Essential investment in plant and microbial research in Norwich, UK, confirmed
2023-06-08
Development of an exciting, ground-breaking plant and microbial science and innovation hub can go ahead with confirmation of funding announced today.
The transformational investment will fund new cutting-edge, world-class facilities for the John Innes Centre (JIC) and The Sainsbury Laboratory (TSL) at the heart of the Norwich Research Park. This will deliver a step change in our capability to translate scientific knowledge into bio-based solutions in response to some of society’s most pressing challenges.
As well as transforming the existing capabilities of the John Innes Centre and The Sainsbury Laboratory, both internationally recognised ...
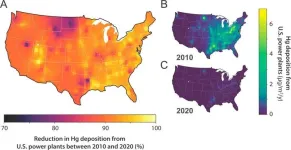
Despite major progress nationally, two mercury emissions hotspots remain
2023-06-07
Missing from partisan political debates over regulations affecting the energy sector is the stunning success of the federal government’s signature environmental laws. A prime example: the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s rules aimed at reducing the harmful effects of hazardous air pollutant (HAP) emissions from fossil fuel-fired power plants known as the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards, or MATS.
A new study from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) shows that in the decade since the standard was ...
What your likes, posts really say about you
2023-06-07
The myriad ways in which we use social media can be grouped into four broad categories, each of which is associated with a cluster of specific personality and behavioral traits, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
“Social media is here to stay, so clarifying how people use social media and raising awareness of these findings are crucial first steps toward ultimately helping people understand how they can avoid the negative aspects of social networking and engage in healthier social media usage,” said Alison B. Tuck, first author of the study and a PhD candidate in clinical psychology in Arts & Sciences.
The study, published online ...
Scientists develop inorganic resins for generating and purifying radium and actinium
2023-06-07
The Science
Targeted alpha therapy can destroy cancerous cells without harming healthy cells. It’s especially useful for treating metastasized cancers. The Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science’s Isotope Program is developing and marketing novel radioactive isotopes for targeted alpha therapy. One method of making one isotope, actinium-225, involves bombarding radium targets with neutrons. This method poses a challenge: how to chemically separate the radium from the actinium. This can destroy typical separation equipment due to a radioactive process called alpha decay. Now, researchers ...
New research: Maybe crying in baseball is a good thing?
2023-06-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – Venturing out of one’s comfort zone to perform a task – and then performing poorly in that task, such as a baseball pitcher trying to hit – can lead to better performance when returning to one’s specialty, according to new research.
Brittany Bond, an assistant professor of organizational behavior in the Cornell School of Industrial and Labor Relations, and Ethan J. Poskanzer of the University of Colorado argue that this phenomenon occurs through a process they call “forced task inferiority,” in which underperformance in tasks outside their specialty frustrates ...
Electronic health records can contain bias, potentially impacting clinical trials
2023-06-07
Results of clinical trials are only as good as the data upon which they rest. This is especially true in terms of diversity — if most people in a trial are from a certain race or socioeconomic group, then the results may not be broadly applicable.
This form of potential bias is not a novel concept. But a group of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues have identified a potential hidden source of bias: electronic health records.
In a recent Contemporary Clinical ...
Yale-led study shows ‘significant overall survival benefit’ when lung-cancer drug is taken after surgery
2023-06-07
New Haven, Conn. — A clinical trial led by Yale Cancer Center shows that the drug osimertinib, a targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer, improved rates of survival and reduced risk of recurrence in patients after surgery.
The results, published June 4 in the New England Journal of Medicine, were presented this week by Dr. Roy Herbst, deputy director of Yale Cancer Center and principal investigator of the ADAURA Phase III clinical trial, during the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Herbst is also assistant dean for translational research, ensign professor of medicine (medical oncology), ...
Temptation at the checkout: 70% of food, drinks within arm’s reach are unhealthy
2023-06-07
We’ve all been there: waiting in line at a store checkout, surrounded by tempting snacks and drinks. Navigating the checkout lane in search of healthy options could be a challenge, according to researchers at the University of California, Davis, who found that 70% of foods and beverages at checkout are unhealthy.
For snack-sized options, an even higher proportion were unhealthy — 89%.
A study published this month in the journal Current Developments in Nutrition suggests most food and beverage options at checkout consist of candy (31%), sugar-sweetened beverages (11%), salty snacks (9%) and sweets (6%).
Healthy ...
