SwRI’s Dr. Natalie Smith receives ASME Dedicated Service Award
2023-06-12
“It is an honor,” Smith said. “The ASME Turbo Expo community has been a valuable part of my professional development and it has been a pleasure to give back." Since joining SwRI in 2016, Smith has performed aerodynamic design and testing of turbomachinery and advanced system analysis for programs related to power generation, aviation, oil and gas, and energy storage, including next-generation supercritical carbon dioxide power cycles.
Smith has also managed three long-duration energy storage projects, developing a pumped thermal energy storage (PTES) demonstration facility, conducting a techno-economic feasibility study of ...
Press registration open for hybrid ACS Fall 2023 meeting
2023-06-12
Journalists who register for the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS) will have access to about 12,000 presentations on topics including agriculture and food, energy and fuels, health and medicine, sustainability and more. ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person in San Francisco on Aug. 13-17 with the theme “Harnessing the Power of Data.”
ACS considers requests for press credentials and complimentary registration to meetings from reporters (staff and freelance) and public information officers at government, nonprofit and ...
Loneliness, insomnia linked to work with AI systems
2023-06-12
Employees who frequently interact with artificial intelligence systems are more likely to experience loneliness that can lead to insomnia and increased after-work drinking, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers conducted four experiments in the U.S., Taiwan, Indonesia and Malaysia. Findings were consistent across cultures. The research was published online in the Journal of Applied Psychology.
In a prior career, lead researcher Pok Man Tang, PhD, worked in an ...
FAU awarded $1.5 million teaching grant for adults with intellectual disabilities
2023-06-12
Florida Atlantic University’s College of Education has received a three-year $1.5 million grant through the Florida Center for Students with Unique Abilities (FCSUA) for the FAU Academy for Community Inclusion. The funds will help sustain the academy, an approved Florida Postsecondary Comprehensive Transition Program (FPCTP) that serves the community through continuing employment and independent living skills opportunities for adults with intellectual disabilities.
Unemployment and under-employment for people with intellectual disabilities far exceed the norm – less than 10 percent of adults with intellectual ...
Many long COVID patients suffer from persistent inflammation, study finds
2023-06-12
An overactive inflammatory response could be at the root of many long COVID cases, according to a new study from the Allen Institute and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center.
Looking at proteins circulating in the blood, the scientists found a set of molecules associated with inflammation that were present only in a subset of patients with long COVID and were not seen in those who recovered from their disease. The researchers published an article describing their findings in the journal Nature Communications today.
Out of 55 patients with long ...
All-electric rideshare fleet could reduce carbon emissions, increase traffic issues
2023-06-12
Two major ridesharing companies have promised all-electric fleets by 2030 in an effort to reduce their carbon footprint. To understand additional impacts of this transition, researchers reporting in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology conducted life-cycle comparisons of battery-powered electric vehicle fleets to a gas-powered one, using real-world rideshare data. They found up to a 45% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from full electrification; however, traffic problems and air pollution could increase.
Ridesharing apps are an increasingly popular way to travel around urban areas, ...
Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprinting
2023-06-12
Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprinting
UMC Utrecht researchers propose solutions for bioprinting living tissue
Bioprinting is the printing of living cells and tissues. It's a promising technique that hopefully, one day, can solve the organ donor shortage by growing organs from patients' own cells. However, printing living tissues and cells is extremely complicated, and many hurdles need to be overcome to be able to get there. In this article, three recent innovations ...
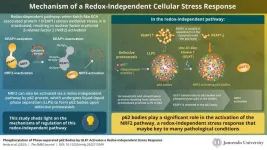
Insights into redox-independent cellular stress response
2023-06-12
Cellular stress, or oxidative stress, occurs when there is a buildup of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which interferes with cellular mechanisms and can even cause damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA. Owing to their destructive nature, all cells have robust mechanisms in place to remove ROS and reduce oxidative stress. One such mechanism is the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2)-mediated stress response, where NRF2 is a master transcription factor that aids in reducing oxidative stress.
Much is known about the redox-dependent activation of NRF2 and its subsequent role in stress response. In this pathway, ...
Chronic exposure to lead, cadmium and arsenic increases risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-06-12
Statement Highlights:
Around the world, most people are regularly exposed to low or moderate levels of lead, cadmium and arsenic in the environment, increasing risk of coronary artery disease, stroke and peripheral artery disease, according to a new American Heart Association statement.
These metals, considered contaminant metals, have no function in the human body. They are found in groundwater, water pipes, paint, tobacco products, fertilizer, plastic, electronics, gasoline, batteries, some foods and other commonly used items.
