Liquid lens based holographic camera for real 3D scene hologram acquisition using end-to-end physical model-driven network
2024-03-06
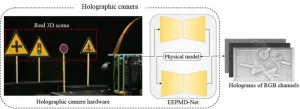
Holography technology can restore the complete light field information of the recorded object, which has important applications in fields like biological microscopic imaging and optical micromanipulation. One important frontier of holography is the reconstruction of realistic 3D scenes. However, the development and application of holographic technology have been hindered by the huge amount of data of the 3D scenes and the laser coherence, which leads to the slow capturing speed of the real 3D scenes ...
Visibility restoration for real-world hazy images via improved physical model and gaussian total variation
2024-03-06
Under real-world haze conditions, the captured images not only suffer from the haze but also are affected by the noise, which significantly deteriorates the visibility of images. However, most of existing haze removal methods mainly focus on the haze degradation and fail to consider the noise interference.
To address the above issue, a research team led by Hailing XIONG and Yun LIU published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a novel unified variational model consisting of multiple effective constraints that simultaneously ...
Breakthrough discovery will improve medical monitoring, preventive care for elephants
2024-03-06
SAN DIEGO–—Elephants are the natural carriers of a virus called Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) that can, for yet unknown reasons, cause profound clinical signs in some young elephants and be rapidly fatal. For nearly two decades, zoos and university partners have been working to study the virus and develop early detection protocols and treatment options.
Veterinarians and clinical pathology researchers at San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance (SDZWA) and the University of Copenhagen, Denmark, have recently made an important discovery, now published in the March 2024 Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine. They found that population-based reference ...
Coaches can boost athletes’ mental health by being ‘authentic leaders’
2024-03-06
Sports coaches could strengthen athletes’ mental health and protect them from mental illness – by adopting an ‘authentic leadership’ style, a new study reveals.
Researchers found when athletes perceived that their coach engaged in behaviours such as openly sharing information, showing understanding of their strengths and weaknesses, acting in an ethical manner, and listening to alternative perspectives, they felt happier and dealt with problems more easily.
Publishing their findings today (6 March) in Psychology of Sport and Exercise, experts from the University of Birmingham reveal ...
Short-term exposure to high levels of air pollution kills 1 million globally every year
2024-03-06
Every year, more than one million deaths globally occur because of exposure to short-term (hours to days) fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in air pollution, according to a new report, with Eastern Asia reporting more than 50% of deaths attributable to short-term PM2.5 globally.
To date most studies have focused on the health impacts of living in cities where pollution levels are consistently high, ignoring the frequent “spikes” in pollution that can impact smaller urban areas that occur for instance landscape fires, dust, and other intermittent ...
Living in “leafy” areas may boost bone density and lower osteoporosis risk
2024-03-06
Living in leafy areas near gardens, parks, and green spaces, may boost bone density and lower the risk of osteoporosis, finds research published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Lower levels of air pollution in green spaces is a significant contributory factor to the associations found, conclude the researchers.
Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them fragile and prone to fracture. It can lead to chronic pain, diminished mobility, and poorer quality of life. Already a major health issue worldwide, its global prevalence is set to rise with the rapid ageing of the population and changes in ...
Taking 9000 to 10000 steps daily may counteract the risk of death and cardiovascular disease in highly sedentary people
2024-03-06
Every additional step up to around 10,000 steps per day reduces the risk of death and cardiovascular disease (CVD), regardless of how much remaining time is spent sedentary, reports a large population-based study published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Some previous studies have shown that greater daily step counts are associated with lower levels of death and CVD, while others have linked high levels of sedentary behaviour with increased risks of CVD and death. However, none of these studies investigated whether high levels of physical activity may offset or lessen the higher risk of death and CVD ...
Even low levels of leisure time physical activity help to lower stroke risk
2024-03-06
Even people whose physical activity levels fall short of recommended guidelines, but who manage to do some during their leisure time, are likely to have a lower risk of stroke than their sedentary peers, suggests a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The effects are independent of age and sex, the findings show, prompting the authors to suggest that everyone should be encouraged to do whatever level of physical activity they can manage in their leisure time.
There’s no doubt that ...
Daily step count of 9,000 to 10,000 may counteract risk of death and cardiovascular disease in highly sedentary people
2024-03-06
In good news for office workers, a new study from the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre (Australia) has found increasing your step count may counteract the health consequences of too much sedentary time each day.
