American Tinnitus Association elects Wayne State researcher as new chair
2023-06-02
DETROIT – The American Tinnitus Association (ATA) has elected Jinsheng Zhang, Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders in Wayne State University’s College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, as the new chair of its board of directors. With decades of experience in tinnitus research and work with the ATA, Zhang aims to assist with proactive recruitment of scientists to the field of tinnitus and engage more researchers in ATA grant opportunities that will spur progress toward more effective treatments and cures.
Tinnitus ...
Media Alert: American College of Cardiology to host Sports Cardiology Conference
2023-06-02
The American College of Cardiology will host the annual Care of the Athletic Heart course on June 8-10, 2023, in Washington, including poster abstracts and educational sessions. The course is designed for all clinicians who provide cardiovascular care for the professional, occupational, tactical or recreational athlete. As the athletic population expands to all demographic groups, it is critical that there is a larger contingent of clinicians who understand the latest care and practice management for athletes at every level.
Dermot Phelan, BAO, MBBCh, PhD, FACC, and Megan Wasfy, ...
Immunotherapy for brain cancer metastases shows clinical benefit
2023-06-02
In a phase 2 clinical trial of the immune checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab, investigators found that 42 percent of patients with metastatic brain cancer benefited from the therapy, with seven patients in the trial surviving longer than two years. The authors caution that these benefits must be weighed against risk of toxicity, but, overall, the study shows promising results that warrant larger studies and efforts to identify patients most likely to benefit from this treatment. Their findings are published in Nature Medicine and presented simultaneously at the 2023 ASCO Annual Meeting on June 2.
“There ...
Commentary calls for equal access to healthcare for DACA recipients and all immigrants
2023-06-02
The paper, published April 17 in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas, was co-authored by Dr. Gunisha Kaur, an associate professor of anesthesiology at Weill Cornell Medicine and medical director of the Weill Cornell Center for Human Rights; Stephen Yale-Loehr, a professor of immigration law practice at Cornell Law School; and Jin K. Park, a medical student at the Harvard School of Medicine and the first DACA recipient awarded a Rhodes Scholarship.
“The erratic enforcement of the DACA program since its inception has led many immigrants and their families to disengage completely from the healthcare system to avoid risking deportation,” said ...
Taming a frenzied immune system
2023-06-02
Researchers at the University of Louisville have received $5.8 million in two grants from the National Institutes of Health to expand their work to better understand and prevent immune system dysregulation responsible for acute respiratory distress, the condition responsible for serious illness and death in some COVID-19 patients. A separate $306,000 NIH Small Business Innovation Research grant supports early testing of a compound developed at UofL as a potential treatment.
The three grants combined total $6.1 million.
During the pandemic, health care providers worked tirelessly to treat patients ...
Veterans exposed to Agent Orange may be at increased risk of developing progressive blood cancers
2023-06-02
WASHINGTON --- Research conducted at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Washington DC VA Medical Center on a database of veterans exposed to Agent Orange found an association for an increased risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), which are acquired stem cell disorders that can lead to overproduction of mature blood cells complicated by an increased risk of blood clots in arteries and veins. When MPNs progress, they can become deadly leukemias.
The findings will be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2023 annual meeting in Chicago in June.
Agent Orange is an herbicide that was utilized by the United States military ...
Hispanic women still at higher risk for births with neural tube defects after voluntary folic acid fortification of corn masa flour
2023-06-02
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandated folic acid fortification of all enriched cereal grains in 1996, and this regulation resulted in a reduction of neural tube defect (NTD)–affected pregnancies for the population in the United States. While this mandatory food fortification strategy is an example of a public health success, Hispanic women in the US continued to be twice as likely to give birth to a child affected by NTD compared to non-Hispanic women. It was not until the year 2016 that the FDA approved voluntary, but not mandatory, folic acid fortification for corn masa flour products in the US to focus on the Hispanic diet staples, such ...
Buckle up! A new class of materials is here
2023-06-02
Usually, the two characterizations of a material are mutually exclusive: something is either stiff, or it can absorb vibrations well – but rarely both. However, if we could make materials that are both stiff and good at absorbing vibrations, there would be a whole host of potential applications, from design at the nano-scale to aerospace engineering.
Buckling does the trick
A team of researchers from the University of Amsterdam has now found a way to create materials that are stiff, but still good at absorbing vibrations – and equally importantly, that can be kept very light-weight. David Dykstra, lead author of the ...
