CU professor leads study on discontinuing therapy for MS patients over 55
2023-06-23
AURORA, Colo. (June 22, 2023) – An article published today in the journal Lancet Neurology evaluates the risk of recurrence of active disease in older patients with multiple sclerosis after discontinuing disease-modifying therapies.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic illness, often presenting in young adulthood. Most commonly, at onset, individuals have acute attacks, or relapses, of intermittent new neurological symptoms such as vision changes, numbness, and weakness that may come and go, seemingly randomly, and then remit completely or incompletely. ...
Mystery of how leaf-cutting ants gauge leaf portion size revealed
2023-06-23
They might not be able to leap tall buildings with a single bound, but leaf-cutting ants are insect superheroes, capable of carrying leaf pieces up to six times their body mass to cultivate fungus in their borrows. But how do the charismatic creatures determine the size of the fragments they carve with their mandibles? Do they use their bodies as a simple ruler, or do they use information about the position of their bodies to adjust how far they cut, adapting to the thickness of a leaf while dismembering it? Knowing that the insects alter the trajectory of a cut when sculpting ®Parafilm of different thicknesses, Flavio ...
Ramón Barthelemy wins 2023 LGBTQ+ Educator of the Year
2023-06-22
Out to Innovate is proud to announce the winners of its 2023 recognition awards for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ+) professionals in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). Out to Innovate has recognized exemplary individuals with LGBTQ+ Educator, Engineer, and Scientist of the Year for over 15 years.
2023 LGBTQ+ Educator of the Year: Ramón S. Barthelemy, Ph.D
The LGBTQ+ Educator of the Year award recognizes an educator who has significantly impacted STEM students through teaching, ...
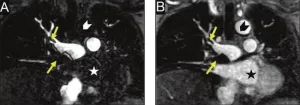
Switch to MR angiography for PE mitigated impact of recent contrast shortage
2023-06-22
Leesburg, VA, June 22, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), preferential use of pulmonary MR angiography (MRA) for diagnosing pulmonary embolus (PE) in the general population helped conserve iodinated contrast media during the 2022 shortage.
“This single-center experience demonstrates use of pulmonary MRA as a practical substitute for pulmonary CTA in emergency settings,” concluded lead investigator Jitka Starekova, MD, from the radiology ...
UW–Madison researchers reveal how the influenza A more effectively infect its hosts
2023-06-22
Influenza A is one of two influenza viruses that fuel costly annual flu seasons and is a near constant threat to humans and many other animals. It's also responsible for occasional pandemics that, like the one in 1918, leave millions dead and wreak havoc on health systems and wider society.
Influenza A was first identified as a health threat nearly a century ago, but only in the last decade have scientists identified one of the virus’s key proteins for infiltrating host cells and short-circuiting their defenses. Now, a team of researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have taken a major step toward understanding how that protein works, ...
Powerful board allies are a CEO's best weapon
2023-06-22
If we’ve learned anything from HBO’s smash hit Succession over the last four years, it’s that, as the authors of a new Strategic Management Journal article state, “Even the most powerful individuals do not work alone.” Given that, whether (SPOILER ALERT!) Tom succeeds in his new role depends less on his business acumen than on who the new CEO has as his allies.
In the upcoming article “Can powerful allies protect the CEO against performance declines? The role of the CEO’s subgroup power in CEO dismissal,” authors Jihae You, Taekjin Shin, and Yunhyung Chung, explore ...
Working toward Black reproductive justice from the Library of Congress
2023-06-22
Historian Tamika Nunley can see the U.S. Supreme Court through the window of her office in the Library of Congress in Washington, D.C., where she is serving as the library’s Cary and Ann Maguire Chair in Ethics and American History this summer. It’s a great vantage point, she said, not only for looking out at landmarks of American government, but also for reflecting on the ways laws and judgements have negatively influenced Black maternal health throughout American history.
“I think the Library of Congress is one of the most democratic institutions we have, one of the best examples of what is possible in our democracy,” said Nunley, ...
Rensselaer researcher uses pressure to understand RNA dynamics
2023-06-22
Just as space holds infinite mysteries, when we zoom in at the level of biomolecules (one trillion times smaller than a meter), there is still so much to learn.
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Catherine Royer, Constellation Chair Professor of Bioinformatics and Biocomputation at the Shirley Ann Jackson, Ph.D. Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies (CBIS) and professor of biological sciences, is dedicated to understanding the conformational landscapes of biomolecules and how they modulate cell function. When biomolecules ...