The study of over 72,000 people, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, found every additional step up to around 10,000 steps a day was linked to reduced risk of death (39 percent) and cardiovascular disease (21 percent) regardless of how much remaining time was spent sedentary.
Previous studies have shown an association between greater daily step count and lower levels ...
Novel device for stomach complaints has successful human trial
2024-03-06
The endoscopic mapping device, developed over more than a decade by scientists at the Auckland Bioengineering Institute, consists of an inflatable sphere covered in sensors, delivered down the oesophagus and able to measure electrical activity in the gut.
In the same way abnormal heart electrical signals can cause serious heart problems, so research has found faulty bioelectric gut waves can lead to stomach pain, nausea, vomiting and bloating.
But often doctors can’t find out what the problem is. ...
Oregon State researchers make key advance toward removing pesticide from groundwater
2024-03-06
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists led by an Oregon State University chemistry researcher are closing in on a new tool for tackling the global problem of weedkiller-tainted groundwater.
Kyriakos Stylianou of the OSU College of Science led an international team that identified a material known as a metal-organic framework, or MOF, that showed an ability to completely remove, and also break down, the oft-used herbicide glyphosate.
The MOF, one of four tested in a collaboration among scientists from Oregon State and Tiangong University in China, is based on scandium, chemical symbol Sc, ...
UTEP clinical trial to encourage healthy walking habits
2024-03-06
EL PASO, Texas (March 5, 2024) – Health researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso are launching a clinical trial to improve walking in the El Paso community, thanks to a $4.4 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The project will enroll local school district employees in 50K 4 Life, a program that challenges them to improve their health by walking at least 50,000 steps per week.
“This is an exciting opportunity to improve our community’s health through the simple, free and life-changing ...
Research explores the cooling effects of ‘scuba-diving’ in lizards
2024-03-06
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Anoles are the scuba-diving champions of the lizard world, able to stay underwater for more than 16 minutes. For animals whose body temperature depends on the environment, time spent in a cool running stream can have some tradeoffs, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
A recent study by Binghamton University doctoral candidate Alexandra M. Martin, Christopher K. Boccia of Queens University in Canada, and Binghamton University Assistant Research Professor of Biological Sciences Lindsey ...
Gender gap on Wikipedia
2024-03-05
Since it was created in 2001, Wikipedia has become a key element of the modern public sphere, which has revolutionized the way we create and share information. However, it has defects when it comes to its decentralization and flexibility, specially regarding inclusion and diversity.
Some gender biases that stand out are shown in its content and its editorial participation. It has a low percentage of women’s biographies and an unequal representation in editing. Also, there are gaps in the gender representation regarding its content, biases in editing and participation, as well as imbalances in readership.
These ...
Scientists to study real-world eating behaviors using wearable sensors and artificial intelligence
2024-03-05
A pedometer measures your steps, but what if you had a similar automated device to measure your eating behavior? Evidence from nutritional studies has long shown that the speed, timing and duration of an individual’s eating behavior are strongly related to obesity and other health issues. While eating behaviors can be accurately measured in a controlled laboratory setting, a blind spot exists when researchers attempt to study how participants actually eat “in the wild.”
A new National Institutes ...
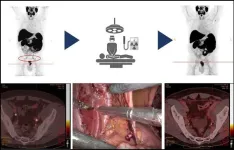
Radioguided surgery accurately detects and removes metastatic lymph nodes in newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients
2024-03-05
Reston, VA — Radioguided surgery can detect and remove metastatic pelvic lymph nodes in patients newly diagnosed with prostate cancer, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Targeting the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), which is overexpressed in most prostate cancer patients, radioguided surgery can improve nodal staging to guide treatment recommendations for this important patient population.
In newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients, nodal involvement correlates with recurrence, and determining if lymph node metastases are present and where they ...
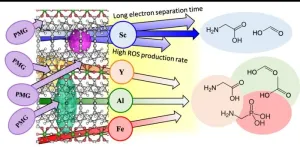
Aluminum nanoparticles make tunable green catalysts
2024-03-05
HOUSTON – (March 5, 2024) – Catalysts unlock pathways for chemical reactions to unfold at faster and more efficient rates, and the development of new catalytic technologies is a critical part of the green energy transition.
The Rice University lab of nanotechnology pioneer Naomi Halas has uncovered a transformative approach to harnessing the catalytic power of aluminum nanoparticles by annealing them in various gas atmospheres at high temperatures.
According to a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Rice ...
