ASCO 2023 - Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center experts available for interviews
2023-06-02
Sarcomas
Dr. Jonathan C. Trent, a medical oncologist specializing in Sarcoma and Connective Tissue Medical Oncology at Sylvester, is available to discuss a wide range of issues related to Sarcoma research and experimental therapeutics. He and collaborators are involved in multiple ASCO23 presentations, including:
Multi-omic characterization of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) in a large real-world patient cohort.
Outcomes in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor who did not have ...
Alcohol dependency in adolescence, but not consumption, linked with later depression risk
2023-06-02
Adolescents who show signs of alcohol dependence are more likely to develop depression by their mid-20s, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) and University of Bristol researchers.
Drinking large amounts of alcohol regularly, but with no signs of dependency, did not predict depression risk, according to the findings published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Co-lead author Dr Gemma Lewis (UCL Psychiatry) said: “By using a large, longitudinal dataset, we have found evidence that problematic drinking patterns in late adolescence may increase the risk of developing ...
Why we need to fall out of love with flaky white fish - study
2023-06-02
The UK’s growing mismatch between the fish we catch and the fish we want to eat has clear implications for our future food security, according to new research.
Led by the University of Essex and the Centre for Environment Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas), the study, published in the international peer-reviewed journal Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, for the first time offers a comprehensive, long-term analysis of how major policy changes in the past 120 years have influenced patterns in UK seafood production, trade and consumption.
It shows that even if we changed our fish-eating habits away from choosing flaky white fish such as cod ...
UK’s poorest children likelier to have less understanding of personal finances, study finds
2023-06-02
A new study of 3,745 families from across the UK demonstrates a “sizeable” gap in the financial knowledge of children depending on which socio-economic group they come from.
The research highlights significant inequalities in young people’s financial capabilities, with the results pointing toward disadvantaged children not developing key financial skills.
In findings published in the peer-reviewed British Journal of Educational Studies, an expert team from UCL are calling for a greater emphasis on developing financial skills amongst children starting at primary school, particularly aimed towards those from disadvantaged social backgrounds, with “a particular need ...
ASCO 23: Thyroid cancer precision approaches that incorporate targeted therapies and other treatments are changing the surgeon’s role
2023-06-02
DOWNLOADABLE B-ROLL/VIDEO
MIAMI, FLORIDA (June 1, 2023) – Historically, surgery was the first line of treatment for patients with thyroid cancer. Now, as targeted therapies and other new medications emerge, surgery for certain patients may become more of a secondary option if those treatments fail. This new context could potentially change how some procedures are conducted.
Otolaryngologist and head and neck surgeon Dr. Zoukaa Sargi, will join a June 2 panel discussion on thyroid cancer care ...
Medical College of Wisconsin cancer researcher & key investigator on study of Pirtobrutinib, now FDA approved for patients previously treated for Mantle Cell Lymphoma
2023-06-02
In a multicenter phase 1 and 2 trial (BRUIN, NCT03740529), researchers from leading cancer centers across the globe, including the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) in Milwaukee, tested Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi), pirtobrutinib, in patients with pre-treated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Results of the study, which assessed the efficacy of the drug in a cohort of 90 patients with poor survival prognosis, demonstrated the reversible BTKi drug to be both safe and effective in achieving inhibition of defective B-cells. The results were published by the Journal of Clinical Oncology on May 16.
MCL is an aggressive, rare subtype of ...
Researchers develop new detection tool for beech leaf disease’s nematode pest
2023-06-02
Beech leaf disease is an emerging threat to North American forest ecosystems. It was first discovered in northeastern Ohio in 2012, and has already spread to 12 additional U.S. states and Canadian provinces. At first the cause of the disease was unknown, and the sick and dying trees were diagnosed on symptoms alone: Dark banding along the leaf veins and shriveled, leathery leaves. But in 2017, nematodes were found in diseased leaves, and by 2020 we had the answer: A newly recognized subspecies of the wormlike creature, Litylenchus crenatae mccannii, was definitely associated with the symptoms.
In order to monitor the spread of the disease, to understand the nemotode’s ...
St. Jude finds NLRP12 as a new drug target for infection, inflammation and hemolytic diseases
2023-06-01
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – June 01, 2023) Infections and other diseases can cause red blood cells to rupture, releasing the oxygen-binding molecule hemoglobin, which breaks down into heme. Free heme can cause significant inflammation and organ damage, leading to morbidity and mortality. Researchers from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital discovered NLRP12, an innate immune pattern recognition receptor, to be the key molecule responsible for inducing inflammatory cell death and pathology in response to heme combined with other cellular damage or infection. The finding provides a new potential drug target to prevent morbidity in certain illnesses. ...
