Research questions value of sagebrush control in conserving sage grouse
2023-06-26
Efforts to improve sage grouse habitat through conventional management practices may be ineffective -- and even counterproductive -- according to research by University of Wyoming and other scientists.
Sagebrush reduction strategies, including mowing and herbicide application, are often employed to enhance habitat for the greater sage grouse and other sagebrush-dependent species. The theory is that clearing large sagebrush shrubs improves food sources in sage grouse nesting and brood-rearing habitats by allowing ...
Study: Potential new treatment identified for liver disease
2023-06-26
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine have led a study to examine a potential new treatment option for patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-related fibrosis.
The results, published in the June 24, 2023, online edition of The New England Journal of Medicine, found that a drug that mimics a hormone in the body improved both liver fibrosis, or scarring of the liver, and liver inflammation in patients with NASH.
“Identifying an effective drug for NASH is extremely promising for patients as currently there are no FDA-approved therapies for this condition,” said Rohit Loomba, MD, the ...
Best papers of 2022 announced by SPIE Journal of Applied Remote Sensing
2023-06-26
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA — The Journal of Applied Remote Sensing (JARS) has honored four of its best papers published in 2022. The awards recognize the journal’s best student paper, as well as papers in interdisciplinary applications, theoretical innovation, and photo-optical instrumentation and design.
JARS is published online in the SPIE Digital Library by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, and optimizes the communication of concepts, information, and progress among the remote-sensing ...
Study finds human impact on wildlife even in protected areas
2023-06-26
HOUSTON – (June 26, 2023) – By 2030, if the 30 by 30 initiative supported by more than 100 countries is successful, 30% of our land and ocean ecosystems will be designated protected areas meant to safeguard biodiversity and help limit the impacts of climate change.
However, a study by Rice University ecologist Lydia Beaudrot and collaborators reports for the first time that tropical mammals living inside protected areas are not spared the effects of human activity even when it occurs outside of the protected boundaries.
Based on the ...
University of Oklahoma researcher to use NSF CAREER Award to study local community's disaster resilience
2023-06-26
University of Oklahoma assistant professor Xiaochen (Angela) Zhang, Ph.D., has received a prestigious Faculty Early Career Development Award, known as a CAREER award, from the National Science Foundation to study how relationships among non-profits, community groups and local government agencies can improve disaster resilience, resource allocation, and emergency management by enabling organizational interactions, rather than top-down responses.
Zhang, who is an assistant professor of public relations for the Gaylord College ...
Research Brief: Investing in nature improves equity, boosts economy
2023-06-26
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (06/26/2023) — A new study shows that current trends in environmental degradation will lead to large economic losses in the coming decades, hitting the poorest countries hardest. But there is hope: investing in nature can turn those losses into gains.
Researchers from the University of Minnesota and Purdue University published their findings in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The team developed a first-of-its-kind, global earth-economy model to capture interactions ...
New geochemistry research confirms megalodon shark was warm-blooded
2023-06-26
William Paterson University PRESS RELEASE
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, JUNE 26, 2023, 3:00 PM EST
WAYNE, NEW JERSEY — A new study shows that the gigantic Megalodon, or megatooth shark, was warm-blooded. This latest research on the Megalodon, which lived in the world’s oceans from 23 million to 3.6 million years ago and measured about 50 feet in length, appears in the peer-reviewed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, conceived of and led by Michael Griffiths ...
Megalodon was no cold-blooded killer
2023-06-26
The largest marine predator that ever lived was no cold-blooded killer.
Well, a killer, yes. But a new analysis by environmental scientists from UCLA, UC Merced and William Paterson University sheds light on the warm-blooded animal’s ability to regulate its body temperature — and might help explain why it went extinct.
After analyzing isotopes in the tooth enamel of the ancient shark, which went extinct about 3.6 million years ago, the scientists concluded the megalodon could maintain a body temperature that was about ...
UCalgary study provides insight into how an infectious parasite uses immune cells as a Trojan Horse
2023-06-26
University of Calgary researchers have discovered how Leishmania parasites hide within the body to cause Leishmaniasis. The tiny parasites are carried by infected sand flies. Considered a tropical disease, one to two million people in more than 90 countries are infected every year. Effects range from disfiguring skin ulcers to enlarged spleen and liver and even death.
This chronic disease has been difficult to detect in the early stages. Scientists realized that the parasite was somehow manipulating immune cells but this process had not been well understood.
“This is the first study that shows how the parasite stalls the process of regular ...
