Supermarket trolleys set to help diagnose common heart rhythm disorder and prevent stroke
2023-06-23
Edinburgh, UK – 23 June 2023: It could be the shopping trip that saves your life: supermarket trolleys are helping to diagnose atrial fibrillation which can then be treated to prevent disabling or fatal strokes. The research is presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“This study shows the potential of taking health checks to the masses without disrupting daily routines,” said study author Professor Ian Jones of Liverpool John Moores University, UK. “Over ...
BU researchers shed light on signaling pathway responsible for head and neck cancers
2023-06-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, June 23, 2023
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
(Boston)—Despite advances in defining the genomic characteristics of head and neck cancers, these malignancies continue to rank among the deadliest cancers with few targeted therapies available. An important challenge in designing effective treatments is intratumor heterogeneity, the presence of multiple subpopulations of cells with distinct genomic and molecular alterations, with some cells inherently more resistant to certain ...
New EIC project to improve CAR T therapies in solid tumors
2023-06-23
Partners in the international consortium CAR T-REX announce the awarding of a highly competitive EIC Pathfinder Open grant, following the positive evaluation of their project entitled ‘CAR T Cells Rewired to Prevent EXhaustion in the Tumour Microenvironment’. One of 57 projects selected amongst 858 submissions, with a total funding of €2.7M, CAR T-REX was recognised for its radical and ambitious vision to improve the efficacy and safety of CAR T-based solid tumour-targeted cell therapies.
By ...
Magdeburg researchers discover a new mechanism of cancer immune defense
2023-06-23
Modern immunotherapies boost the body's own defenses against cancer. They activate killer T cells of the immune system that can specifically recognize and destroy cancer cells. In many patients, however, cancer cells adapt and become invisible to killer T cells so that the treatment is no longer effective. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Magdeburg has now discovered a new mechanism that enables the immune system to also eliminate such invisible cancer cells. These findings open up new possibilities ...
City buildings could blow air taxi future off course
2023-06-23
The air taxi market is almost ready for take off, with companies such as Boeing, Hyundai, Airbus and Toyota building fleets to have commuters flitting through the sky. Europe and the US have both drafted new rules to pave the way for air taxis to begin operations within the decade, with Australia’s Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA) to follow suit.
Increasingly sophisticated studies over recent years, including a recent paper by RMIT University’s Uncrewed Aircraft Systems (UAS) Research Team, have measured how sudden wind gusts form around city buildings and destabilise aircraft.
Lead researcher and aerospace engineer, Dr Abdulghani Mohamed, who’s ...
Customized treatment for heart failure patients through the use of AI, Amsterdam UMC launches a global consortium
2023-06-23
Heart failure is the leading cause of hospitalisation in those over 65 and research predicts that the condition will increase in global prevalence by almost 50% by 2030. Currently heart failure affects more 64 million people worldwide. In order to reduce the burden of disease on both health systems and patients, Amsterdam UMC is launching, thanks to a Horizon Europe grant of almost 6 million euros, a consortium to look for an AI-powered solution.
Consortium leader and Professor of Precision Medicine at Amsterdam UMC, Folkert Asselbergs explains ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces cultivated meat spinout company
2023-06-23
(LOS ANGELES) – June 23, 2023 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is excited to unveil their first spinout company, Omeat, an organization dedicated to technology for the sustainable production of beef and other meats on a global scale. Omeat produces cultivated meat, using cost-effective, humane, and efficient methods to collect regenerative factors for cell cultivation from healthy, living cows.
The Omeat technology was initially conceived and developed by TIBI scientists four years ago, under the leadership of TIBI Director ...
A new species of early toothed whale
2023-06-23
Have you ever wondered what the earliest ancestors of today’s dolphins looked like? Then look no further, meet Olympicetus thalassodon, a new species of early odontocete, or toothed whale, that swam along the North Pacific coastline around 28 million years ago. This new species is one of several that are helping us understand the early history and diversification of modern dolphins, porpoises and other toothed whales. The new species is described in a new study published in the open access journal ...
Yearly re-scanning not needed for common brain tumor detected in 1 in 10 people
2023-06-23
People with a common type of benign brain tumour detected in around 1 in 10 don’t require annual scans, a new national study has found.
The largest study of its kind has been published in the European Journal of Endocrinology and looks at clinical data on a type of tumour growth in the pituitary gland in the brain. The common growth, called a non-functioning pituitary microadenoma (NFPA), is less than 1cm across, is predicted to affect around 10% of the population and usually doesn’t cause any symptoms.
In the ...
