Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time
2023-06-09
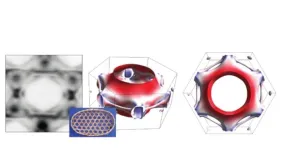
An international research team has succeeded for the first time in measuring the electron spin in matter - i.e., the curvature of space in which electrons live and move - within "kagome materials", a new class of quantum materials.
The results obtained - published in Nature Physics - could revolutionise the way quantum materials are studied in the future, opening the door to new developments in quantum technologies, with possible applications in a variety of technological fields, from renewable energy to biomedicine, from electronics to quantum computers.
Success was ...
Seismic Waves tell lithospheric delamination mechanism in south China
2023-06-09
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Haijiang from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Prof. HOU Zengqian from Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, revealed the seismically imaged lithospheric delamination and its controls on the Mesozoic Magmatic Province in South China by using a new joint seismic inversion algorithm. The study was published in Nature Communications.
Based on the latest developed seismic joint inversion algorithm, the researchers made use of the seismic body wave travel time, surface wave dispersion ...
Program for underrepresented undergraduate students in STEM receives NIH funding
2023-06-09
Alexandra Hanlon, director of the Virginia Tech Center for Biostatistics and Health Data Science, was recently awarded a $1.25 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for a summer program aimed at promoting and diversifying the field of collaborative biostatistics.
The Collaborative Undergraduate Biostatistics Experience (CUBE), an eight-week summer program geared toward underrepresented undergraduate students, will receive $250,000 per year over the next five years through the NIH Research Education Program.
This R25 award, which is funded in a joint effort ...
USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers
2023-06-09
In a study published online in Nano Letters, the team led by Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Dr. XU Jinshi from the University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress in enhancing the fluorescence of single silicon carbide spin defects. The researchers leveraged surface plasmons to markedly boost the fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide double vacancy PL6 color centers, leading to an improvement in the efficiency of spin control using the properties of co-planar waveguides. This low-cost method neither calls for complex micro-nano processing ...
Researchers determine quantitative composition of ultrahigh-pressure fluid in deep subduction zones
2023-06-09
In a study published in PNAS, Prof. XIAO Yilin’s group from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) quantitatively determined, for the first time, the chemical composition of supercritical fluids in deep subduction zones, through 3D imaging modelling of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) multiphase fluid inclusions, and revealed the important role of supercritical fluids in the cycling of carbon and sulfur in subduction zones, which is of great importance ...
USTC reveals reconfiguration process of solar eruptions
2023-06-09
Recently, a research team led by Prof. GOU Yanyu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found that the solar outburst structure undergoes a complex reconfiguration evolution during the early outbursts, thus making important advances in the study of solar outburst activity. This study was published in Nature Astronomy.
In classical images, the core structure of a solar eruption is a magnetic rope consisted of spirally wound magnetic lines. When the eruption begins, the magnetic ropes around the core are transformed by magnetic reconnection ...
DNA facilitates escape from metastability
2023-06-09
Prof. LIANG Haojun from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a new method to escape from metastability for self-assembly in a far-from-equilibrium system. The study was published in PNAS.
Self-assembly refers to the process in which assembled primitive elements (molecules, nanoparticles, etc.) spontaneously form ordered structures through non-covalent interactions. Its excellent capacity to create new materials has drawn attention. In an ...
Single quantum bit achieves complex systems modeling
2023-06-09
A team led by Academician GUO Guangcan from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), with collaborative efforts from the University of Manchester, and Nanyang Technological University, has achieved new progress in applying quantum technologies in complex systems modeling. The results were published in Nature Communications on May 6.
Stochastic modeling can help us to predict the future behavior of complex processes, which are non-Markovian. In order to simulate a non-Markovian process, a memory is of necessity to store a large amount of observed information about the past of the system. However, ...
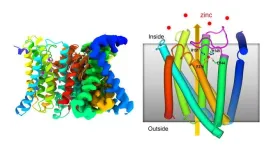
Zinc transporter has built-in self-regulating sensor
2023-06-09
UPTON, NY — Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have determined the atomic-level structure of a zinc-transporter protein, a molecular machine that regulates levels of this crucial trace metal micronutrient inside cells. As described in a paper just published in Nature Communications, the structure reveals how the cellular membrane protein shifts its shape to move zinc from the environment into a cell, and temporarily blocks this action automatically when zinc levels inside the cell get too high.
“Zinc is important for many biological ...