Poop and prey help researchers estimate that gray whales off Oregon Coast consume millions of microparticles per day
2023-06-26
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University researchers estimate that gray whales feeding off the Oregon Coast consume up to 21 million microparticles per day, a finding informed in part by poop from the whales.
Microparticle pollution includes microplastics and other human-sourced materials, including fibers from clothing. The finding, just published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, is important because these particles are increasing exponentially and predicted to continue doing so in the coming decades, according to researchers Leigh Torres and Susanne Brander.
Microparticle pollution is a threat to the health of ...
A smarter way to monitor critical care patients
2023-06-26
Surgical and intensive care patients face a higher risk of death and longer hospital stays because they are susceptible to both hypotension and hemodynamic instability – or unstable blood flow.
These potential complications require round-the-clock monitoring of several cardiac functions by nurses and physicians, but there’s currently no singular, convenient device on the market that can measure the most vital aspects of a patient’s cardiovascular health.
Ramakrishna Mukkamala, professor of bioengineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering, and Aman Mahajan, ...
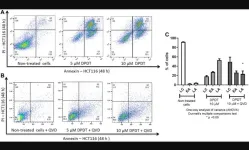
DPDT anticancer activity in human colon cancer HCT116 cells
2023-06-26
“Altogether, our results show that DPDT preferentially targets HCT116 colon cancer cells likely through DNA topoisomerase I poisoning.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 21, 2023, entitled, “Diphenyl ditelluride anticancer activity and DNA topoisomerase I poisoning in human colon cancer HCT116 cells.”
Diphenyl ditelluride (DPDT) is an organotellurium (OT) compound with pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, antigenotoxic and antimutagenic activities when applied at low concentrations. However, ...
Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging announces 2023 fellows
2023-06-26
Chicago, Illinois – The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging recognized ten new SNMMI Fellows today during a plenary session at the society’s 2023 Annual Meeting, held June 24-27. The SNMMI Fellowship was established in 2016 to recognize distinguished service to the society as well as exceptional achievement in the field of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. It is among the most prestigious formal recognitions available to long-time SNMMI members.
In keeping with tradition, SNMMI’s 2022-23 president, Munir Ghesani, MD, FACNM, FACR, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, ...
Purdue-launched solid rocket motor-maker Adranos flies off with Anduril
2023-06-26
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Adranos Inc., a Purdue-originated company that grew from a doctoral project into an impactful company, has been acquired by a major Costa Mesa, California-based defense products company, Anduril Industries.
Terms of the deal were settled, and the acquisition was announced on Sunday (June 25) in The Wall Street Journal that Anduril Industries is to purchase Adranos, manufacturer of solid rocket motors and maker of ALITEC, a high-performance solid rocket fuel that gives greater payload capacity, range and speed to launch systems.
“The success of Adranos is the latest manifestation ...
Webb makes first detection of crucial carbon molecule
2023-06-26
A team of international scientists has used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to detect a new carbon compound in space for the first time. Known as methyl cation (pronounced cat-eye-on) (CH3+), the molecule is important because it aids the formation of more complex carbon-based molecules. Methyl cation was detected in a young star system, with a protoplanetary disk, known as d203-506, which is located about 1,350 light-years away in the Orion Nebula.
Carbon compounds form the foundations of all known life, ...
Despite environmental trade-offs, dairy milk is a critical, low-impact link in global nutrition
2023-06-26
Philadelphia, June 26, 2023 – Along with all global sectors, the dairy industry is working to reduce its environmental impact as we look toward a shared 2050 net zero future. Research is currently focused on greenhouse gas mitigation strategies that do not compromise animal health and production, but many discussions maintain that a radical transformation—involving reducing animal-based foods and increasing plant-based foods—is needed in our agriculture production systems in order ...
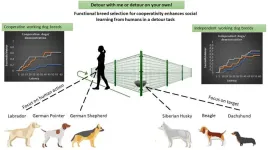
Would you detour with me? – Well, that depends on the dog breed!
2023-06-26
A new study from the Department of Ethology, Eötvös Loránd University, showed that dogs may not equally benefit from observing the ‘helpful action’ of a human demonstrator in the classic detour around a V-shaped fence task.
Those who are experienced with the world of ethological conferences, know all too well that if you present your work about dog behavior, the first (or second) question from the audience will be: “And did you check whether the breed of the dog had an effect on your results?”
Actually, this is not surprising as most people are familiar with the mindboggling variability of hundreds of ...
