After decades of Arctic sea ice getting faster and more hazardous for transport, models suggest a dramatic reversal is coming, York University study finds
2024-03-05
TORONTO, March 5, 2024 – Will ice floating in the Arctic Ocean move faster or slower over the coming decades? The answer to this question will tell us whether marine transportation can be expected to get more or less hazardous. It might also have important implications for the rate of ice cover loss, which is hugely consequential for Northern Indigenous communities, ecosystems, and the global climate system.
While observational data suggest the trend has been towards faster sea ice speeds, ...
Pioneering work in computational and theoretical neuroscience is awarded the world’s largest brain research prize
2024-03-05
The Lundbeck Foundation has announced the recipients of The Brain Prize 2024, the world’s largest award for outstanding contributions to neuroscience. This year’s award recognizes the pioneering work of three leading neuroscientists – Professor Larry Abbott at Columbia University (USA), Professor Terrence Sejnowski at the Salk Institute (USA), and Professor Haim Sompolinsky at Harvard University (USA) and the Hebrew University (Israel).
Theoretical and computational neuroscience permeates neuroscience today ...
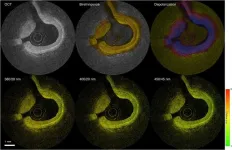
New cardiovascular imaging approach provides a better view of dangerous plaques
2024-03-05
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new catheter-based device that combines two powerful optical techniques to image the dangerous plaques that can build up inside the arteries that supply blood to the heart. By providing new details about plaque, the device could help clinicians and researchers improve treatments for preventing heart attacks and strokes.
Atherosclerosis occurs when fats, cholesterol and other substances accumulate on the artery walls, which can cause these vessels to become thick ...
BU study finds robotic-assisted surgery for gallbladder cancer as effective as traditional surgery
2024-03-05
(Boston)—Each year, approximately 2,000 people die annually of gallbladder cancer (GBC) in the U.S., with only one in five cases diagnosed at an early stage. With GBC rated as the first biliary tract cancer and the 17th most deadly cancer worldwide, pressing attention for proper management of disease must be addressed. For patients diagnosed, surgery is the most promising curative treatment. While there has been increasing adoption of minimally invasive surgical techniques in gastrointestinal malignancies, including utilization of laparoscopic ...
We know the Arctic is warming -- What will changing river flows do to its environment?
2024-03-05
AMHERT, Mass.– Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently combined satellite data, field observations and sophisticated numerical modeling to paint a picture of how 22.45 million square kilometers of the Arctic will change over the next 80 years. As expected, the overall region will be warmer and wetter, but the details—up to 25% more runoff, 30% more subsurface runoff and a progressively drier southern Arctic, provides one of the clearest views yet of how the landscape will respond to climate change. The results were published in the journal The Cryosphere.
The Arctic is defined ...
BU researcher examines clinicians’ attitudes towards major changes from the 2020 ACS Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines
2024-03-05
(Boston)—Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). New evidence has led to dramatic changes in cervical cancer screening recommendations over the past 20 years. In 2020, the American Cancer Society (ACS) released updated guidelines for cervical cancer screening. The main changes to current practices were to initiate screening at age 25 instead of age 21 and to screen using primary HPV testing rather than cytology (PAP test) alone or in combination with HPV testing. Since adoption of guidelines often occurs slowly, understanding clinician attitudes is important ...
The Arctic could become ‘ice-free’ within a decade
2024-03-05
The Arctic could see summer days with practically no sea ice as early as the next couple of years, according to a new study out of the University of Colorado Boulder.
The findings, published March 5 in the journal Nature Reviews Earth ­­& Environment, suggest that the first ice-free day in the Arctic could occur over 10 years earlier than previous projections, which focused on when the region would be ice-free for a month or more. The trend remains consistent under all future emission scenarios.
By ...
Habitual short sleep duration, diet, and development of type 2 diabetes in adults
2024-03-05
About The Study: In this study involving 247,000 UK residents, habitual short sleep duration was associated with increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This association persisted even among participants who maintained a healthy diet. To validate these findings, further longitudinal studies are needed, incorporating repeated measures of sleep (including objective assessments) and dietary habits.
Authors: Christian Benedict, Ph.D., of Uppsala University in Uppsala, Sweden, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Screen time, sociodemographic factors, and psychological well-being among young children
2024-03-05
About The Study: In this multiyear cross-sectional study of a representative sample of young children in the U.S., the increased prevalence of high screen time in 2020 returned to pre-pandemic levels in 2021; however, it remained elevated in children living in poverty. Two hours or more of daily screen time was associated with lower psychological well-being among preschool-aged children.
