(Press-News.org) Los Angeles, CA (February 22, 2013) Studies report that since 2004, suicides rates in the U.S. Army have been on the rise. While researchers debate the cause, a new study finds that among suicide cases from 2007 – 2010, young white males were more at risk than any other demographic. This study, out today, will be published in Armed Forces & Society, a SAGE journal published on behalf of the Inter-University Seminar on Armed Forces and Society.
Army Research Psychologists James Griffith and Mark Vaitkus analyzed data from the Army National Guard's (ARNG) personnel data system, from a routine data collection of ARNG soldiers returning from deployment, and Army reserve soldiers' responses to the 2009 Status of Forces Questionnaire. They found that 17-24 year-olds were an average of 1.59 times more likely to have committed suicide than their older peers, that males were 3.05 times more likely to have committed suicide than females, and that white soldiers were 1.85 times more likely to have committed suicide than other race groups.
Additionally, researchers found that for soldiers that had been deployed, combat exposure and other military-related variables showed little to no associations with suicide risk. These findings are consistent with those reported in other, independently conducted Army studies.
Researchers offered explanations for each of the three suicide patterns among ARNG soldiers. For example, as suicides in the Army are more likely to occur among 17 to 24 year-olds, Griffith and Vaitkus discussed how this younger age group is one in which individuals are likely to be struggling to define who they are and how they relate to others. "Self-identity provides the individual with a sense of worth and meaning, characteristics often absent in suicide cases," authors stated.
Griffith and Vaitkus also stated that African American, compared to white, communities often have better support systems, higher participation in religion, and have also been described to be more resilient in adapting to difficult life experiences.
With regards to differences between male and female soldiers, researchers stated that males are more likely to engage in behavior that would put them at risk for suicide such as familiarity with and use of fire arms and alcohol/substance abuse, that men are less likely to seek or develop social support, and that women benefit more from social integration than men.
Researchers stated that they hoped their findings would help identify those who are at risk for suicide and concluded, "after identifying those at risk, soldiers need to be managed and provided appropriate support and care." Nevertheless, they also noted that this is complicated for reservists who spend most of their time in "part-time" or civilian status. As reservists now number about one-half the active duty Army, the researchers argued for more deliberate thought on how best to screen reserve soldiers who are at-risk for suicide, especially with the recent increased reliance on the reserves. At present, reservists identified as at risk must rely on their own private health care for treatment, which is likely to be inadequate.
INFORMATION:
Find out more by reading the article, "Perspectives on Suicide in the Army National Guard," in Armed Forces & Society (AFS). For access to this article, please email camille.gamboa@sagepub.com.
Armed Forces & Society (AFS), a quarterly publication, publishes articles on military institutions, civil-military relations, arms control and peacemaking, and conflict management. The journal is international in scope with a focus on historical, comparative, and interdisciplinary discourse. The editors and contributors include political scientists, sociologists, historians, psychologists, scholars, and economists, as well as specialists in military organization and strategy, arms control, and peacekeeping. http://afs.sagepub.com/
Two-Year Impact Factor: 0.815
Ranked: 67 out of 137 in Sociology and 52 out of 148 in Political Science
Five-Year Impact Factor: 0.918
Ranked: 64 out of 137 in Sociology and 52 out of 148 in Political Science
Source: 2011 Journal Citation Reports® (Thomson Reuters, 2012)
Ranked in the top 10 Military Studies Journals in Google Scholar
The Inter-University Seminar on Armed Forces and Society (IUS) is a forum for the interchange and assessment of research and scholarship in the social and behavioral sciences dealing with the military establishment and civil-military relations. The Fellows who make up the IUS include academics, military officers, researchers, and students representing a variety of private and public institutions and various academic disciplines. http://www.iusafs.org/
SAGE is a leading international publisher of journals, books, and electronic media for academic, educational, and professional markets. Since 1965, SAGE has helped inform and educate a global community of scholars, practitioners, researchers, and students spanning a wide range of subject areas including business, humanities, social sciences, and science, technology, and medicine. An independent company, SAGE has principal offices in Los Angeles, London, New Delhi, Singapore and Washington DC. www.sagepublications.com
END
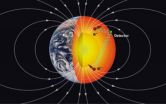
National Science Foundation- (NSF) funded researchers at Amherst College in Massachusetts and the University of Texas at Austin have described a new technique based in particle physics that might one day reveal, in more detail than ever before, the composition and characteristics of the deep Earth.