New “atlas” maps bacteria and metabolites associated with elevated risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-06-22
CLEVELAND - A Cleveland Clinic research team recently published an “atlas” of metabolites associated with cardiovascular disease in the European Heart Journal. The novel findings provide key details about the routes and potential branching paths taken by bacteria and metabolic by-products, metabolites.
The study mapped out the multiple by-products of bacteria processing amino acids associated with cardiovascular disease and then compared that to patient data to assess disease risk in two large cohorts – one in the US and another in Europe.
Bacteria in and on our bodies produce metabolites through processing certain molecules, referred to as precursors. ...
Brigham researchers identify factors associated with lower breastfeeding duration for mothers with higher BMIs
2023-06-22
A multi-nation cohort analysis found that inflammation and cesarean section delivery in mothers with higher body mass index are connected to shorter duration of breastfeeding, providing potential targets for intervention.
Breastfeeding has significant benefits for both maternal and child health. Research has indicated that women with higher body mass index (BMI) have shorter durations of breastfeeding, but few underlying mechanisms have been identified. To address this gap, a new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s ...
Muhammad Rabnawaz to be inducted into National Academy of Inventors
2023-06-22
For creating technologies that have the potential to change the world and providing opportunities for future inventors, Muhammad Rabnawaz, an associate professor and Faculty Laureate in the College of Agriculture and Natural Resources at Michigan State University, will be inducted into the National Academy of Inventors as a senior member on June 26.
The NAI senior member program was established to highlight academic inventors who have demonstrated a prolific spirit of innovation in creating or facilitating outstanding inventions that hold the promise of making a tangible impact on the public’s quality of life, economic development and the welfare of society. Election ...
The nose knows: Career Awardee developing bioinspired optical sniffer sensor
2023-06-22
The human nose, which has around 6 million olfactory receptors, can distinguish between at least 1 trillion different odors. Dogs have about 300 million of these receptors, with some scientists estimating their sense of smell is up to 100,000 times more powerful than humans’. This allows dogs to detect the scent of dangerous materials like bombs and illicit substances, as well as medical conditions such as COVID-19 and Parkinson’s disease.
University of Arizona assistant professor Judith Su is developing an optical nose “as sensitive as ...
The impact of populism on multinational corporations’ investment
2023-06-22
A stable economic and political environment is necessary for firms to feel secure while making long-term investment decisions, such as those related to investing in foreign countries (also known as foreign direct investment or FDI). Any threat to change legislative procedures in the foreign country can make it difficult for firms to predict the outcomes of such decisions. Populist leaders, who claim to represent the will of the people, often come to power by threatening to alter the established rules and procedures, generating ...
Is the U.S. ready for an African swine fever outbreak?
2023-06-22
In a new study, researchers from North Carolina State University used a computer model to understand how African swine fever (ASF) might spread among swine farms in the southeastern U.S. – and examined the effectiveness of existing response plans. They found that although control actions would help, an outbreak could still prove persistent and costly.
ASF is a highly contagious viral disease in pigs, with a mortality rate that can reach 100%. Additionally, infected pigs may not show symptoms before they die, potentially allowing the ...
NFL and NFL Players Association fund Emory University-led study of innovative pain management solutions
2023-06-22
The National Football League and the NFL Players Association (NFLPA) announced today they are awarding a grant to Emory University researchers to study innovative, first-of-their-kind, alternative pain management methods that could benefit NFL players and society at large. The researchers will investigate mindfulness-based intervention in sports medicine injuries.
The $200,000 grant was awarded by the NFL-NFLPA Joint Pain Management Committee (PMC), which aims to facilitate research to better understand and improve potential alternative pain management treatments for NFL players.
Emory’s winning ...
Research links increase in depression, COVID diagnosis in student-athletes
2023-06-22
Background
COVID-19 survivors may experience persistent neuropsychological disruptions such as lower satisfaction with life (SWLS), depression, and anxiety. While student-athletes are at low risk for severe COVID complications, the effect of COVID on mental health remains to be elucidated.
Objective
Compare patient-reported mental health outcomes for incoming collegiate athletes who did (COVID+) and did not (COVID-) have COVID-19.
Methods
79 COVID+ (79/178, 44.4%, 18.90±0.16 years) and 99 COVID- (99/178, 55.6%,18.95±0.16 ...
Heat spots reveal growth rate of a galaxy 12 billion years ago
2023-06-22
An international team of astronomers has drawn a temperature map of the dust drifting within one of the oldest spiral galaxies of the Universe which provides new insights into how fast the galaxy is growing. Until now researchers have only been able to measure the temperature of most distant galaxies in broad terms, without showing how temperatures vary in individual areas.