Women with common heart rhythm disorder have faster cognitive decline than men
2023-06-23
Edinburgh, UK – 23 June 2023: Women with atrial fibrillation progress more rapidly to cognitive impairment and dementia than men with the heart rhythm condition, according to research presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)1 and published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
“Symptoms of atrial fibrillation in women are often ignored by healthcare providers or attributed to stress or anxiety so it can go undiagnosed for long period of time, while men are more likely to be diagnosed and ...
Race-neutral testing could have given access to life-saving lung transplants for more black patients
2023-06-23
June 21, 2023 – NEW YORK, NY— Race-neutral lung function interpretation could increase access to lung transplants for Black patients with respiratory disease, according to new research published in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society online ahead of print.
In “Race-Specific Interpretation of Spirometry: Impact on the Lung Allocation Score,” lead researcher J. Henry Brems, MD, MBE of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and colleagues investigated how race-specific versus race-neutral equations alter the lung allocation score (LAS) and the priority for lung transplant across races. The lung allocation score determines ...
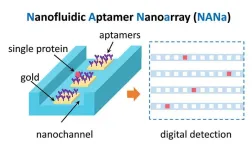
Bridging the gap for precision medicine: nanofluidic aptamer nanoarray measures individual proteins
2023-06-23
In the evolving world of precision medicine, the need for methods that can measure biomolecules with supreme accuracy and specificity is paramount. Recognizing this, Associate Professor Yan Xu of the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University and his international research team have made a great stride in this direction. They have developed an innovative nanofluidic device capable of capturing single proteins stochastically and detecting them digitally at their naturally high concentrations. This breakthrough could potentially ...
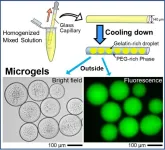
Smart yet simple – creating uniform DNA-encapsulating microgels that mimic a living cell
2023-06-23
The living cell harbors physiologically relevant components such as the genetic material (DNA) and proteins in a ‘self-organized’ setting. Understanding this process of self-assembly can reveal the underlying mechanism of self-organization of living matter. Water/oil (w/o) or water/water (w/w) droplets may be used as prototypes or “models” that mimic cells and can be used to study cellular self-assembly. These models also have major implications in the field of biomedical research. Although cell mimetics can be generated using complicated and high-cost equipment, the associated methods are costly, ...
Even a modest reduction in kidney function increases health risks in young adults
2023-06-23
A study of more than 8 million adults in Ontario, Canada suggests that even a modest loss of kidney function is associated with increased health risks. The study, published in The BMJ, could lead to better approaches to prevent chronic kidney disease and related conditions, particularly in younger adults.
“The dogma is that healthy, young adults don’t need to worry about kidney function unless it drops to around 50% of the normal level, but our research suggests that even a more modest 20-30% drop may have consequences and we may want to have earlier conversations ...
Forensic bitemark analysis for court trials is not supported by sufficient data and “is leading to wrongful convictions”
2023-06-23
The commonly-used evidence in trials, bitemark analysis, is not backed up by scientific research – an analysis of current literature, and 12 new studies, shows.
Published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the California Dental Association, the research suggests 26 people have been wrongfully convicted, and some even sentenced to death, from the use of this forensic science.
“The scientific community does not uphold the underlying premises that human teeth are unique and their unique features transfer to human skin,” states lead author Mary Bush, Associate Professor at the State University of New York in Buffalo, NY.
“We find bitemark transfer ...
COVID-19's impact on socioeconomic inequality in health behaviors among Japanese adolescents
2023-06-23
Key Findings
This study is the first worldwide to investigate time trend in socioeconomic inequality in various health behaviors among adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study found widening socioeconomic inequality among Japanese adolescents in achieving recommended physical activity levels before and during the pandemic, alongside narrowing inequality in breakfast intake. Specifically, despite no observed differences in physical activity by income in 2019, by 2021, adolescents from families with lower equivalent household incomes were less likely to engage in physical activity.
Research is needed to continue monitoring the impact these phenomena will have ...
More exposure needed for cosmetic breast enhancement risks
2023-06-23
Complications after cosmetic breast augmentation are more common than other cosmetic plastic surgery yet many women who undergo such procedures are often in the dark about the associated risks say QUT researchers.
The authors of a new paper argue the need for more disclosure early (and in much simpler terms) of those risks and the high likelihood of revision surgery being required so when women give their consent, they have a greater understanding of what may happen.
“The Australian cosmetic surgery industry is worth billions but there are concerns inside the industry on potential issues surrounding whether patients ...
