Hip fracture burden to nearly double worldwide by 2050
2023-06-15
An international group of researchers led by the Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), and including Douglas P Kiel, MD, MPH, Director Musculoskeletal Research Center, Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife, and Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, evaluated the secular trends in hip fracture incidence, treatment patterns following a hip fracture, and all-cause mortality in 19 countries and regions from 2005 to 2018. While the age- and sex-standardised hip fracture incidence rates decreased ...
Research findings „Study on Adult Learning and Education“
2023-06-15
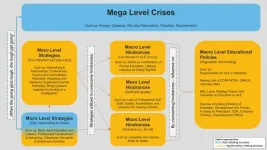
From August 2022 until October 2022, interviews with 25 experts from the selected countries were conducted and then analyzed trough a Ground Theory approach. From this, a model emerged, showing how factors and actors at different societal levels - mega, macro, meso and micro - interact to shape adult learning and education in different contexts.
Mega level comparisons show that overarching issues such as war and conflict, historical and systemic discrimination, disease and extreme poverty as well as political authoritarianism act both as an impetus and as barriers to ALE activities.
Comparative analysis shows that at the macro level, with ...
New tool uncovers COVID-19 susceptibility mechanism
2023-06-15
Researchers have discovered a mechanism for COVID-19 susceptibility using a newly created tool. The tool, GASPACHO, captures dynamic changes in gene expression along the innate immune response, allowing researchers to identify genes and molecular pathways associated with disease risk that have previously been too complex to detect or interpret.
Using GASPACHO (GAuSsian Processes for Association mapping leveraging Cell HeterOgeneity), researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the National Center for Child Health and Development in Japan, Tel Aviv University and their collaborators have identified a gene variant that affects COVID-19 susceptibility. ...
Jefferson Lab oversight roles filled by DOE
2023-06-15
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has selected Craig Ferguson to lead the Thomas Jefferson Site Office (TJSO) at the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility in Newport News, Va. As TJSO manager, Ferguson will lead in the oversight and contract management of Jefferson Lab. Additionally, Donté Davis has been confirmed as TJSO deputy manager, a role he first stepped into earlier this year.
Ferguson is familiar with Jefferson Lab and its mission, having already served in a leadership role at the lab. In 2005-2008, he was the lab’s associate director for environment, safety, health & quality.
“I am excited to return ...
High-quality child care contributes to later success in science, math
2023-06-15
Children who receive high-quality child care as babies, toddlers and preschoolers do better in science, technology, engineering and math through high school, and that link is stronger among children from low-income backgrounds, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our results suggest that caregiving quality in early childhood can build a strong foundation for a trajectory of STEM success,” said study author Andres S. Bustamante, PhD, of the University of California Irvine. “Investing in quality child care and early childhood education could help ...
Study finds that a small number of teachers effectively double the racial gaps among students referred for disciplinary action
2023-06-15
Washington, June 15, 2023—The top 5 percent of teachers most likely to refer students to the principal’s office for disciplinary action do so at such an outsized rate that they effectively double the racial gaps in such referrals, according to new research released today. These gaps are mainly driven by higher numbers of office discipline referrals (ODRs) issued for Black and Hispanic students, compared to White students. The study, published in Educational Researcher, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research ...
Previously overlooked algae toxin widespread in southern Indian River Lagoon
2023-06-15
Spanning about one-third of Florida’s East coast, the Indian River Lagoon has faced frequent harmful algal blooms in recent years. Among them, Pseudo-nitzschia spp., algae that produces the neurotoxin domoic acid.
Domoic acid can bioaccumulate within food webs, causing sickness and death in higher trophic level organisms such as marine mammals and birds, and have been documented in sea turtles in Florida coastal waters and in bull sharks within the Indian River Lagoon system. In humans, consumption of shellfish contaminated with domoic acid can cause harmful symptoms.
Unlike other harmful algal blooms, Pseudo-nitzschia are not bioluminescent and do not cause water discoloration ...
Amsterdam UMC to lead global hunt for new interventions in the battle against unhealthy behavior
2023-06-15
Chronic diseases (NCDs) are a global health epidemic and almost 80% of them occur in low- and middle-income countries. While the WHO have developed policies to combat chronic diseases, research shows that, in certain regions, they are not having the desired effect, leaving fragile health systems increasingly overwhelmed. In order to combat this, thanks to a Horizon Europe grant, Amsterdam UMC is set to lead a global consortium with the aim of developing interventions that work in practice.
Consortium leader and Professor of Global Migration, Ethnicity and Health at Amsterdam UMC, Charles Agyemang notes that, ...