Devastating heart condition can be reversed, study shows for the first time
2023-06-07
Three men who had heart failure caused by the build-up of sticky, toxic proteins are now free of symptoms after their condition spontaneously reversed in an unprecedented case described by a team at UCL (University College London) and the Royal Free Hospital.
The condition, a form of amyloidosis affecting the heart, is progressive and has until now been seen as irreversible, with half of patients dying within four years of diagnosis.
The new study, published as a letter in The New England Journal of Medicine, reports ...
DNAmFitAge: Biological age indicator incorporating physical fitness
2023-06-07
“We expect DNAmFitAge will be a useful biomarker for quantifying fitness benefits at an epigenetic level and can be used to evaluate exercise-based interventions.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 7, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 10, entitled, “DNAmFitAge: biological age indicator incorporating physical fitness.”
Physical fitness is a well-known correlate of health and the aging ...
Now is already too late – The European and international endocrine community calls for immediate action on chemicals legislation is the only way forward to address Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals
2023-06-07
Brussels, Belgium 7 June 2023 – The call for action reverberated across the halls of the European Parliament as a diverse group of scientists, policy makers and interest organisations gathered in a packed room, to discuss how to address the gaps between science and legislation and "Shape an ambitious legislative framework for endocrine disruptors."
“Through such meetings with experts, we as policy makers can obtain valuable insight into the latest available science and benefit from it in our legislative ...
Trouble falling asleep, staying asleep linked to increased risk of stroke
2023-06-07
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have insomnia symptoms such as trouble falling asleep, staying asleep and waking up too early, may be more likely to have a stroke, according to a study published in the June 7, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. In addition, researchers found the risk was much higher in people under 50 years old. The study does not prove that insomnia symptoms cause stroke; it only shows an association.
“There are many therapies that can help people improve the quality of their sleep, so determining which sleep ...
Seizures while driving and why it’s important to diagnose epilepsy ASAP
2023-06-07
MINNEAPOLIS – Prior to being diagnosed with epilepsy, 5% of people with a type of epilepsy called focal epilepsy had a seizure while driving, according to a new study published in the June 7, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Focal epilepsy accounts for more than half of all cases of epilepsy. People with this form of epilepsy have recurring seizures that affect one half of the brain.
“Seizures while driving pose substantial risks for those experiencing them and for others ...
Creating less-allergenic shrimp using pressure and steam
2023-06-07
With the start of summer, many people will be firing up their grills and roasting everything from hot dogs to steaks. Shrimp won’t be on the menu for millions of Americans with seafood allergies, though a method reported in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry could change that. The researchers say that reverse-pressure sterilization can produce a less-allergenic shrimp product that, when tested in mice sensitive to the crustaceans, did not cause severe reactions.
Some of the most common foods that people are allergic to are dairy products, wheat, peanuts and seafood. The immune system mistakes some proteins from these foods for an intruder and ...
Mechanical engineers lend fresh insight into battery-based desalination technology
2023-06-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — To achieve more effective saltwater desalination, mechanical engineers focused on fluid movement rather than new materials in a new study. By adding microchannels to the inside of battery-like electrodes made of Prussian blue – an intense blue pigment often used in art that also has special chemical properties – researchers increased the extent of seawater desalination five times over their non-channeled counterparts to reach salinity levels below the freshwater threshold.
The study, led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign ...
Alcohol drinking cut in half with diabetes medication
2023-06-07
Semaglutide is sold under brand names such as Ozempic. Since this medication was also approved for the treatment of obesity, demand has increased, which has resulted in difficulties in procuring the drug in recent times. There is anecdotal evidence of patients with obesity or diabetes saying that their craving for alcohol has lessened since they started taking the drug.
Today, individuals with alcohol dependence are treated with a combination of various psychosocial methods and medications. Four approved medications are available. Since alcohol dependence is a disease with many causes, the efficacy of these medications varies, and so it is important that we develop additional treatment medications.
Reduced ...
Detection dog can sniff out highly-endangered great crested newts
2023-06-07
A trained detection dog was highly accurate at finding great crested newts underground or at a distance, which might aid conservation efforts for this highly-endangered species, according to a study published June 7, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Nicola Jayne Glover from the University of Salford, UK, and colleagues.
The highly-endangered great crested newt (Triturus cristatus) is a species of special conservation concern across the UK and central and northern Europe. While much is known about the great crested newts’ aquatic life phase, comparatively little is known about their terrestrial ...