Authors: Soyang Kwon, Ph.D., of Northwestern University in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Too little sleep raises risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-03-05
Adults who sleep only three to five hours a day are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is demonstrated in a new study from Uppsala University, published in JAMA Network Open. It also shows that chronic sleep deprivation cannot be compensated by healthy eating alone.
“I generally recommend prioritising sleep, although I understand it’s not always possible, especially as a parent of four teenagers,” says Christian Benedict, Associate Professor and sleep researcher at the Department of Pharmaceutical Biosciences at Uppsala University and leading researcher behind the study.
He and a team of researchers have examined the link between type 2 ...
Toward understanding sperm quality
2024-03-05
A novel screening system developed at Kyoto University enables researchers to investigate sperm cell development and health at the molecular level. The new approach, published in Cell Genomics, promises breakthroughs in male contraception and infertility treatments.
The study, led by Professor Jun Suzuki of the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS), addresses a critical gap by directly targeting genes within testicular cells inside living organisms. Utilizing a genetic tool called CRISPR, which can ...
Game-changing sensor unveiled for spotting chemical threats
2024-03-05
Scientists have unveiled a groundbreaking sensor that can wirelessly detect chemical warfare agents, marking a significant leap in public safety technology. This innovative device, capable of identifying substances like dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP), offers a new level of efficiency and reliability in monitoring and responding to chemical threats, without the need for direct power sources or physical connections.
The urgent need for advanced detection of chemical warfare agents (CWAs) to ensure global security has led to the development of a novel gas sensor. This sensor is distinguished ...
The many faces of a zinc anode: Configurations can make a difference in performance
2024-03-05
Sometimes the solution to a problem can be as simple as changing the way the components are structured
Researchers have proposed a reconfiguration of zinc anodes, a component of renewable energy sources, to help improve the battery and reduce the reliance society has on fossil fuels. The potential that different configurations of a zinc anode can have could reduce costs and side reactions while increasing the safety of the rechargeable zinc metal battery (RZMB) and, of course, improve its “green” rating.
The results were published in Energy Materials and Devices ...
Team successfully synthesizes atomically precise metal nanoclusters
2024-03-05
A research team has successfully synthesized a metal nanocluster and determined its crystal structure. Their study provides experimental evidence for understanding and designing nanoclusters with specific properties at the atomic level. Metal nanoclusters have wide-ranging applications in the biomedical field.
Their work is published in the journal Polyoxometalates on February 6, 2024.
Scientists have shown interest in ligand-protected atomically precise metal nanoclusters because they have definite atomic structures and exceptional ...
Rising alcohol-related liver cancer prompts new prediction tool
2024-03-05
Liver cancer, unfortunately, is the sixth most common cancer and the third most frequent cause of cancer-related death globally. However, its distribution and causes vary greatly across different regions. While areas like Eastern Asia and sub-Saharan Africa see the most cases, the reasons behind them differ significantly.
In high-income countries, liver cancer has been on the decline thanks to widespread newborn hepatitis B vaccination and antiviral drugs. Meanwhile, low-income countries witness a worrying rise, ...
Sprinting ‘like a jet’ will produce Premier League strikers of tomorrow
2024-03-05
Sprinting “like a jet plane taking off” will help produce Premier League star strikers of tomorrow, new research has revealed.
A University of Essex study of Tottenham Hotspur’s academy has shown that just a few words can instantly boost sprinting speed by 3 per cent over 20 metres.
It would normally take weeks of targeted training to achieve such a large increase.
These short bursts of acceleration are largely seen in goal-scoring situations and could be the difference in beating a defender and finding the net.
Dr Jason Moran, from the School of Sport, Rehabilitation and Exercise Sciences, discovered simple analogies increased ...
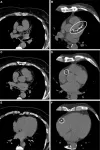
Coronary artery calcium score predictive of heart attacks, strokes
2024-03-05
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Coronary artery calcium scoring with CT can identify symptomatic patients with a very low risk of heart attacks or strokes, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Researchers said the findings may one day help some patients with stable chest pain avoid invasive coronary angiography.
Coronary artery calcium scoring with CT was developed to noninvasively measure the amount of calcium in the arteries of the heart. Higher scores are linked with atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque in the arteries. A score of 1 to 399, for instance, suggests a moderate amount of plaque, while 400 ...
