows the extent to which human activities are influencing the atmosphere, scientists have concluded that the heat generated by everyday activities in metropolitan areas alters the character of the jet stream and other major atmospheric systems. This affects temperatures across thousands of miles, significantly warming some areas and cooling others, according to the study in Nature Climate Change.
The extra "waste heat" generated from ...