Researchers reveal mechanism of protection against breast and ovarian cancer
2023-06-21
In a new paper published today in Nature, researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have outlined the structure and function of a protein complex which is required to repair damaged DNA and protect against cancer.
Every time a cell replicates, mistakes can happen in the form of mutations, but specialised proteins exist to repair the damaged DNA.
People with mutations in a DNA repair protein called BRCA2 are predisposed to breast, ovarian and prostate cancers, which often develop at a young age. In the clinic, these cancers are treated with a drug that inhibits PARP, ...
Atoms realize a Laughlin state
2023-06-21
The discovery of the quantum Hall effects in the 1980's revealed the existence of novel states of matter called "Laughlin states", in honor of the American Nobel prize winner who successfully characterized them theoretically. These exotic states specifically emerge in 2D materials, at very low temperature and in the presence of an extremely strong magnetic field. In a Laughlin state, electrons form a peculiar liquid, where each electron dances around its congeners while avoiding them as much as possible. Exciting such a quantum liquid generates collective states that physicists associate to fictitious particles, whose ...
Ovarian cancer study identifies key genes for potential treatments
2023-06-21
New research is increasing our understanding about why some women with the most lethal form of ovarian cancer respond much better to treatment than others.
Researchers at Imperial College London have confirmed that the tumours of some women with high-grade serious ovarian cancer (HGSOC) contain a type of lymphoid tissue – known as tertiary lymphoid structures, or TLS – and that the presence of this tissue gives women a significantly better prognosis. They have also identified genes in HGSOC ...
Detection of an echo emitted by our Galaxy's black hole 200 years ago
2023-06-21
An international team of scientists has discovered that Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*)1, the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way, emerged from a long period of dormancy some 200 years ago. The team, led by Frédéric Marin2, a CNRS researcher at the Astronomical Strasbourg Observatory (CNRS/University of Strasbourg), has revealed the past awakening of this gigantic object, which is four million times more massive than the Sun. Their work is published in Nature on 21 June. Over a period of one year at the beginning of the 19th century, the black ...
Study hints at how cancer immunotherapy can be safer
2023-06-21
New Haven, Conn. — Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment of many forms of cancer by unleashing the immune system response against tumors. Immunotherapies that block checkpoint receptors like PD-1, proteins that limit the capacity of T cells to attack tumors, have become the choice for the treatment of numerous types of solid cancer.
However, the introduction of PD-1-blocking agents can often result in T cells attacking healthy tissues in addition to cancer cells, causing severe, sometimes life-threatening, side effects that can blunt the benefits of immunotherapy.
A new study published by researchers ...
Drug-resistant fungi are thriving in even the most remote regions of Earth
2023-06-21
New McMaster research has found that a disease-causing fungus — collected from one of the most remote regions in the world — is resistant to a common antifungal medicine used to treat infections.
The study, published today in mSphere, showed that seven per cent of Aspergillus fumigatus samples collected from the Three Parallel Rivers region in Yunnan, China were drug resistant.
Perched 6,000 metres above sea level and guarded by the staggering glaciated peaks of the Eastern Himalayas, the region is sparsely populated and undeveloped, which makes the presence of antimicrobial-resistant strains of A. fumigatus all the more striking for Jianping Xu, ...
Direct photons point to positive gluon polarization
2023-06-21
UPTON, NY— A new publication by the PHENIX Collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) provides definitive evidence that gluon “spins” are aligned in the same direction as the spin of the proton they’re in. The result, just published in Physical Review Letters, provides theorists with new input for calculating how much gluons—the gluelike particles that hold quarks together within protons and neutrons—contribute to a proton’s ...
Mutant KRAS regulates Y chromosome gene in colorectal cancer, driving metastasis and inhibiting anti-tumor immunity
2023-06-21
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have uncovered a gene on the Y chromosome that is upregulated in KRAS-mutated colorectal cancer (CRC), increasing tumor cell invasiveness and reducing anti-tumor immunity in male patients.
The preclinical study, published today in Nature, provides novel insights into the longstanding mystery of molecular and cellular mechanisms that drive increased metastasis and poor prognosis in men with CRC. The results highlight the Y chromosome gene KDM5D, which codes for an epigenetic enzyme, as a potential therapeutic target and uncover ...
Conservation policies risk damaging global biodiversity, researchers argue
2023-06-21
‘Green’ farming policies may accelerate global biodiversity loss, two leading academics have warned.