Paris will host the 25th International Conference of the Redox Medicine Society with 61 communications this June in Paris
2023-06-07
The 25th International Conference on Redox Medicine 2023 which will be held in Paris on June 1-2 will welcome 61 communications (major, short and poster presentations), and gather international in-person and virtual participants from 31 countries.
Redox Medicine 2023: What are the recent advances and perspectives?
On its 25th anniversary, Redox Medicine 2023 will be held to bring together academic and industry experts in redox to discuss advances and recent innovation in this vast field.
The new president of the Redox Medicine Society, Dr. Carole Nicco, Université ...
Ancient genomes show that the farming lifestyle in northwestern Africa was ignited by oversea-migrants from Iberia 7,400 years ago
2023-06-07
A genomic analysis of ancient human remains from Morocco in northwest Africa revealed that food production was introduced by Neolithic European and Levantine migrants and then adopted by local groups. A research team from Sweden, Spain and Morocco present their results in Nature on June 7th.
In northwestern Africa, lifestyle transitioned from foraging to farming some 7,400 years ago, but what sparked that change remained unclear. Previous studies support conflicting views: that migrant European Neolithic farmers brought the new way of life to North Africa, or that local hunter-gatherers adopted farming practices.
“We found a remarkable population continuity ...
Calculation shows why heavy quarks get caught up in the flow
2023-06-07
UPTON, NY—Using some of the world’s most powerful supercomputers, a group of theorists has produced a major advance in the field of nuclear physics—a calculation of the “heavy quark diffusion coefficient.” This number describes how quickly a melted soup of quarks and gluons—the building blocks of protons and neutrons, which are set free in collisions of nuclei at powerful particle colliders—transfers its momentum to heavy quarks.
The answer, it turns out, is very fast. As described in a paper just published in Physical Review Letters, the momentum transfer from the “freed up” ...
Bilingual, digital health tool helps reduce alcohol use, UC Irvine-led study finds
2023-06-07
Irvine, Calif., June 7, 2023 –– An automated, bilingual, computerized alcohol screening and intervention health tool is effective in reducing alcohol use among Latino emergency department patients in the U.S., according to a study led by the University of California, Irvine.
“This is the first bilingual, large-scale, emergency department-based, randomized clinical trial of its kind in the country focused on English- and Spanish-speaking Latino participants,” said lead author Dr. Federico Vaca, UCI professor of emergency medicine. “Our aim was to overcome well-known barriers to alcohol screening and intervention from the emergency department while ...
Value of chemotherapy post immunotherapy in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer
2023-06-07
“[...] large multicenter prospective randomized trials are needed to provide the clinical evidence for the use of [chemotherapy] in second line and third-line post [immunotherapy] failure.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 7, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 26, 2023, entitled, “Value of chemotherapy post immunotherapy in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).”
Lung cancer is the number one cause of mortality among all types of cancer worldwide. Its ...
Pioneer of multicore processor design receives the ACM-IEEE CS Eckert-Mauchly Award
2023-06-07
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today announced that Kunle Olukotun, a Professor at Stanford University, is the recipient of the ACM-IEEE CS Eckert-Mauchly Award for contributions and leadership in the development of parallel systems, especially multicore and multithreaded processors.
In the early 1990s, Olukotun became a leading designer of a new kind of microprocessor known as a “chip multiprocessor”—today called a “multicore processor.” His work demonstrated the performance advantages of multicore processors ...
Using genomics to unlock the full potential of industrial hemp
2023-06-07
Plant biologist Alex Harkess, PhD, and his lab at HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology are on a mission to change the future of food and fiber crops, one flowering plant species at a time. Much of plant breeding and global food production relies on the pollination of flowers to produce fruits that are eaten and used to produce further progeny. This process might sound straightforward, but it is actually complicated by the fact that some flowers contain only male or female reproductive organs, others contain both (hermaphrodites), and some can even switch sexes.
How flowers become male, ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for June 7, 2023
2023-06-07
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a molecularly driven Phase I trial of the ATR inhibitor camonsertib, an artificial intelligence model to predict immunotherapy responses in lung cancer, an analysis of cognitive and functional outcomes following treatment ...
[1] ... [1870]
[1871]
[1872]
[1873]
[1874]
[1875]
[1876]
[1877]
1878
[1879]
[1880]
[1881]
[1882]
[1883]
[1884]
[1885]
[1886]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.