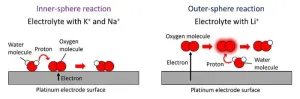
Electrolyte cation types control electrochemical reactions on an electrode surface
2024-03-05
1. An international research group consisting of NIMS and the Finnish University of Jyväskylä has discovered through its electrode-electrolyte system research that electron and proton (i.e., hydrogen ion) transfer mechanisms during oxygen reduction reactions (ORRs) on electrode surfaces vary depending on the types of cations dissolved in the electrolytic solution. These results suggest that the energy conversion efficiencies and selectivity of electrochemical systems (e.g., fuel cells and water electrolysis hydrogen production systems) can be improved by selecting optimal reaction pathways and that this could be achieved without using expensive electrode ...
The dangers of misaligned product co-development contracts—and how they can derail innovation in high-tech firms
2024-03-05
Researchers from Mansoura University and University of Guelph published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines how misaligned contracts can erode innovation outcomes of high-tech firms.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Collaborating to Innovate: Balancing Strategy Dividend and Transactional Efficiencies” and is authored by Nehal Elhelaly and Sourav Ray.
When a giant multinational like Unilever partners with one of its major suppliers, such as the industrial enzyme-producer Novozyme, the collaboration can fast-track ...
New publication highlights urgency of parasitic wasp release to save native bird
2024-03-05
DENVER/March 5, 2024 – Researchers with the University of Minnesota, funded by Morris Animal Foundation, hope to release highly-specialized parasitic wasps to serve as a biological control method to save Darwin’s finches from a dire threat: the invasive avian vampire fly, Philornis downsi.
This species has been devastating finch populations on the Galapagos Islands by laying eggs in their nests, with the emerging larvae harming the nestlings.
To protect these iconic birds and other endemic species impacted by the fly, ...
Tiny worms tolerate chornobyl radiation
2024-03-05
The 1986 disaster at the Chornobyl nuclear power plant transformed the surrounding area into the most radioactive landscape on Earth. Humans were evacuated, but many plants and animals continue to live in the region, despite the high levels of radiation that persist nearly four decades later.
A new study led by researchers at New York University finds that exposure to chronic radiation from Chornobyl has not damaged the genomes of microscopic worms living there today—which doesn’t mean that the region is safe, the scientists caution, but suggests that these worms are exceptionally resilient.
In ...
Restoration of degraded areas in semi-arid region contributes to ‘return’ of soil microorganisms, study shows
2024-03-05
Strategies deployed for the restoration of degraded land have had promising results in Brazil’s semi-arid region, improving the microbial properties of the soil and contributing to a return of native ecosystem services. The techniques include removal of cattle or restriction of their access to specific areas of pasture; cultivation of cover crops; and terracing to control erosion. Recovery of soil microbial properties maintains biodiversity and raises crop yields, contributing to agricultural ...
New research details negative consumer impacts of BLM support on major companies and brands
2024-03-05
INFORMS Journal Marketing Science New Study Key Takeaways:
Brands that supported BLM on social media during the height of the movement suffered negative impacts on social media.
Negative impacts were felt from both Democratic and Republican consumers.
The ‘bandwagon effect’ was one of the more significant factors.
Some brands with more historical prosocial posting on social media and socially oriented missions suffer less from the negative effects and may even benefit from supporting ...
Having self-control leads to power
2024-03-05
Out-of-control behavior by CEOs and other powerful people constantly makes headlines – so much so that some might consider impulsivity a pathway to power. New research from the UC San Diego Rady School of Management and Texas A&M University finds that having self-control is often what leads to power.
In a paper published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, researchers find that showing self-control influences how powerful an individual is perceived to be by their peers, as well as how much power they are granted by those peers. In a series of seven experiments with roughly 3,500 participants, both students ...
Endocrine Society elects Lange as 2025-2026 President
2024-03-05
WASHINGTON—Endocrine Society members elected Carol Lange, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, Minn., as its 2025-2026 President. She will serve as President-Elect for a year beginning in June 2024 before becoming President in June 2025.
Lange is a Professor of Medicine and Molecular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, holds the Tickle Family Land Grant Endowed Chair of Breast Cancer Research, and is the Associate Director for Basic Science and the Director of the Molecular, Genetic, and Cellular Targets of Cancer Training Program at the University of Minnesota Masonic ...
[1] ... [1327]
[1328]
[1329]
[1330]
[1331]
[1332]
[1333]
[1334]
1335
[1336]
[1337]
[1338]
[1339]
[1340]
[1341]
[1342]
[1343]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.