Association of population well-being with cardiovascular outcomes
2023-07-05
About The Study: Assessing the association of well-being and cardiovascular outcomes, higher well-being, a measurable, modifiable, and meaningful outcome, was associated with lower cardiovascular disease mortality, even after controlling for structural and cardiovascular-related population health factors, indicating that well-being may be a focus for advancing cardiovascular health.
Authors: Erica S. Spatz, M.D., M.H.S., of the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.21740)
Editor’s ...
From atoms to materials: Algorithmic breakthrough unlocks path to sustainable technologies
2023-07-05
New research by the University of Liverpool could signal a step change in the quest to design the new materials that are needed to meet the challenge of net zero and a sustainable future.
Publishing in the journal Nature, the Liverpool researchers have shown that a mathematical algorithm can guarantee to predict the structure of any material just based on knowledge of the atoms that make it up.
Developed by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Liverpool’s Departments of Chemistry and Computer Science, the algorithm systematically evaluates entire sets of possible structures at once, rather than considering them one at a time, to accelerate identification ...
An international team identifies the mutations that cause the most frequent congenital heart defects
2023-07-05
Bicuspid aortic valve is the most common congenital defect in humans, affecting between 1% and 2% of the population. Instead of the usual three symmetric leaflets, affected individuals have two asymmetric valve leaflets. This defect is a frequent cause of aortic stenosis and endocarditis and is associated with early calcification of the aortic valve. Currently the only effective treatment is valve replacement surgery.
But this situation could be changed by the results of a new study published by an international team co-led by CNIC group leader Dr. José ...
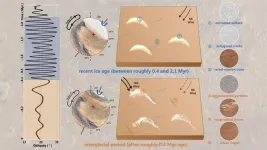
Utah seismologist peer into Earth's inner core
2023-07-05
Media contacts:
--Keith Koper, professor, Department of Geology and Geophysics, University of Utah, keith.koper@utah.edu 801-585-3669
--Brian Maffly, research communications, University of Utah, brian.maffly@utah.edu 801-573-2382
--Syl Kacapyr, Cornell Engineering, Associate Director, Marketing and Communications
vpk6@cornell.edu 607.339.6450
At the center the Earth is a solid metal ball, a kind of “planet within a planet,” whose existence makes life on the surface possible, at least as we know it.
How Earth’s inner core formed, grew and evolved over ...
Martian dunes eroded by a shift in prevailing winds after the planet's last ice age
2023-07-05
Detailed analysis of data obtained by the Zhurong rover of dunes located on the southern Utopian Plain of Mars suggests the planet underwent a major shift in climate that accompanied changes in prevailing winds. This shift likely occurred about 400,000 years ago, which coincides with the end of the last glacial period on Mars.
Researchers from the National Astronomical Observatories, Institute of Geology and Geophysics and Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with colleagues from Brown University, assessed the surface structure and chemical composition of Martian dunes to ...
A single molecule upsets symbiosis
2023-07-05
A new study on the coexistence of bacteria and fungi shows that a mutually beneficial, functioning symbiosis can be very fragile. Researchers at the Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology (Leibniz-HKI) in Jena found out that the bacterial species Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica lives happily in the hyphae of the fungus Rhizopus microsporus only when the bacteria produce a certain protein.
In a symbiosis, two organisms join together and benefit from each other; in endosymbiosis, one of ...
Potent greenhouse gas produced by industry could be readily abated with existing technologies
2023-07-05
CAMBRIDGE, MD (July 5, 2023)—Researchers have found that one method of reducing greenhouse gas emissions is available, affordable, and capable of being implemented right now. Nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance, could be readily abated with existing technology applied to industrial sources.
“The urgency of climate change requires that all greenhouse gas emissions be abated as quickly as is technologically and economically feasible,” said lead author Eric Davidson, a professor with the University of Maryland Center for Environmental ...
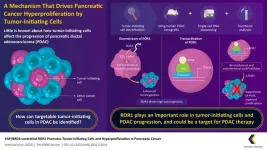
A cell surface marker for identifying tumor-initiating cells in pancreatic cancer
2023-07-05
Tumor-initiating cells, or cancer stem cells, are gaining attention in cancer therapy, as they can travel through the body and cause cancerous tumors at other sites through metastasis. These cells also may cause resistance to chemotherapy. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a type of cancer that has a poor prognosis. The problem of metastasis is particularly prominent in this type of cancer. Though the tumor-initiating cells are implicated in the disease progression of some cancers, their specific role, unique traits, and the underlying signaling pathways of their action in pancreatic adenocarcinoma remain poorly understood. ...
New study aims to assess bleeding complications in patients undergoing high-risk PCI
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON (July 5, 2023) – A new multicenter, single-arm, open-label study is the first to exclusively assess bleeding complications in patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) with Impella with independent adjudication via a clinical events adjudication committee and will gather meaningful real-world data based on contemporary practice. The design and rationale of the study was published online today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI).
Nearly one in every five patients1 will experience a bleeding complication during a large-bore endovascular procedure. Periprocedural ...