Lupus Therapeutics partners to evaluate potential treatment for SLE and lupus nephritis through North American trial network
2023-06-02
NEW YORK, N.Y. — June 2. Lupus Therapeutics announced the start of a collaboration to conduct three Phase 3 clinical trials testing an investigational therapeutic ianalumab for systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Lupus Therapeutics, the clinical research affiliate of the Lupus Research Alliance, will help Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (Novartis) conduct the trials through the Lupus Clinical Investigators Network (LuCIN) at top academic centers throughout North America.
Lupus is a devastating heterogeneous autoimmune disease affecting millions worldwide with symptoms that can range from debilitating fatigue to ...
Sensory adaptations to improve physiological, behavioral distress during dental visits in autistic children
2023-06-02
About The Study: In this randomized crossover trial of autistic children, using a sensory-adapted dental environment was safe and efficacious in decreasing physiological and behavioral distress during dental care. This is important because enhancing oral care is critical for autistic children; this intervention may also be beneficial for populations beyond autism.
Authors: Leah I. Stein Duker, Ph.D., O.T.R./L., of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Awareness of racial, ethnic bias and potential solutions to address bias with use of health care algorithms
2023-06-02
About The Study: This qualitative study found that participants perceived widespread and increasing use of algorithms in health care and lack of oversight, potentially exacerbating racial and ethnic inequities. Increasing awareness for clinicians and patients and standardized, transparent approaches for algorithm development and implementation may be needed to address racial and ethnic biases related to algorithms.
Authors: Peter Treitler, M.S.W., of Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Reentry services may help stabilize substance use risks after mass prison release
2023-06-02
Contrary to expectations, the risk for relapses, overdoses and deaths related to substance use disorder didn’t increase after a large-scale prison release in New Jersey, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in JAMA Health Forum, examined whether post-release overdose deaths and drug-related hospital and emergency department visits increased after more than 2,000 individuals were released from prison in late 2020 as the result of a pandemic-era policy.
“Risk of relapse and adverse health events is high following prison release, with risk of fatal overdose ...
Memory killer cells can improve survival for melanoma patients
2023-06-02
Our skin contains specialised long-lived killer cells that protect against intruders. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have now identified how these cells are formed, and shown that high levels of memory killer cells in cancer tissue correlate with a better survival rate in people with melanoma. The study is published in the journal Immunity.
Certain immune T cells called tissue-resident memory cells are formed locally in the skin and other tissue, and protect against infections that they have encountered before. Some of ...
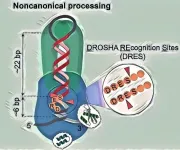
HKUST researchers unveil long-sought noncanonical cleavage mechanism in miRNA biogenesis
2023-06-02
To discover and thoroughly demonstrate the newly identified noncanonical cleavage mechanism, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) research team, led by Prof. Tuan Anh Nguyen, Assistant Professor of the Division of Life Science, used several sophisticated techniques, such as miRNA sequencing, pri-miRNA structure analysis, and high-throughput pri-miRNA cleavage assays for approximately 260,000 pri-miRNA sequences. In contrast to the canonical mechanism, the noncanonical mechanism does not rely on several essential protein and RNA elements ...
Immune system discovery could benefit spinal cord injuries
2023-06-02
New research suggests that the immune system’s ability to respond to spinal cord injuries diminishes with age – and identifies potential avenues to improve that response and help patients heal.
The new findings offer important insights into how the immune system responds to spinal-cord injuries, and why that response becomes blunted with the passing years. Further, it reveals an important role for the membranes surrounding the spinal cord in mounting the immune response to spinal-cord injury. With this information, doctors one day may be able to bolster the body’s natural immune response to improve patient outcomes, particularly among older adults.
“Recently, ...
UTHSC researchers’ work on human pangenome aids understanding of common chromosomal abnormality
2023-06-02
Researchers from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center have made a foundational discovery about chromosome biology through their work on the first-ever human pangenome reference.
Published recently by the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium in the journal Nature, the draft pangenome uses complete genome assemblies to provide a diverse look at the genetic makeup of humans. Researchers in the UTHSC Department of Genetics, Genomics and Informatics created the technical tools to build the pangenome, and then used the tools to understand variation in parts of the genome that could not be seen before.
The pangenome ...
Mysterious dashes revealed in Milky Way’s center
2023-06-02
New radio telescope images reveal hundreds of filaments along the galactic plane, each measuring 5 to 10 light-years in length
These structures likely originated a few million years ago when outflow from our supermassive black hole interacted with surrounding materials
Researcher: ‘I was actually stunned when I saw these’
EVANSTON, Ill. — An international team of astrophysicists has discovered something wholly new, hidden in the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
In the early 1980s, Northwestern University’s Farhad Yusef-Zadeh discovered gigantic, one-dimensional filaments dangling vertically near Sagittarius A*, our ...