New model offers a way to speed up drug discovery
2023-06-09
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Huge libraries of drug compounds may hold potential treatments for a variety of diseases, such as cancer or heart disease. Ideally, scientists would like to experimentally test each of these compounds against all possible targets, but doing that kind of screen is prohibitively time-consuming.
In recent years, researchers have begun using computational methods to screen those libraries in hopes of speeding up drug discovery. However, many of those methods also take a long time, as most of them calculate each target protein’s ...
Black, Hispanic survivors of breast cancer have higher death rates from second cancers
2023-06-09
Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black female survivors of breast cancer experience higher death rates after being diagnosed with a second primary cancer than members of other ethnic and racial groups, according to recent research from investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
In a study of nearly 40,000 adult survivors of breast cancer, the risk of death from a second cancer was 12% higher among non-Hispanic Black survivors and 8% higher among Hispanic survivors compared with non-Hispanic white survivors. Survivors in racial and ethnic minorities were diagnosed with second cancers ...
Mouse models of adolescent binge drinking reveal key long-lasting brain changes
2023-06-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa — Heavy alcohol consumption may cause permanent dysregulation of neurons, or brain cells, in adolescents, according to a new study in mice. The findings suggest that exposure to binge-levels of alcohol during adolescence, when the brain is still developing, lead to long-lasting changes in the brain’s ability to signal and communicate — potentially setting the stage for long-term behavioral changes and hinting towards the mechanisms of alcohol-induced cognitive changes in humans.
“What we’re seeing here,” said Nikki Crowley, assistant professor in biology and biomedical engineering ...
Infants and toddlers up to 5 years old can participate in Shape Up! Keiki study at Pennington Biomedical
2023-06-09
The Pennington Biomedical Research Center is looking for children 5 years old and younger to participate in the Shape Up! Keiki research study. The purpose of the Shape Up! Keiki research study is to create a better way to measure and describe health from body shape.
“Parents can learn more about their child’s health by joining the Shape Up! Keiki study, while also providing important information that will help us find quick ways to measure obesity status and health based on a child’s body ...
Seenu Hariprasad named University of Chicago Chair of Ophthalmology and Visual Science
2023-06-09
Seenu M. Hariprasad, MD, the Shui-Chin Lee Professor of Ophthalmology, will be appointed Chair of the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, effective July 1, 2023. He has been serving as Interim Chair since 2020.
Hariprasad is an internationally recognized vitreoretinal surgeon who originally joined the University of Chicago in 2005. Over the course of his career, he has developed a strong track record as a clinician, surgeon, researcher, educator, and leader in his department. He is a leading specialist in various vitreoretinal disorders, including macular degeneration, diabetic ...
Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent
2023-06-09
Everyday materials such as paper and plastic could be transformed into electronic “smart devices” by using a simple new method to apply liquid metal to surfaces, according to scientists in Beijing, China. The study, published June 9 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, demonstrates a technique for applying a liquid metal coating to surfaces that do not easily bond with liquid metal. The approach is designed to work at a large scale and may have applications in wearable testing platforms, flexible devices, and soft robotics.
“Before, we thought that it was impossible for liquid metal ...
Estimated reductions in opioid overdose deaths with public health interventions
2023-06-09
About The Study: In this decision analytical model study of the opioid epidemic in four U.S. states, sustained implementation of interventions, including increased delivery of medications for opioid use disorder and naloxone supply, was found to be needed to reduce opioid-related overdose deaths and prevent deaths from increasing again.
Authors: Jagpreet Chhatwal, Ph.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14925)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Racial, ethnic, sex differences in methadone-involved overdose deaths before, after federal policy change expanding take-home methadone doses
2023-06-09
About The Study: In this study of monthly methadone-involved overdose deaths, the take-home policy may have helped reduce deaths for Black and Hispanic men but had no association with deaths of Black or Hispanic women or white men or women. The urgency of the overdose crisis requires that national methadone policy debates and decisions address the heterogeneity of people in treatment; relaxing methadone restrictions may help some particularly at-risk groups.
Authors: Rebecca Arden Harris, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Graphene-based Carbocatalysts: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications—Beyond Boundaries
2023-06-09
Introducing "Graphene-based Carbocatalysts: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications (Volume 2)"—a concise yet comprehensive compendium for the scientific community, professors, and students alike. This authoritative volume - published by Bentham Science - delves into the forefront of Graphene-based carbocatalysis, providing a wealth of factual knowledge and exploration. The book opens with an in-depth analysis of electrocatalysis by Graphene materials, unraveling the intricate relationship between Graphene and electrochemical reactions. It sheds light on the catalytic prowess exhibited by Graphene-based materials, offering promising avenues for advancing energy ...