Ancient viruses discovered in coral symbionts’ DNA
2023-06-01
HOUSTON – (June 1, 2023) – An international team of marine biologists has discovered the remnants of ancient RNA viruses embedded in the DNA of symbiotic organisms living inside reef-building corals.
The RNA fragments are from viruses that infected the symbionts as long ago as 160 million years. The discovery is described in an open-access study published this week in the Nature journal Communications Biology, and it could help scientists understand how corals and their partners fight off viral infections today. But it was a surprising find because most RNA viruses are not known ...
NEC Society launches neonatal probiotics toolkit
2023-06-01
Davis, CA - The Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Society is thrilled to release the Neonatal Probiotics Toolkit. The Toolkit provides structure to clinicians in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) as they consider the complex process and decision of whether to implement probiotics to help prevent NEC. The Toolkit is not a recommendation for or against the routine use of probiotics in the NICU, nor for or against the use of any product or preparation method.
NICUs and clinicians are encouraged to use the Toolkit to foster thoughtful, intentional dialogue and inclusive conversations amongst key stakeholders in the NICU, including the need for patient-families to understand ...
Cancer cells rev up synthesis, compared with neighbors
2023-06-01
Tumors are composed of rapidly multiplying cancer cells. Understanding which biochemical processes fuel their relentless growth can provide hints at therapeutic targets.
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis have developed a technology to study tumor growth in another dimension — literally. The scientists established a new method to watch what nutrients are used at which rates spatially throughout a tissue.
By using this multidimensional imaging approach, they identified pathways whose activities are uniquely elevated in brain cancer, offering clues for potential treatment strategies. The study was published May 19 in Nature Communications.
“We ...
Eye drops slow nearsightedness progression in kids, study finds
2023-06-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The results of a new clinical trial suggest that the first drug therapy to slow the progression of nearsightedness in kids could be on the horizon.
The three-year study found that a daily drop in each eye of a low dose of atropine, a drug used to dilate pupils, was better than a placebo at limiting eyeglass prescription changes and inhibiting elongation of the eye in nearsighted children aged 6 to 10.
That elongation leads to myopia, or nearsightedness, which starts in young kids and ...
New LUX search tool offers unprecedented access to Yale’s vast collections
2023-06-01
New Haven, Conn. — Yale University’s museums, libraries, and archives contain vast troves of cultural and scientific heritage that fire curiosity and fuel research worldwide. Now there’s a simple new way to make astonishing connections among millions of objects.
Starting today, anyone can explore the university’s unparalleled holdings online through LUX: Yale Collections Discovery — a groundbreaking discovery and research platform that provides single-point access to more than 17 million items, including defining specimens ...
Bremen researchers cultivate archaea that break down crude oil in novel ways
2023-06-01
Microbial communities are especially active near hydrothermal seeps like those in the Guaymas Basin in the Gulf of California. The team of researchers has been working on understanding these communities for many years. Organic material deposited in the Guaymas Basin is cooked by heat sources from within the Earth, which breaks it down into crude oil and natural gas. Their components provide the primary source of energy for microorganisms in an otherwise hostile environment. In their latest study, the researchers have demonstrated that archaea use a previously unknown mechanism to degrade liquid petroleum ...
Owkin powers a new era in oncology research with MOSAIC – an unprecedented $50 million spatial atlas of cancer cells
2023-06-01
– Cutting-edge spatial omics technologies to map cancer cells and their immune environment in high resolution, allowing AI to unlock potential for new breakthrough treatments –
– Landmark research project is 100x larger than existing efforts –
– Data will be generated from thousands of patients across multiple cancers –
– University of Pittsburgh, Gustave Roussy, Lausanne University Hospital, Uniklinikum Erlangen/Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg , Charité ...
Adolescents are aware of and invested in the potential impacts of abortion restrictions, study says
2023-06-01
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – On July 1, North Carolina’s new abortion limits go into effect. As restrictions on abortions are being tightened across the United States, adolescents may encounter mounting obstacles that could prevent them from accessing abortion care.
Bianca A. Allison, MD MPH, an assistant professor in the Department of Pediatrics, sought to examine the awareness and knowledge that adolescents have about the legal landscape of abortion and how these changes might affect them and their communities.
The study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, found that many adolescents – across a diversity of ...
Family resemblance: How T cells could fight many coronaviruses at once
2023-06-01
LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) are investigating how the immune system's T cells react to a wide variety of coronaviruses, ranging from SARS to common cold coronaviruses. Their goal is to guide the development of vaccines that could halt future pandemic by combatting many types of coronaviruses at once.
"While it was recognized that coronaviruses were potentially dangerous viruses, because of SARSCoV and MERS viruses causing very severe disease in humans, nobody knew that the next pandemic was going to be caused by SARS-CoV-2," says LJI Professor Alessandro Sette, Dr.Biol.Sci. ...