Rewilding, organic farming and the ‘nature friendly farming’ measures included in some government conservation policies risk worsening the global biodiversity crisis by reducing how much food is produced in a region, driving up food imports and increasing environmental damage overseas.
In an article published today in the journal Nature, Professor Ian Bateman of the University of Exeter and Professor Andrew Balmford of the University of Cambridge urge policy-makers to consider a bolder approach known as ...
Stellenbosch University selects Symplectic Elements to support and streamline research outputs submissions to the DHET
2023-06-21
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Stellenbosch University (SU) has selected Symplectic Elements from Digital Science’s flagship products to support its goal of advancing knowledge in service of society.
Symplectic Elements will provide SU with a Researcher Profiles and Research Outputs Management Solution, supporting and streamlining DHET (Department of Higher Education and Training) submissions and providing a public profiling system for its researchers.
SU is one of South Africa’s leading tertiary institutions, and is recognised internationally ...
Study proposes simple low-cost solutions to improve thermal comfort in social housing
2023-06-21
Brazil has a housing deficit of 5.876 million units (5.044 million in urban areas and 832,000 in rural areas), according to the latest government survey. The number corresponds to 8.1% of the nation’s total stock of private dwellings, permanent and improvised. To make good at least part of this huge social debt, the federal government launched a low-income housing program called Minha Casa Minha Vida (“My Home My Life”) in 2009.
However, funding was insufficient to meet demand of this size, and low investment allocated to construction of each unit resulted in problems such as lack of thermal comfort, a constant ...
National SFIREG meeting hosted at West Tennessee AgResearch and Education Center
2023-06-21
You may not think about the registration, distribution, sale and use of pesticide products that help control insects, weeds and diseases, but a lot of people in state and federal government do. They meet annually to discuss developments that can affect your health daily. From June 5-7, the State Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) Issues Research and Evaluation Group (SFIREG) hosted their national annual in-person meeting at the University of Tennessee’s West Tennessee AgResearch and Education Center in Jackson. ...
Equity in computer science impossible without review of curriculum, say researchers
2023-06-21
England’s girls and other underrepresented groups are at risk of being failed by the current computing curriculum, which excludes their interests, according to new research published recently.
A study by University of Reading, in partnership with Kings College London, published in the International Journal of Science Education, found the current school system creates a gender imbalance in computer science that is reflected in the workplace. The solution, they say, could ...
Blood pressure drug could prevent posttraumatic headaches
2023-06-21
A study led by VA Puget Sound Health Care System researchers has shown that prazosin, a drug used to treat high blood pressure, can prevent posttraumatic headaches.
Senior study author Dr. Murray Raskind, director of the VA Northwest Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center in Seattle, Washington, explained that few treatment options exist for this type of headache.
“Persistent posttraumatic headaches are the most common long-term consequence of mild traumatic brain injuries (concussions) in Veterans and active-duty service members, causing substantial distress ...
Ketone supplements worsen performance in trained endurance athletes, researchers find
2023-06-21
Hamilton, ON, June 21, 2023 – Kinesiologists at McMaster University have found ketone supplements, used by some athletes hoping to cross the finish line faster, may in fact worsen performance.
The new study, published in the latest print edition of the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, tackles contradictory research findings related to the effectiveness of ketone supplements, which have gained popularity among athletes seeking a competitive advantage.
Some previously published studies had shown the supplements improve performance, while others have reported they had no effect or even worsened performance.
Natural ketones can ...
Exoplanet may reveal secrets about the edge of habitability
2023-06-21
ITHACA, N.Y. – How close can a rocky planet be to a star, and still sustain water and life? A recently discovered exoplanet may be key to solving that mystery.
“Super-Earth” LP 890-9c (also named SPECULOOS-2c) is providing important insights about conditions at the inner edge of a star’s habitable zone and why Earth and Venus developed so differently, according to new research led by Lisa Kaltenegger, associate professor of astronomy at Cornell University.
Her team found LP 890-9c, which orbits close to the inner ...
The art and science of living-like architecture
2023-06-21
“This technology is not alive,” says Laia Mogas-Soldevila. “It is living-like.”
The distinction is an important one for the assistant professor at the Stuart Weitzman School of Design, for reasons both scientific and artistic. With a doctorate in biomedical engineering, several degrees in architecture, and a devotion to sustainable design, Mogas-Soldevila brings biology to everyday life, creating materials for a future built halfway between nature and artifice.
The architectural technology she describes is unassuming ...