Lead, ...
Which women should receive more than mammograms to screen for breast cancer?
2023-06-12
Study’s findings point to the importance of considering other risk factors beyond breast density.
Dense breast tissue, which contains a higher proportion of fibrous tissue than fat, is a risk factor for breast cancer and also makes it more difficult to identify cancer on a mammogram. Many states have enacted laws that require women with dense breasts to be notified after a mammogram, so that they can choose to undergo supplemental ultrasound screening to improve cancer detection. A recent study published ...
Twenty species of sea lettuce found along the Baltic and Scandinavian coasts
2023-06-12
The number of species of the green alga sea lettuce in the Baltic Sea region and Skagerak and is much larger than what was previously known. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have surveyed 10,000 kilometres of coast and found twenty species of sea lettuce.
Green macroalgae of the genus Ulva, also known as sea lettuce, are almost ubiquitous in the wider Baltic Sea region and and can be found from the Atlantic waters all the way up to the Bay of Bothnia in the Baltic Sea. Sea lettuce reproduce easily and grow ...
Cancer diagnoses dropped sharply in Alberta during COVID-19 response
2023-06-12
Pandemic restrictions corresponded with a significant drop in diagnoses of breast, colorectal and prostate cancers as well as melanoma, according to a new Alberta study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221512.
"The sweeping and unprecedented measures enacted at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Alberta had an inevitable impact on cancer care," writes Dr. Darren Brenner, an epidemiologist in Calgary, Alberta, and associate professor at the University of Calgary's Cumming School of Medicine, with coauthors. "Even though treatment and urgent surgeries for cancers were prioritized ...
Canada’s carbon pricing poses a $256 billion financial risk for borrowers and banks
2023-06-12
By putting a price on the cost of carbon, the Government of Canada aims to curtail greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, but it comes with an increased risk for financial lenders and borrowers with high carbon emissions.
In a first-of-its-kind study, University of Waterloo researchers analyzed the effects of Canada’s carbon price regime on the economy. The results indicate that as carbon costs rise, high-emitting carbon industries such as mining and energy are at the greatest risk of default, with total assets of $256 billion at risk of being lost and almost a quarter ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers uncover new insights into why individuals are affected differently by COVID-19 infection
2023-06-12
Abu Dhabi, UAE (June 12): A team of researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi, led by Associate Professor of Biology Youssef Idaghdour and working in collaboration with clinicians at several Abu Dhabi hospitals, investigated the association between microRNAs, a class of small RNA molecules that regulate genes, and COVID-19 severity among 259 unvaccinated COVID-19 patients living in Abu Dhabi. The team identified microRNAs that are associated with a weakened immune response and admission to ICU.
During this process, ...
Vaccine against deadly chytrid fungus primes frog microbiome for future exposure
2023-06-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A human or animal’s microbiome — the collection of often beneficial microorganisms, including as bacteria and fungi, that live on or within a host organism — can play an important role in the host’s overall immune response, but it is unclear how vaccines against harmful pathogens impact the microbiome. A new study led by researchers at Penn State found that a new vaccine against the deadly chytrid fungus in frogs can shift the composition of the microbiome, making frogs more resilient to future exposure to the ...
Should robots be given a human conscience?
2023-06-12
Modern-day society relies intrinsically on automated systems and artificial intelligence. It is embedded into our daily routines and shows no signs of slowing, in fact use of robotic and automated assistance is ever-increasing.
Such pervasive use of AI presents technologists and developers with two ethical dilemmas – how do we build robots that behave in line with our values and how to we stop them going rogue?
One author suggests that one option which is not explored enough is to code more humanity into robots, gifting robots with traits such as empathy and compassion.
Is ...
Research brings hope for early treatment of brain degeneration in ‘children of the night’
2023-06-12
Glasgow, UK: Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare and devastating genetic disorder characterised by an inability to repair skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. As a result, patients with XP develop skin cancers, usually in childhood. Once diagnosed, they can be protected by avoiding sunlight (hence sometimes being called ‘children of the night’), wearing special clothing and sunglasses, and using sunscreen. But some will also develop neurodegenerative conditions such as hearing loss, loss of intellectual function, poor co-ordination and seizures. Finding out why this is, and which ...
Polygenic risk scores could improve colorectal cancer screening
2023-06-12
Glasgow, UK: Rates of colorectal cancer are high despite widespread adoption of screening programmes in many high-income European countries. Such programmes tend to use a one-size-fits-all approach where most people are screened starting from the same age, and no individual factors are considered in organised population screening. Now, based on one of the largest genomics studies on the topic to date, researchers from Finland have outlined how common genetic factors could be used to identify individuals at high risk of developing the disease and hence improve current colorectal screening strategies.