Aston University wins £1.8m to boost West Midlands low carbon markets
2023-06-09
Aston University and local industry to develop technology to convert organic material into commercially valuable products
Sawdust, diseased trees and dried chicken litter among what can be transformed into sustainable bioproducts
West Midlands companies are invited to join a cluster to develop new low carbon products for growing markets.
Aston University is to receive £1.8 million to transform the West Midlands into a powerhouse of low-carbon product development and commercialisation.
The University will be building on its existing research facilities to lead the region’s Biochar CleanTech Accelerator as part of the West Midlands Innovation Accelerator.
The project ...
Price vs. health: Food shoppers choose price
2023-06-09
Key Takeaways:
When food consumers are properly incentivized, they will choose healthier options.
When financial incentives are removed, consumers are more likely to choose less healthy options by comparison.
BALTIMORE, MD, June 9, 2023 – A new study of food consumer shopping behaviors has found that when faced with a choice – lower prices or healthier foods – they will likely choose lower prices.
The study found that when you give food consumers temporary incentives to buy ...
Advances in eco-friendly gas insulating medium for next-generation SF6-free equipment
2023-06-09
Gas-insulated equipment (GIE) that utilizes the most potent greenhouse gas sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) as insulation and arc-quenching medium has been widely used in the power industry. Seeking eco-friendly insulating gas with advanced performance for next-generation SF6-free GIE is significant for the “net-zero” goal and sustainable development.
A research team led by Xiaoxing Zhang of Hubei University of Technology in China and scientists from Wuhan University, Southeast University, North China Electric Power University, Université de ...
BU/VA doc honored by the American Psychological Foundation
2023-06-09
(Boston)—Jillian C. Shipherd, PhD, a clinical research psychologist at the Women’s Health Sciences Division of the National Center for PTSD at VA Boston Healthcare System and a professor of psychiatry at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has been selected to receive a 2023 American Psychological Foundation (APF) Gold Medal Award for Impact in Psychology. The award recognizes the work of a psychologist or group of psychologists that is impactful, innovative and transformational.
Additionally, Shipherd, along with Sarah E. Valentine, PhD, assistant professor psychiatry at the School, were honored with an Editor’s ...
Wiley and European Hematology Association announce partnership
2023-06-09
HOBOKEN, NJ, USA and THE HAGUE, THE NETHERLANDS – June 9, 2023 – Wiley, one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in research and education, today announced that it will publish the open access journal HemaSphere on behalf of the European Hematology Association (EHA), the largest community of European hematologists, beginning in January 2024.
“Wiley continues to prioritize open access publishing and EHA is a membership organization committed to promoting excellence in patient care through research, and education,” said Shawn Morton, ...
New biracial study finds pre-teen girls that drink fruit juice have better diets with no adverse effect on weight
2023-06-09
Washington, DC – A new study was recently published on-line in Beverages by Dr. Lynn L. Moore, a Professor of Medicine, at the Boston University Chobanian and Avedisian School of Medicine. Moore and her colleagues found that pre-teen girls who drank 100% fruit juice had long term positive dietary benefits with no adverse effect on weight, throughout adolescence, regardless of race.
“While total fruit intake and particularly whole fruit intake may have increased in recent years, among younger children, this is not the case for older children,” said Dr. Moore, “In fact, teens generally consume only about half the recommended ...
Telemedicine visits cut health system employee care costs by nearly 25%
2023-06-09
Visits with a 24/7, co-payment-free telemedicine program established by Penn Medicine for its employees were 23 percent less expensive than in-person visits for the same conditions, according to a new analysis published in the American Journal of Managed Care. Researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found that the per-visit costs for the telemedicine program, called Penn Medicine OnDemand, averaged $380 while in-person encounters in primary care offices, emergency departments, or urgent care clinics during the same timeframe cost $493 to conduct, a $113 difference per patient.
“The conditions most often handled by OnDemand are ...
[1] ... [1878]
[1879]
[1880]
[1881]
[1882]
[1883]
[1884]
[1885]
1886
[1887]
[1888]
[1889]
[1890]
[1891]
[1892]
[1893]
[1894]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.