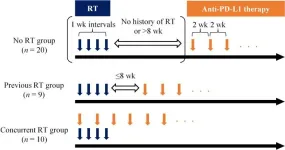
Combination therapy effective against canine melanoma
2023-06-23
A combination of radiotherapy followed by immunotherapy is a promising strategy for the treatment of oral malignant melanomas in dogs.
Melanomas are the most common oral cancers in dogs. It is highly metastatic and conventional chemotherapy does not increase survival time. Canine oral melanomas are similar to human melanomas; thus, research is being conducted into adapting treatments developed for human melanomas for dogs.
A particularly effective therapy for treating human melanomas is a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy. A team of researchers led by Professor Satoru Konnai at Hokkaido University has investigated ...
Building the semiconductor workforce of the future
2023-06-23
The University of Utah is one of thirteen founding partner members of the Northwest University Semiconductor Network, a partnership with and created by Micron Technology, Inc. whose goal is to help develop the next generation of the United States’ semiconductor industry’s workforce.
Micron, one of the world’s largest semiconductor companies, made the announcement on Monday. In a press release the company stated the Northwest University Semiconductor Network will “drive foundational and emerging research to increase students’ ...
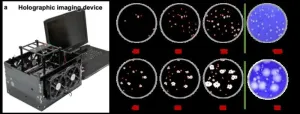
New rapid viral plaque detection system, aided by deep learning and holographic imaging, can help accelerate vaccine and drug development
2023-06-23
Findings
In a new paper published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, a team of scientists led by Professor Aydogan Ozcan from the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at UCLA and an associate director of the California NanoSystems Institute, developed a rapid, stain-free, and automated viral plaque detection system enabled by holography and deep learning. This system incorporates a cost-effective and high-throughput holographic imaging device that continuously monitors the unstained virus-infected cells during their incubation process. At each imaging cycle, these ...
New ruling on care of dying will force some to live life “of machine-related suffering”
2023-06-23
The newly revised ruling on advance medical directives and withholding/withdrawing medical support for the dying in India will inevitably force some terminally ill patients to “live a life of machine-related suffering” and deprive them of their autonomy and dignity in death, suggest specialist doctors in a letter published online in the journal BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.
While a progressive step, the 2023 ruling still has important shortcomings, they add.
In the absence of any specific legislation ...
Global diabetes cases to soar from 529 million to 1.3 billion by 2050
2023-06-23
***Embargo: 23.30 UK time / 18:30 ET / 15:30 PT Thursday, 22 June 2023***
SEATTLE, Wash. June 22, 2023 – More than half a billion people are living with diabetes worldwide, affecting men, women, and children of all ages in every country, and that number is projected to more than double to 1.3 billion people in the next 30 years, with every country seeing an increase, as published today in The Lancet.
The latest and most comprehensive calculations show the current global prevalence rate is 6.1%, making diabetes one of the top 10 leading causes of death and disability. At the super-region level, the ...
Surrey expert recognized on International Women in Engineering Day
2023-06-23
The Women’s Engineering Society has named the University of Surrey’s Dr Kelly Kousi as one of the finalists in its Top 50 Women in Engineering Awards (WE50) 2023: Safety and Security. The announcement coincides with International Women in Engineering Day 2023, a celebration of women in engineering.
Dr Kousi, a lecturer in the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, leads a research group of scientists and engineers who work on emission control, synthetic fuel production ...
Gloss is less effective camouflage in beetles compared to matte, according to latest study
2023-06-23
When combined with iridescent colouration, a matt target surface appearance confers greater survival benefits in beetles than a glossy surface, scientists at the University of Bristol have found.
The findings, published in Behavioural Ecology, suggest that iridescence provides camouflage independent of glossiness, which means that it is the colour of iridescent surfaces and its changeability, that is the most important aspect of iridescence in enabling camouflage.
Iridescence is a type of structural colouration that produces bright, vibrant hues. These are often angle-dependent, meaning the observed colour appears to ...
UW–Madison researchers reveal how key protein might help influenza A infect its hosts
2023-06-23
Influenza A is one of two influenza viruses that fuel costly annual flu seasons and is a near constant threat to humans and many other animals. It's also responsible for occasional pandemics that, like the one in 1918, leave millions dead and wreak havoc on health systems and wider society.
Influenza A was first identified as a health threat nearly a century ago, but only in the last decade have scientists identified one of the virus’s key proteins for infiltrating host cells and short-circuiting their defenses. Now, a team of researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have taken a major step toward ...
[1] ... [1838]
[1839]
[1840]
[1841]
[1842]
[1843]
[1844]
[1845]
1846
[1847]
[1848]
[1849]
[1850]
[1851]
[1852]
[1853]
[1854]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.