Max Tamlander, MD at the Institute ...
Results from first randomised controlled trial of genetic counselling for familial and inherited colorectal cancer show significant improvements in patient empowerment
2023-06-11
Glasgow, UK: Genetic counselling is essential when dealing with individuals who are affected by, or at risk of, inherited disease. Although it is known to be useful in helping patients cope with test results and deal with uncertainty, there have been very few randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of its effectiveness. Dr Andrada Ciuca, a post-doctoral researcher at Babes-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, will tell the annual conference today (Sunday 11 June) that the results of the first RCT of genetic counselling in familial colorectal cancer (fCRC) show that it provided significant ...
Blood biomarkers plus genomics predict common disease risk more accurately than genomic information alone
2023-06-10
Glasgow, UK: Being to identify people at high risk of chronic disease means that they can be targeted with prevention measures before they become sick. Polygenic risk scores, where genomic information alone is used to assess the risk of developing diseases, have been receiving a lot of attention recently, but research to be presented at the annual conference of the European Society of Human Genetics today (Saturday 10 June) suggests that combining blood biomarkers with genomic information gives more accurate, cost-effective results.
Dr Jeffrey Barrett, Chief Scientific Officer, Nightingale Health, Helsinki, ...
The use of AI in eye scans helps improve diagnosis of inherited disease of the retina
2023-06-10
Glasgow, UK: Inherited retinal diseases (IRDs), single-gene disorders affecting the retina, are very difficult to diagnose since they are uncommon and involve changes in one of many candidate genes. Outside specialist centres, there are few experts who have adequate knowledge of these diseases, and this makes it difficult for patients to access proper testing and diagnosis. But now, researchers from the UK and Germany have used artificial intelligence (AI) to develop a system that they believe will enable more widespread provision of testing, together with improved efficiency.
Dr ...
University of Tennessee, Knoxville, partners on multi-university NSF Engines Development Award
2023-06-09
The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, is partnering with other Southeastern universities in a coalition exploring methods for driving U.S. economic competitiveness. The initiative is supported by a two-year, Type 1 Development Award worth $1 million, funded by the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Regional Innovation Engines. The team was one of only 44 out of 497 Type-1 applications the NSF funded, marking the first time the NSF has distributed Regional Innovation Engines grants.
Thomas Goldsby, Dee and Jimmy Haslam Chair in Logistics at UT’s Haslam College of Business Department of Supply Chain Management, ...
The future of industrial chemicals: OU engineers seek more efficient processes
2023-06-09
A study by a team of University of Oklahoma researchers has been featured in Cell Reports Physical Science, an open-access journal highlighting cutting-edge research in the physical sciences.
The study, “Cooperative roles of water and metal-support interfaces in the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde over cobalt boride catalysts,” explores the role of water in the selective hydrogenation of carbonyl over alkene bonds. Utilizing cobalt and cobalt boride catalysts, OU researchers analyzed the hydrogenation ...
Jiu Jitsu club stage physical assaults to help advance forensic research
2023-06-09
Researchers from Northumbria University and King’s College London have published findings outlining the extent that textile fibres transfer during controlled assault scenarios.
Their work, recently published in the academic journal Science & Justice, is the first time the number of fibres transferred between garments during physical assaults has been assessed by simulating the act with real people through Northumbria University’s Jiu Jitsu club.
Dr Kelly Sheridan, Assistant Professor of Forensic Science in Northumbria’s Department of Applied Sciences, believes the findings will ...
University of Chicago mathematician Vladimir Drinfeld wins prestigious Shaw Prize
2023-06-09
Vladimir Drinfeld, the Harry Pratt Judson Distinguished Service Professor of Mathematics at the University of Chicago, is one of two recipients of the prestigious Shaw Prize in Mathematical Sciences for 2023.
He shares this year’s honor jointly with Shing-Tung Yau of Tsinghua University for their “contributions related to mathematical physics, to arithmetic geometry, to differential geometry and to Kähler geometry.”
The Shaw Prize honors individuals who have recently achieved distinguished and significant advances in the fields of astronomy, life science and medicine, and mathematical sciences. Each category carries a monetary award of ...
[1] ... [1864]
[1865]
[1866]
[1867]
[1868]
[1869]
[1870]
[1871]
1872
[1873]
[1874]
[1875]
[1876]
[1877]
[1878]
[1879]
[1880]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.