A ‘pinch’ of mineral salts helps the noncaloric sweeteners go down
2023-06-15
Perfect noncaloric replacements for sugar and high fructose corn syrup just don’t exist yet. For example, some alternatives have a lingering sweet aftertaste and lack a sugar-like mouthfeel, leaving consumers unsatisfied. Now, researchers in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry propose adding blends of nutritionally important mineral salts to make noncaloric sweeteners seem more like the real thing. Taste-testers indicated that these blends gave zero- and low-calorie drinks a better ...
New tracking device to keep better tabs on wolves
2023-06-15
Keeping up with the journeys of wolves and welfare of wild horses has never been easier. With a GPS wildlife tracker powered by an animal's own movements, University of Copenhagen researchers have solved a problem faced by biologists and wildlife managers seeking to track wild animals year after year: dead batteries.
The wolf’s comeback in Europe has preoccupied people all across the continent over the last years. Where is it? What is its range? What does it live on? The only way to get solid answers to these questions is through GPS tracking. In ...
Nearly 1 in 3 Black adults may develop PAD; disparities in care increase amputation risk
2023-06-15
Statement Highlights:
Nearly 1 in 3 Black adults may develop peripheral artery disease (PAD), compared to about 1 in 5 Hispanic or white adults. If amputation is necessary for treatment, Black, Hispanic and American Indian adults experience lower survival rates and worse quality of life after amputation compared to white adults.
Multiple social, economic and health variables contribute to disparities by sex, race and ethnicity in the development, diagnosis and treatment of PAD.
Opportunities to address disparities include greater focus on prevention in health care systems, ...
Mapping the evolution of E. coli’s main virulence factor offers a refined drug target
2023-06-15
This new work focused on a particular subset of E. coli with a specific capsule - the extracellular barrier that surrounds a bacterium - which scientists have called K1. E. coli with this type of capsule are known to cause invasive diseases such as bloodstream or kidney infections, and meningitis in newborns. This is because this particular cover allows them to mimic molecules already present in human tissues and enter the body unnoticed.
The researchers present evidence that targeting the capsule can be used ...
Only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with facial hair trimming ban, new study reveals
2023-06-15
New research published in the CABI journal Human-Animal Interactions has revealed that only 30% of show horse owners surveyed in Australia agreed with a ban on the trimming of facial hair prior to its implementation in July 2022.
The research found that when asked if facial hair trimming should be banned in all equine competitions, most disciplines broadly agreed (60.5% to 84.6%) apart from showing with only 22.9% of respondents agreeing with a ban.
Indeed, some who took part in the research also believed that horses did ...
Chronic wound healing using glass
2023-06-15
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have demonstrated that silver retains antimicrobial activity for longer when it is impregnated into ‘bioactive glass’, and shown for the first time how this promising combination delivers more long-lasting antimicrobial wound protection than conventional alternatives.
Bioactive glasses are a unique class of synthetic biomaterials made from silicone and have been used for some years in bone grafting.
Silver has long been known to prevent or reduce the growth ...
Finding out you’re autistic in later life can be a positive experience
2023-06-15
Receiving an autism diagnosis in your 20, 30s, 40s, 50s or even 60s may seem daunting, but a new study from psychologists in Bath and London finds that the link between the age at which someone gets diagnosed has little bearing on their quality of life.
So-called ‘late diagnosis’ for autism has hit the headlines recently thanks to autism campaigner Christine McGuiness. Whereas autism is usually diagnosed in childhood, it is increasing being diagnosed in adults and especially among women.
Parents often wonder if their child finding out they are autistic earlier or later will have an impact on their lives in the long term. Whilst many people who discover they are autistic as adults ...
Rising rates of benzodiazepine toxicity among young people spark concern
2023-06-15
Toronto, ON, June 15, 2023 – The rate of hospital encounters for benzodiazepine-related toxicity rose by 67 per cent for young adults (aged 19 to 24) and 44 per cent for youth (aged 18 or below) in Ontario between 2013 and 2020, according to a new study from ICES and Unity Health Toronto.
Though there was an overall decline of 7 per cent in the provincial rate of benzodiazepine toxicity, this was largely driven by reductions in rates among people aged 35 years and older.
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety ...
How antelopes under threat from the climate crisis have responded to rising temperatures
2023-06-15
The climate crisis is turning the temperature up all over the world, but in southern Africa, the rise has been particularly concerning. Wild animals dependent on delicate ecosystems which are already dry, so that food and water scarcity limits their ability to cope with increased heat, are at serious risk. Scientists studied the behavior of three different species of antelope with overlapping ranges in Namibia to try to understand how animals of different sizes and behaviors adapt to the heat.
“Even the indigenous wildlife, adapted to hot and arid conditions, shows sensitivity to extreme heat,” said Paul Berry of the University of Potsdam, lead author of the study in ...