There's just one catch: the technique relies on a fifth force of nature that has not yet been detected, but some particle physicists think it might exist. The fifth force would be in addition to gravity, the weak and strong nuclear forces and electromagnetism.
Physicists ...
The study combines the cycles of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon in the ecosystem, as it shows that the molecular clusters need sulphuric acid, amines and oxygenated organics for growth. When the clusters reach a size of 1.5-2 nm, their growth increases considerably. The measurements were conducted at the University of Helsinki SMEAR II (Station for Measuring Forest Ecosystem-Atmosphere Relations) measurement station in Hyytiälä, southern Finland, which is among the most comprehensive stations in the world for atmosphere and biosphere research.
During the last five years, ...
When fruit flies sense parasitic wasps in their environment, they lay their eggs in an alcohol-soaked environment, essentially forcing their larvae to consume booze as a drug to combat the deadly wasps.
The discovery by biologists at Emory University is being published in the journal Science on Friday, February 22.
"The adult flies actually anticipate an infection risk to their children, and then they medicate them by depositing them in alcohol," says Todd Schlenke, the Emory evolutionary geneticist whose lab led the research. "We found that this medicating behavior ...
This press release is available in German.
Silicon nanocrystals have a size of a few nanometers and possess a high luminous potential. Scientists of KIT and the University of Toronto/Canada have now succeeded in manufacturing silicon-based light-emitting diodes (SiLEDs). They are free of heavy metals and can emit light in various colors. The team of chemists, materials researchers, nanoscientists, and opto-electronic experts presents its development in the "Nano Letters" journal (DOI: 10.1021/nl3038689).
Silicon dominates in microelectronics and photovoltaics ...
Our ancestors evolutionarily split from those of rhesus monkeys about 25 million years ago. Since then, brain areas have been added, have disappeared or have changed in function. This raises the question, 'Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?'. Scientists have entertained the idea before but conclusive evidence was lacking. By combining different research methods, we now have a first piece of evidence that could prove that humans have unique cortical brain networks.
Professor Vanduffel explains: "We did functional brain scans in humans and rhesus monkeys ...
Researchers at Umeå University in Sweden conclude that public opposition to dam removal is not based on knowledge deficiency, as is sometimes argued in dam removal science. It is instead a case of different understandings and valuation of the environment and the functions it provides. The findings are now published in the journal Ecology and Society.
Dam removal is an increasingly common practice as old splash dams and small hydropower dams have become obsolete. Although the removal of these dams has ecological benefits by restoring rivers to their former courses, local ...
PITTSBURGH—At a time when the U.S. government is contemplating changes to federal guidelines governing research with humans, serious questions are being raised about the role of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in overseeing such research. Particularly, vocal critics have cited lost time, money and even lives under a system that they claim consumes scarce resources and stifles academic freedom. In response, defenders of the IRB system point to the need to protect research participants from abuse.
Carnegie Mellon University's Alex John London, an internationally renowned ...
Despite years of research, the genetic factors behind many human diseases and characteristics remain unknown. The inability to find the complete genetic causes of family traits such as height or the risk of type 2 diabetes has been called the "missing heritability" problem.
A new study by Princeton University researchers, however, suggests that missing heritability may not be missing after all — at least not in yeast cells, which the researchers used as a model for studying the problem. Published in the journal Nature, the results suggest that heritability in humans ...
State supreme court justices who don't face voters are generally more effective than their elected counterparts, according to research led by Princeton University political scientists.
The research combines data about almost 6,000 state supreme court rulings nationwide between 1995 and 1998 with a new theoretical model to reach the conclusions that appointed justices generally bring a higher quality of information to the decision-making process, are more likely to change their preconceived opinions about a case, and are less likely to make errors than elected justices.
"Judges ...
WASHINGTON, DC – With only one week left before sequestration is to take effect, America's research community sustained its call for an end to the across-the-board cuts to discretionary spending that will severely restrict the nation's ability to invest in the basic scientific research that drives innovation and produces economic growth. Sequestration will reduce federal funding for scientific research by nearly $95 billion over the next nine years, which will result in a reduction of U.S. GDP by at least $203 billion. The net impact will be 200,000 fewer jobs per year ...