This research, described in a paper published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS) shows unambiguous temperature variation within the distant galaxy indicating two distinct heat sources – a supermassive black hole at the centre of the galaxy, and the heat generated ...
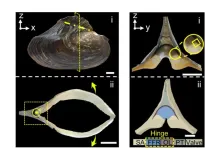
Scientists learn from hinge in bivalve about fatigue resistance of materials
2023-06-22
Recently, flexible and foldable devices have developed at a dramatic rate. More and more foldable devices appear in people's lives. Long-term service requires the folded parts to endure repeated deformation which might cause fatigue damage to the devices. Consequently, the damage will affect the normal function of the devices. Inspired by the hinge of bivalve Cristaria plicata, which experiences hundreds of thousands of repeating opening-and-closing valve motions throughout the bivalve’s lifetime, a research team led by Prof. YU Shuhong collaborating with Prof. WU Hengan from the University of Science and Technology of China ...
Bias in AI algorithms could be mitigated by implementing new checklist
2023-06-22
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Digital Health: https://journals.plos.org/digitalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pdig.0000278
Article Title: Bias in artificial intelligence algorithms and recommendations for mitigation
Author Countries: Jordan, United States, Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
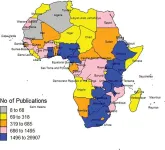
Africa's share of global HIV research output has increased from 5.1% to 31.3% over the last 35 years, but is still low compared to its relative burden of infections
2023-06-22
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0000544
Article Title: HIV research output in African Countries between 1986–2020
Author Countries: Nigeria, USA, UK
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
How might generative AI models distort human beliefs?
2023-06-22
Generative AI models such as ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney all have features that may distort human beliefs through their transmission of false information and stereotyped biases, according to Celeste Kidd and Abeba Birhane. In this Perspective, they discuss how research on human psychology can explain why generative AI could be particularly powerful in distorting beliefs. The capabilities of generative AI have been exaggerated at this point, they suggest, leading to a belief that these models exceed human capabilities. People are predisposed to adopt the information of knowledgeable, confident agents like generative AI ...
Large herbivores slow Arctic tundra diversity losses associated with sea ice decline
2023-06-22
Tundra diversity, including plants, lichens and fungi, declined over a 15-year experiment in the Arctic due to warming temperatures mediated by the disappearance of sea ice, according to Eric Post and colleagues. However, the presence of large herbivores such as caribou and musk oxen slowed this decline, by affecting the plant understory with their different browsing behaviors, the researchers concluded. Their findings offer support for the idea that encouraging herbivore diversity in the tundra could temper some of the impacts of climate warming. Post et al. observed the interacting effects of warming temperatures, sea ice changes, tundra diversity and herbivore exclusion in ...
Hard and soft materials form a fatigue-resistant fan in the mussel’s hinge
2023-06-22
How does a mussel shell open and shut easily and without damage for hundreds of thousands of cycles during the bivalve’s lifetime? Such fatigue-resistant materials would be useful in electronics, aerospace and tissue engineering designs, where components need to operate repeatedly without failure. Xiang-Sen Meng and colleagues took a closer look at the hinge on the shell of the bivalve Cristaria plicata, and found that the answer lies in a combination of design and materials that resist brittle fracture over time. Microscopic observations by Meng et al. show that the hinge gets its ...
Laws restricting abortion have ethical, legal and practical impacts for research on people who may become pregnant
2023-06-22
In this Policy Forum, Jeremy Sugarman and colleagues describe the risks that increasingly limited access to abortion may pose to clinical research participants and staff, one year after the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Woman’s Health Organization. People who may become pregnant are already an understudied population in clinical research. The authors suggest that new laws restricting abortion access may lead to ethical, legal and practical problems that make the risk of conducting research with this population unreasonable ...
Are viruses keeping sea lice at bay in wild salmon?
2023-06-22
More than 30 previously unknown RNA viruses in sea lice have been identified by University of British Columbia (UBC) researchers. Sea lice are parasitic copepods (small crustaceans) found in many fresh and saltwater habitats, and have been implicated in the decline of wild salmon populations. The research sheds greater light on the types of viruses being carried by sea lice, and how the viruses and host are interacting.
“We found many more types of viruses than are known in sea lice or their distant relatives; the lice are mounting an immune defense response to many of these viruses indicating that they are replicating,” says UBC marine microbiologist Dr. Curtis Suttle, ...
[1] ... [1839]
[1840]
[1841]
[1842]
[1843]
[1844]
[1845]
[1846]
1847
[1848]
[1849]
[1850]
[1851]
[1852]
[1853]
[1854]
[1855]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.