Dialogues across language and culture
2023-06-15
Teacher talk seems intuitive – the expert imparts knowledge onto novices, who passively receive expertise like a car or machine receives parts at every station on an assembly line. In reality, an effective teacher in an era of dynamic and higher literacies is less of a factory worker and more of an active negotiator who tries to understand where their students are coming from in order to reach them. The language classroom amplifies this challenge where the negotiation not only centers on the knowledge itself but the means of communication for that knowledge. ...
Access to financial services linked to lower COVID mortality rates
2023-06-15
New research shows that some of the best tools to decrease COVID-19 mortality rates weren’t found in the ER, but rather at the bank.
A study of COVID-19 mortality rates across 142 nations has demonstrated a surprisingly strong link between access to formal financial services and lower COVID-19 mortality rates. In fact, it’s proved to be as strong a predictor of lower COVID-19 death rates as several comorbidities are of higher COVID-19 death rates.
“The reduction is surprisingly large, similar in magnitude to, but opposite in direction from, the mortality risks associated with higher rates of lung cancer and hypertension,” says Todd Watkins, ...
Men died of overdose at 2-3 times greater a rate than women in the U.S. in 2020-2021
2023-06-15
Men were significantly more vulnerable than women to overdose deaths involving opioid and stimulant drugs in 2020-2021, according to a new study analyzing death records data from across the United States. The study found that men had a 2–3 times greater rate of overdose mortality from opioids (like fentanyl and heroin) and psychostimulants (like methamphetamine and cocaine). While it has been known that men use drugs at higher rates than women, the researchers found that this alone does not explain the gap in overdose deaths, noting that biological, behavioral, and social factors likely ...
A marine mystery: Discovering the link between climate change and sea sponge loss
2023-06-15
Sea sponges are essential to marine ecosystems. They play critical roles in the ocean, as they provide shelter and food to a plethora of marine creatures, recycle nutrients by filtering thousands of litres of sea water daily, and are hosts to microbes that may be the key to some of the most pressing medical challenges we face today.
Now, scientists from UNSW have discovered that when a tropical sea sponge is exposed to warmer temperatures, it loses an important microbe, which could explain why the sponge tissue dies. The latest study, published today in ISME Communications, has revealed that by exposing sea sponges ...
International expert panel revises management of concussion in sport for optimal care of athletes at all levels of participation
2023-06-15
Journals from BMJ Press Release:
Embargoed 23:30 hours UK (BST) time Wednesday 14 June 2023
Please click on links for full articles and contact authors direct for further comment - details can be found under Notes for Editors. Please remember to credit the relevant journal - this assures your audience it is from a reputable source.
BRITISH JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE
Externally peer reviewed? Yes
Evidence type: Consensus Statement
Subjects: People
Latest Consensus Statement on Concussion in Sport includes:
-New and updated age appropriate tools to aid identification ...
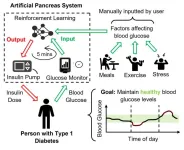
Machine-learning method used for self-driving cars could improve lives of type-1 diabetes patients
2023-06-15
The same type of machine learning methods used to pilot self-driving cars and beat top chess players could help type-1 diabetes sufferers keep their blood glucose levels in a safe range.
Scientists at the University of Bristol have shown that reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning in which a computer program learns to make decisions by trying different actions, significantly outperforms commercial blood glucose controllers in terms of safety and effectiveness. By using offline reinforcement learning, where the algorithm learns from patient records, the researchers improve ...
A plant-based, oral delivery of insulin regulates blood sugar levels similar to natural insulin
2023-06-15
Insulin production has, for the last 50 or so years, come with some risks to the patient. Even so, the medication is lifesaving for the estimated 537 million adults living with diabetes worldwide, with that number expected to grow.
Recent clinical studies show that injection via insulin pens can cause insulin to reach the bloodstream so quickly that hypoglycemia, or blood sugar levels that dip below the healthy range, may result. Automated insulin pumps can deliver precise insulin and minimize this risk but are expensive and available only to a small portion of diabetes patients around the world.
Now, a plant-based, oral delivery of proinsulin could address these drawbacks, ...
Nursing homes serving Black residents have greater hospitalizations, emergency department visits
2023-06-15
Staffing levels likely drive the differences in hospitalizations and emergency department visits among nursing homes, the researchers report in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Studies show that nursing homes serving high proportions of Black residents may experience poor healthcare outcomes. To better understand the environmental and structural characteristics of nursing homes that may lead to these outcomes, the researchers examined data from 14,121 U.S. nursing homes using multiple ...
[1] ... [1854]
[1855]
[1856]
[1857]
[1858]
[1859]
[1860]
[1861]
1862
[1863]
[1864]
[1865]
[1866]
[1867]
[1868]
[1869]
[1870]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.