New UNC study quantifies disparity among minority communities exposed to traffic-related air pollution across the U.S.
2023-06-01
Traffic-related air pollution is a pervasive problem across the United States. Vehicle emissions are highest near major roadways with around 19% of the U.S. population living in the vicinity of a major roadway. In more densely populated states, like California, up to 40% live near a major roadway. Exposure to these pollutants, such as fine particulate matter (PM2.5 ) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a byproduct of burning fossil fuel, can lead to a host of health effects including premature death. Minority communities often live along these corridors and experience disproportionate exposures.
A ...
Study identifies boat strikes as a growing cause of manatee deaths in Belize
2023-06-01
The endangered Antillean manatee faces a growing threat from boat strikes in Belize, according to a new study that raises concerns about the survival of what had been considered a relatively healthy population.
Belize hosts a population of around 1,000 manatees. With the growth of tourism in recent decades, however, Belize has seen a substantial increase in boat traffic, making boat strikes an increasingly important cause of manatee deaths and injuries.
The new study, published June 1 in Endangered Species Research, used 25 years of data on manatee strandings (dead or injured ...
Biologists to create ‘toolbox’ for understanding complex genetic traits
2023-06-01
Driven by a lifelong curiosity about the natural world and the diversity of life, Elizabeth King, associate professor in the Division of Biological Sciences at the University of Missouri, found inspiration to spend her formative years studying science — and along the way she discovered her passion for biology. That foundation has led her to pursue an ongoing career working to develop a better understanding of genetic traits from a biological perspective.
Recently, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) awarded King a five-year, $1.9 million grant to expand her lab’s research ...
Salton Sea environment detrimental to respiratory health of local children
2023-06-01
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- In the United States, low-income immigrant and minority children often live in environments that have highly polluted air. A study led by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, demonstrates this among the Latinx and Purépecha immigrant children and caregivers living along Inland Southern California’s Salton Sea, a highly saline drying lakebed surrounded by agricultural fields. The Purépecha community is an Indigenous group from the Mexican state of Michoacán.
“Children of Latinx ...
Fellowship offers reporters valuable insight as America ages
2023-06-01
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) has received renewed grant support to welcome a new class of reporters for the Journalists in Aging Fellows Program. The 2023 funders to date include Silver Century Foundation, The John A. Hartford Foundation, Archstone Foundation, and NIHCM Foundation.
Since its founding in 2010, this program has been responsible for more than 800 news stories produced by 217 alumni. It has two goals: to educate journalists about issues in aging, better allowing them to spread a new awareness to general-audience, ethnic, and other minority populations; ...
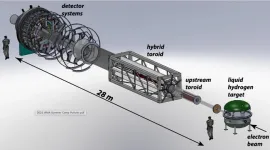
Critical decision-3A clears way toward standard model test
2023-06-01
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has given the greenlight for the MOLLER experiment to begin procurement of key components with its granting of Critical Decision-3A (CD-3A): Approve Long Lead Procurements. The determination allows the MOLLER project at DOE’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility to begin spending $9.14 million for long-lead procurements of critical items for which designs are complete.
After imagining what it would look like for 17 years, Krishna Kumar felt chills the first time he saw fully engineered drawings of the MOLLER experiment.
“Seeing the designs on paper gave me pins and needles,” said Kumar, professor of ...
Sandia scientists achieve breakthrough in tackling PFAS contamination
2023-06-01
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A team at Sandia National Laboratories is developing materials to tackle what has become one of the biggest problems in the world: human exposure to a group of chemicals known as PFAS through contaminated water and other products. Sandia is now investing more money to take their research to the next level.
“It’s in the news constantly. It seems every day we hear of another product that is contaminated. We saw sparkling water with PFAS, toilet paper with PFAS, so it’s ...
Better search for the cause of hereditary diseases
2023-06-01
So far, it has not been possible to explain the causes of around half of all rare hereditary diseases. A Munich research team has developed an algorithm that predicts the effects of genetic mutations on RNA formation six times more precisely than previous models. As a result, the genetic causes of rare hereditary diseases and cancer can be identified more precisely.
Variations of genetic sequence occur relatively frequently – on average, one in a thousand nucleotide of a person’s genome is affected. In rare cases, these changes can lead to defective RNAs and hence non-functional proteins. This can lead to dysfunction in individual organs. If a rare disease is suspected, computer-assisted ...
[1] ... [1880]
[1881]
[1882]
[1883]
[1884]
[1885]
[1886]
[1887]
1888
[1889]
[1890]
[1891]
[1892]
[1893]
[1894]
[1895]
[1896]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.