Phone communication spurs a cascading effect on social influence
2023-06-21
AUSTIN, Texas – Social influence from phone communications is significant, reaching as far as four degrees of separation from the original caller, according to a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, who developed a new framework to more precisely study the phenomenon.
The researchers created a framework that distinguishes between people behaving in similar ways because of peer influence or because they’ve sought out friends with similar behaviors and beliefs. It’s an important distinction to make for marketing and public health agencies looking to effectively ...
New findings show mitochondrial DNA fragments in blood as important biomarkers for aging and inflammation
2023-06-21
In an eight-year study of more than 600 community-dwelling older adults, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have further linked levels of cell-free DNA (DNA fragments resulting from cell death) circulating in the blood to chronic inflammation and frailty. The study is novel and expands on previous work, the investigators say, because it focused on mitochondrial DNA rather than solely genomic DNA, as previously reported in October 2022.
The new findings, published May 23 in Immunity ...
Engineers “strike gold” with innovation that recovers heavy metals from biosolids
2023-06-21
Engineers in Melbourne have developed a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to remove heavy metals, including copper and zinc, from biosolids.
The team’s work, led by RMIT University in collaboration with South East Water and Manipal University in India, advances other methods for heavy-metal removal by recycling the acidic liquid waste that is produced during the recovery phase, instead of throwing it away.
Lead senior researcher Professor Kalpit Shah from RMIT said the heavy metals found in biosolids ...
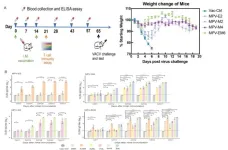
Multi-valent mRNA vaccines against monkeypox enveloped or mature viron surface antigens for enhanced protection
2023-06-21
A team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology have made significant progress in developing multi-valent mRNA vaccines against monkeypox virus (MPV), the agent that can cause smallpox-like disease in humans. Their study showed the multi-valent mRNA vaccines with different combinations of monkeypox enveloped viron (EV) or mature viron (MV) surface antigens induced dynamic immune responses with a robust IgG response and correlating neutralizing activities. The ...
People who develop diabetes after pregnancy are less likely to regain control of blood sugar if they had gestational diabetes
2023-06-21
People who develop diabetes following pregnancy were significantly less likely to be able to bring it under control if they had experienced gestational diabetes during their pregnancy, especially if they were Black or Hispanic, according to a Mount Sinai study published on June 21 in the journal Diabetes Care.
The study also found that people who experienced gestational diabetes were more than 11 times as likely as those whose pregnancies did not involve gestational diabetes to develop diabetes within nine years after delivery.
The researchers, from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, found that the ...
Helping ‘good’ gut bacteria and clearing out the ‘bad’ — all in one treatment
2023-06-21
Probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome or restore populations of “good bacteria” after a heavy course of antibiotics. But now, they could also be used as an effective treatment strategy for certain intestinal diseases, such as Crohn’s disease. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a microgel delivery system for probiotics that keeps “good” bacteria safe while actively clearing out “bad” ones. In mice, the system treated intestinal inflammation without side effects.
In the digestive system, there’s a delicate balance of bacterial populations. ...
FDA grants de novo clearance to Tristel ULT™ as a high-level disinfectant for ultrasound applications
2023-06-21
FAIRFIELD, NJ—Parker Laboratories Inc., a worldwide leader in ultrasound supplies and accessories, has announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted clearance for a unique disinfecting foam, called Tristel ULT, as a high-level disinfectant for ultrasound probes used within body cavities and for skin-surface transducers.
Tristel ULT is manufactured and distributed for US markets by Parker Laboratories under an exclusive commercial partnership with UK-based Tristel plc (AIM: TSTL). Tristel ULT is a high-level disinfectant using a proprietary ...
Banks still offer Black entrepreneurs inferior loans, service even when they are better qualified than peers
2023-06-21
Nearly a decade ago, researchers from Brigham Young University, Utah State University and Rutgers published a disheartening study revealing how discrimination in bank loan services was tainting the American Dream for minority entrepreneurs.
Unfortunately, even in 2023, not much has changed. A newly published paper from this core group of authors finds banks still offer Black customers inferior loan products and service, even when those Black customers have objectively stronger financial profiles and FICO ...
[1] ... [1857]
[1858]
[1859]
[1860]
[1861]
[1862]
[1863]
[1864]
1865
[1866]
[1867]
[1868]
[1869]
[1870]
[1871]
[1872]
[1873]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.