UCLA researchers uncover potential biomarkers of positive response to immunotherapy
2023-06-26
FINDINGS
Scientists at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have identified potential new biomarkers that could indicate how someone diagnosed with metastatic melanoma will respond to immunotherapy treatment.
The researchers found when T cells are activated, they release a protein called CXCL13, which helps attract more B cells and T cells to the tumor site. The B cells then show the T cells specific parts of the tumor, which leads to increased activation of the T cells and their ability to fight the cancer. This cooperation between T cells and B cells was associated with improved survival in patients diagnosed with metastatic melanoma ...
American Dental Association releases new tooth decay treatment guideline
2023-06-26
CHICAGO, June 26, 2023 – A new American Dental Association (ADA) clinical practice guideline suggests conservative methods to treat tooth decay in primary and permanent teeth could lead to better outcomes when used with common restorative materials like fillings or caps. An expert panel of dentists developed the first-ever guideline on this topic after extensive review of approximately 300 published studies.
The guideline, published in the July issue of The Journal of the American Dental Association, contains 16 recommendations regarding treatment ...
School suspensions amplify Black, Hispanic students’ risk of later arrest
2023-06-26
Research shows that school suspensions do not deter but instead amplify future punishment, what has been termed labeling theory: the idea that the symbolic label that comes with a suspension shapes how others perceive students. But few studies have examined racial and ethnic differences in this process, even though critical race theory (CRT) suggests that the consequences of suspension likely differ across racial and ethnic groups due to stereotypes.
In a new study, researchers examined how the relation between suspension and subsequent arrest differs for White, Black, and Hispanic students. They found that suspension ...
Penn State researchers discover one-of-a-kind fish is local to lower Susquehanna
2023-06-26
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In an attempt to rescue a rare darter in the lower Susquehanna River, a Penn State research team, working with the Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission, has determined that the fish is a distinct subspecies found nowhere else. And that makes the effort to restore its population even more important, the researchers say.
A yellow- to olive-colored member of the darter family with dark bars often arrayed in zebra fashion, the Chesapeake logperch is typically just a few inches long, with a small mouth and a short, conical snout. It is believed to only ever have inhabited the lower drainages of the Susquehanna and Potomac rivers, and it has not been seen ...
CHEST® Critical Care launches first issue
2023-06-26
Glenview, Illinois – A new scientific publication, CHEST® Critical Care, published its inaugural issue June 22, 2023. As part of the journal CHEST® portfolio, this online-only publication is dedicated entirely to the field of critical care medicine.
“I’m ecstatic for this launch. We are grateful to our authors for the trust they put in us and are excited to share their work with our critical care colleagues around the world,” says Hayley Gershengorn, ...
Fighting loneliness by finding purpose
2023-06-26
A new study co-authored by Patrick Hill, associate professor of psychological and brain sciences, offers an important message for our times: A sense of purpose in life — whether it’s a high-minded quest to make a difference or a simple hobby with personal meaning — can offer potent protection against loneliness.
“Loneliness is known to be one of the biggest psychological predictors for health problems, cognitive decline, and early mortality,” Hill said. “Studies show that it can ...
Worse than diesel and gasoline? Bioenergy as bad as fossils if there is no pricing of CO2 emissions from land-use change
2023-06-26
Demand for modern biofuels is expected to grow substantially in order to mitigate climate emissions. However, they are far from being a climate neutral alternative to gasoline and diesel. A new study in Nature Climate Change shows that under current land-use regulations, CO2 emission factors for biofuels might even exceed those for fossil diesel combustion due to large-scale land clearing related to growing biomass. Before bioenergy can effectively contribute to achieving carbon neutrality, international agreements need to ensure the effective protection of forests and other natural lands by introducing carbon ...
New research clarifies connection between autism and the microbiome
2023-06-26
The biological roots of autism continue to perplex researchers, despite a growing body of studies looking at an increasing array of genetic, cellular and microbial data. Recently, scientists have homed in on a new and promising area of focus: the microbiome. This collection of microbes that inhabit the human gut has been shown to play a role in autism, but the mechanics of this link have remained awash in ambiguity. Taking a fresh computational approach to the problem, a study published today in Nature Neuroscience sheds new light on the relationship between the microbiome and autism. This research — which originated ...
[1] ... [1846]
[1847]
[1848]
[1849]
[1850]
[1851]
[1852]
[1853]
1854
[1855]
[1856]
[1857]
[1858]
[1859]
[1860]
[1861]
[1862]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.