(Press-News.org) This press release is available in Spanish.
Farmers can fine-tune their use of cover crops to help manage costs and maximize benefits in commercial organic production systems, according to U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists.
Production expenses for high-value organic crops like lettuce and broccoli can exceed $7,000 per acre, so producers often try to streamline costs with an annual two- to three-crop rotation. Agricultural Research Service (ARS) horticulturalist Eric Brennan designed a long-term investigation that examined several different cover cropping strategies for an annual organic lettuce-broccoli production system. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency, and this work supports the USDA priority of promoting international food security.
The researcher selected three winter cover crops often grown in the Salinas, Calif., area—rye, mustard, and a legume-rye mix—and planted each cover crop using either a typical seeding rate or a seeding rate that was three times higher. Seeding rates can influence a cover crop's ability to smother weeds.
During lettuce and broccoli production, Brennan ensured all systems received the same fertilizer and irrigation inputs and pest management. The harvest and sale of the crops, which met all USDA organic standards, were conducted by a commercial harvester.
Brennan's results indicated that all three cover crops yielded more dry matter than the two tons of crop residue per acre often recommended for maintaining soil organic matter. The legume-rye and rye cover crops produced approximately 25 percent more dry matter biomass than the mustard crops. But effectively suppressing weeds with the legume-rye crops required seeding at three times the typical rate, while rye and mustard crops appeared to suppress weeds adequately with typical seeding rates.
The long-term study also provided Brennan with more data about year-to-year yield variations in the legume-rye mix, including why legumes, which make up most of the seed costs, are not consistently abundant. Brennan thinks cooler early-season weather helps legumes compete with the rye. So when a hot and dry autumn is expected, producers might want to use a rye cover crop and skip spending the money on a cover crop with legumes.
Brennan works at the ARS Crop Improvement and Protection Research Unit in Salinas.
###
Read more about this research in the February 2013 issue of Agricultural Research magazine.
http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/AR/archive/feb13/organic0213.htm
USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. To file a complaint of discrimination, write: USDA, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, Office of Adjudication, 1400 Independence Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410 or call (866) 632-9992 (Toll-free Customer Service), (800) 877-8339 (Local or Federal relay), (866) 377-8642 (Relay voice users).
USDA scientists say mix-and-match cover cropping can optimize organic production
2013-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Little House books' Mary Ingalls probably did not go blind from scarlet fever, U-M study says
2013-02-04
Ann Arbor, Mich. — In the beloved American stories of the Little House on the Prairie, author Laura Ingalls Wilder writes emotionally about how scarlet fever robs her big sister Mary of her sight.
But in a new study published today in the journal Pediatrics, University of Michigan researchers found it is likely scarlet fever had nothing to do with Mary's blindness.
Senior author Beth A. Tarini, M.D., and her co-authors used evidence from newspaper reports, Laura Ingalls' memories and school registries to conclude Mary's blindness was probably caused by viral meningoencephalitis.
"Since ...
Can cancer be turned against itself?
2013-02-04
Though a small group of proteins, the family called Ras controls a large number of cellular functions, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival. And because the protein has a hand in cellular division, mutated Ras, which can be detected in one-third of all tumors, contributes to many human cancers by allowing for the rapid growth of diseased cells.
Now Prof. Yoel Kloog of Tel Aviv University's Department of Neurobiology, along with Dr. Itamar Goldstein of TAU's Sackler Faculty of Medicine and the Sheba Medical Center and their students Helly Vernitsky and ...
Study finds incentive price for reducing HIV risk in Mexico
2013-02-04
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Studies have found that conditional cash transfer programs, in which governments pay citizens if they consistently practice societally beneficial behaviors, have improved pediatric health care and education in Mexico, increased HIV testing in Malawi, and reduced sexually transmitted infections in Tanzania. Public health researchers therefore investigated whether the idea could be applied to HIV risk behaviors among gay men and male sex workers in Mexico City. A new study reports not only that some members of those populations would ...
New kind of extinct flying reptile discovered by scientists
2013-02-04
A new kind of pterosaur, a flying reptile from the time of the dinosaurs, has been identified by scientists from the Transylvanian Museum Society in Romania, the University of Southampton in the UK and the Museau Nacional in Rio de Janiero, Brazil.
The fossilised bones come from the Late Cretaceous rocks of Sebeş-Glod in the Transylvanian Basin, Romania, which are approximately 68 million years old. The Transylvanian Basin is world-famous for its many Late Cretaceous fossils, including dinosaurs of many kinds, as well as fossilised mammals, turtles, lizards and ancient ...
In combat vets and others, high rate of vision problems after traumatic brain injury
2013-02-04
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 4, 2013) - Visual symptoms and abnormalities occur at high rates in people with traumatic brain injury (TBI)—including Iraq and Afghanistan War veterans with blast-related TBI, reports a study, "Abnormal Fixation in Individuals with AMD when Viewing an Image of a Face", in the February issue of Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Vision problems are similar for military and civilian patients with TBI, ...
Study shows Facebook unfriending has real life consequences
2013-02-04
DENVER (Feb. 4, 2013) – Unfriending someone on Facebook may be as easy as clicking a button, but a new study from the University of Colorado Denver shows the repercussions often reach far beyond cyberspace.
"People think social networks are just for fun," said study author Christopher Sibona, a doctoral student in the Computer Science and Information Systems program at the University of Colorado Denver Business School. "But in fact what you do on those sites can have real world consequences."
Sibona found that 40 percent of people surveyed said they would avoid in real ...
In a fight to the finish, Saint Louis University research aims knockout punch at hepatitis B
2013-02-04
ST. LOUIS – In research published in the Jan. 24 edition of PLOS Pathogens, Saint Louis University investigators together with collaborators from the University of Missouri and the University of Pittsburgh report a breakthrough in the pursuit of new hepatitis B drugs that could help cure the virus. Researchers were able to measure and then block a previously unstudied enzyme to stop the virus from replicating, taking advantage of known similarities with another major pathogen, HIV.
John Tavis, Ph.D., study author and professor of molecular microbiology and immunology ...
University of Leicester announces discovery of King Richard III
2013-02-04
UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER REVEALS:
Wealth of evidence, including radiocarbon dating, radiological evidence, DNA and bone analysis and archaeological results, confirms identity of last Plantagenet king who died over 500 years ago
DNA from skeleton matches TWO of Richard III's maternal line relatives. Leicester genealogist verifies living relatives of Richard III's family
Individual likely to have been killed by one of two fatal injuries to the skull – one possibly from a sword and one possibly from a halberd
10 wounds discovered on skeleton - Richard III killed ...
Human brain is divided on fear and panic
2013-02-04
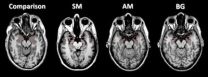
When doctors at the University of Iowa prepared a patient to inhale a panic-inducing dose of carbon dioxide, she was fearless. But within seconds of breathing in the mixture, she cried for help, overwhelmed by the sensation that she was suffocating.
The patient, a woman in her 40s known as SM, has an extremely rare condition called Urbach-Wiethe disease that has caused extensive damage to the amygdala, an almond-shaped area in the brain long known for its role in fear. She had not felt terror since getting the disease when she was an adolescent.
In a paper published ...
New criteria for automated preschool vision screening
2013-02-04
San Francisco, CA, February 4, 2012 – The Vision Screening Committee of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, the professional organization for pediatric eye care, has revised its guidelines for automated preschool vision screening based on new evidence. The new guidelines are published in the February issue of the Journal of AAPOS.
Approximately 2% of children develop amblyopia, sometimes known as "lazy eye" – a loss of vision in one or both eyes caused by conditions that impair the normal visual input during the period of development of ...