Harvard neuroscientist Haim Sompolinsky awarded Brain Prize
2024-03-05
Haim Sompolinsky, Professor in Residence in Harvard’s Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology and Department of Physics, has received the Brain Prize for his pioneering contributions to computational and theoretical neuroscience.
Considered the world’s most prestigious prize for neuroscience research, the Brain Prize 2024 is shared by Sompolinsky, Larry Abbott of Columbia University, and Terrence Sejnowski of the Salk Institute. All three scientists have helped uncover key principles governing the brain’s structure, ...
Smoking during pregnancy may increase the risk of behavioral disorders in newborns, predicts AI
2024-03-05
Although several studies have linked smoking during pregnancy with neurodevelopmental disorders, the results of behavioral experiments in mice prenatally exposed to nicotine have been inconsistent. In a recent study, scientists from Japan developed a deep learning-based framework to automatically observe and classify mice behavior in such experiments, producing more accurate and unbiased results. They show that prenatal exposure to nicotine could increase the risk of autism spectrum- and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders in newborns.
The fact that smoking is a risk factor for several diseases, including cancer, stroke, and diabetes, has been known for approximately ...
Dive into the future of molecular life sciences at #DiscoverBMB 2024
2024-03-05
Which natural products are helping solve biotech challenges? How can enzymes supercharge biodegradation for a greener tomorrow? What role does RNA play in cancer and other diseases? You’ll find the answers to these questions and more at Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, to be held March 23–26 in San Antonio.
Secure your front-row seat to cutting-edge findings, approaches and technologies in the biological sciences by registering for a complimentary ...
Call for articles: Trends in Peace and Sustainability
2024-03-05
The Network for Education and Research on Peace and Sustainability (NERPS) at Hiroshima University is inviting submissions for Trends in Peace and Sustainability (TRENDS), an innovative academic platform dedicated to exploring the complex interplay between peace and sustainability. TRENDS aims to become a forum for scholars, professionals, and advocates to share their research, insights, and viewpoints on the pursuit of peace amid sustainability challenges. It aims to promote interdisciplinary engagement, stimulating conversation ...
2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award-Call for nominations
2024-03-05
The call for the 2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award is open!
About The Award
Tsinghua University Press announces the 2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award. This award is intended to recognize and encourage outstanding early career researchers in the areas of carbon-related materials, catalysis, energy conversion and storage, as well as low carbon emission process and engineering. The award includes an honorarium of $1,000 for each awardee (up to 10 awardees).
Eligibility
The nominee must be a current PhD student or postdoctoral researcher.
The nominee’s ...
Multinational collaborative research to improve climate-smart grain for Ethiopian farmers receives $4.9 million grant
2024-03-05
ST. LOUIS, MO, March 5, 2024 – The Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR) have received a $4.9 million grant from The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to build on previous advances in gene editing of tef for reduced height and lodging resistance in advanced, farmer preferred tef lines.
The grant will support research to validate the improved semi dwarf tef in Ethiopia under greenhouse and multi location field conditions and generate lodging resistance ...
Groundbreaking survey reveals secrets of planet birth around dozens of stars
2024-03-05
In a series of studies, a team of astronomers has shed new light on the fascinating and complex process of planet formation. The stunning images, captured using the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) in Chile, represent one of the largest ever surveys of planet-forming discs. The research brings together observations of more than 80 young stars that might have planets forming around them, providing astronomers with a wealth of data and unique insights into how planets arise in different regions of our galaxy.
“This is really a shift in our field of study,” says Christian Ginski, a lecturer at the University of Galway, Ireland, ...
Food web flexibility through time
2024-03-05
A theoretical experiment characterized the network architecture of a species-rich ecosystem over 8 months. Predator–prey interaction networks play a key role in structuring ecosystems, but ecological research has often treated such networks as static, despite the broadly accepted understanding of ecosystems as dynamic. Hirokazu Toju and colleagues followed the complex food webs between 50 predatory spider species and 974 prey species, including midges, springtails, mosquitoes, and aphids, for eight months. The studied ecosystem is a warm-temperate grassland ...
[1] ... [1329]
[1330]
[1331]
[1332]
[1333]
[1334]
[1335]
[1336]
1337
[1338]
[1339]
[1340]
[1341]
[1342]
[1343]
[1344]
[1345]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.