ASCO: Adding ribociclib to hormone therapy improves outcomes in patients with early breast cancer
2023-06-02
A study involving UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers found when ribociclib, a targeted therapy drug, is added to hormone therapy there are a significant invasive disease-free survival benefit in patients with early hormone-receptor (HR) positive/HER2 negative breast cancer.
Researchers found that patients who took the combination therapy had substantially longer invasive disease-free survival compared to those who were treated with the hormone therapy alone, regardless of whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The addition of the targeted therapy reduced the risk of recurrence by 25%.
The results were shared today during the American Society of Clinical ...
New research suggests wheat crops may be threatened by unprecedented heat and drought
2023-06-02
The world is getting hotter, causing shifts in seasonal patterns and increasing the amount of extreme weather such as severe droughts and heat waves, which can affect crop yields and food supplies. A recent study led by a researcher at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University found that the likelihood of extreme temperatures that could affect crop yields has increased significantly in wheat-producing regions of the U.S. and China.
The findings predict heat waves that happened approximately ...
Eventually everything will evaporate, not only black holes
2023-06-02
New theoretical research by Michael Wondrak, Walter van Suijlekom and Heino Falcke of Radboud University has shown that Stephen Hawking was right about black holes, although not completely. Due to Hawking radiation, black holes will eventually evaporate, but the event horizon is not as crucial as had been believed. Gravity and the curvature of spacetime cause this radiation too. This means that all large objects in the universe, like the remnants of stars, will eventually evaporate.
Using a clever combination of quantum physics and Einstein’s theory of gravity, Stephen Hawking argued that the spontaneous creation and annihilation ...
Underwater forest's recovery offers hope for marine restoration across the globe
2023-06-02
Human activity has degraded ecosystems and damaged biodiversity around the world, but ecosystem restoration offers hope for the future. Scientists studying the restoration of underwater seaweed forests which provide other species with food and shelter have found that 10 years of restoration efforts have helped a damaged forest regrow to richness and strength comparable to forests that have never been disturbed.
“Macroalgal forests are found along over one-third of the world’s coastlines and underpin ...
Developing technologies to reduce the cost of green hydrogen production
2023-06-02
Green hydrogen, which produces hydrogen without the use of fossil fuels or the emission of carbon dioxide, has become increasingly important in recent years as part of efforts to realize a decarbonized economy. However, due to the high production cost of water electrolysis devices that produce green hydrogen, the economic feasibility of green hydrogen has not been very high. However, the development of a technology that drastically reduces the amount of rare metals such as iridium and platinum used in polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis devices is opening the way to lower production costs.
A research team led by Dr. Hyun S. Park and Sung Jong ...
ASCO 2023 - Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center experts available for interviews
2023-06-02
Sarcomas
Dr. Jonathan C. Trent, a medical oncologist specializing in Sarcoma and Connective Tissue Medical Oncology at Sylvester, is available to discuss a wide range of issues related to Sarcoma research and experimental therapeutics. He and collaborators are involved in multiple ASCO23 presentations, including:
Multi-omic characterization of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) in a large real-world patient cohort.
Outcomes in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor who did not have ...
Alcohol dependency in adolescence, but not consumption, linked with later depression risk
2023-06-02
Adolescents who show signs of alcohol dependence are more likely to develop depression by their mid-20s, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) and University of Bristol researchers.
Drinking large amounts of alcohol regularly, but with no signs of dependency, did not predict depression risk, according to the findings published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Co-lead author Dr Gemma Lewis (UCL Psychiatry) said: “By using a large, longitudinal dataset, we have found evidence that problematic drinking patterns in late adolescence may increase the risk of developing ...
Why we need to fall out of love with flaky white fish - study
2023-06-02
The UK’s growing mismatch between the fish we catch and the fish we want to eat has clear implications for our future food security, according to new research.
Led by the University of Essex and the Centre for Environment Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas), the study, published in the international peer-reviewed journal Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, for the first time offers a comprehensive, long-term analysis of how major policy changes in the past 120 years have influenced patterns in UK seafood production, trade and consumption.
It shows that even if we changed our fish-eating habits away from choosing flaky white fish such as cod ...
[1] ... [1888]
[1889]
[1890]
[1891]
[1892]
[1893]
[1894]
[1895]
1896
[1897]
[1898]
[1899]
[1900]
[1901]
[1902]
[1903]
[1904]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.