First ultraviolet data collected by ESA’s JUICE mission
2023-07-05
SAN ANTONIO — July 5, 2023 —The Southwest Research Institute-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) aboard ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) spacecraft has successfully completed its initial commissioning following the April 14 launch. The UVS instrument is one of three instrument projects comprising NASA’s contribution to the JUICE mission. The mission’s science goals focus on Jupiter and its system, making multiple flybys of the planet’s large, ocean-bearing satellites with a particular emphasis on investigating Ganymede ...
Investigational three-month TB regimen is safe but ineffective, NIH study finds
2023-07-05
The first clinical trial of a three-month tuberculosis (TB) treatment regimen is closing enrollment because of a high rate of unfavorable outcomes with the investigational course of treatment. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 5362, also known as the CLO-FAST trial, sought to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a three-month clofazimine- and high-dose rifapentine-containing regimen. An interim data analysis showed that participants taking the investigational regimen experienced ongoing or recurring TB at rates above thresholds set in the study protocol. Based on these findings, ...
Public support for militarily defending NATO allies
2023-07-05
Voters in North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states are far more willing to militarily defend another country if the country joins NATO, versus if the same country does not join NATO, according to a study. To explore the possible consequences of expanding NATO membership, Michael Tomz and colleagues surveyed 14,000 voters in 13 NATO countries. Each survey participant was presented with a hypothetical Russian attack on one of four possible targets: Bosnia, Finland, Georgia, or Sweden—the four countries (other than Ukraine) furthest along in their bids for NATO accession at the time of ...
Mount Sinai launches Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health
2023-07-05
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has launched the Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health, the first of its kind in New York and one of the first in the United States. The Center is dedicated to advancing artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of ophthalmology, further positioning the Mount Sinai Health System as a leader in providing patient care through pioneering innovations and technologies.
In partnership with the Windreich Department of Artificial Intelligence and Human Health at Icahn Mount Sinai, the Center aims to ...
Sunscreen leaching poses minimal threat to aquatic wildlife
2023-07-05
New research reveals that sunscreen contamination may be less harmful to wildlife than previously thought. This study by Aaron Boyd, a PhD candidate at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada, demonstrates how exposure to sunscreen is actually a low risk for small aquatic animals compared to some of the suncream’s individual chemicals.
Sunscreens contain ultraviolet filters (UVFs) which have been found to be toxic to marine life such as corals, leading to the ban of some UVFs in Hawaii and Palau. If sunscreen is applied to the skin before swimming in lakes and rivers, these UVFs and other chemicals will leach into surrounding waters.
Mr ...
Exterminating greenhouse pests with bat-inspired drones
2023-07-05
Researchers have been testing real-life Batman-style gadgets to eradicate moth pests from greenhouses, including bat-inspired flying drones that hunt down and destroy moths – but new research reveals that the noise from drones can alter moth flight behaviour.
“The idea of using drones as an alternative solution to eliminating moths all started in the bedroom of one of the co-owners of the PATS startup company,” says Dayo Jansen, a PhD student from student from Wageningen University and Research in the Netherlands. ...
New telehealth certification available to health care professionals
2023-07-05
Embargoed until 8 a.m. ET/ 7 a.m. CT on Wednesday, July 5, 2023
DALLAS, July 5, 2023 — The COVID-19 pandemic radically changed the way health care professionals serve their patients. Over the past three years, a huge proportion of care has shifted to the virtual landscape as clinicians and patients search for a safe, reliable way to receive needed care.[1]
As part of its longstanding commitment to ensuring equitable access to high-quality health care, the American Heart Association has launched its first individual ...
An easier way to learn quantum processes
2023-07-05
Imagine a world where computers can unravel the mysteries of quantum mechanics, enabling us to study the behavior of complex materials or simulate the intricate dynamics of molecules with unprecedented accuracy.
Thanks to a pioneering study led by Professor Zoe Holmes and her team at EPFL, we are now closer to that becoming a reality. Working with researchers at Caltech, the Free University of Berlin, and the Los Alamos National Laboratory, they have found a new way to teach a quantum computer how to understand and predict the behavior of quantum systems, even with a few simple examples.
Quantum neural networks (QNNs)
The researchers worked on “quantum neural networks” ...
Fast, automated, affordable test for cement durability developed at U of I
2023-07-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Engineers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new test that can predict the durability of cement in seconds to minutes – rather than the hours it takes using current methods. The test measures the behavior of water droplets on cement surfaces using computer vision on a device that costs less than $200. The researchers said the new study could help the cement industry move toward rapid and automated quality control of their materials.
The results of the study, led by Illinois civil and environmental engineering professor Nishant ...
Study finds younger kidney cancer survivors at significant risk for heart problems
2023-07-05
New research out of VCU Massey Cancer Center indicates that many adolescent and young adult kidney cancer survivors are at a significantly elevated risk for heart issues.
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of health complications and death among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) diagnosed with cancer, where AYAs are characterized as patients between the ages of 15 and 39.
A study publishing July 5 in the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network assessed the incidence and risk of hypertension — high blood pressure — and heart failure among AYA patients diagnosed ...
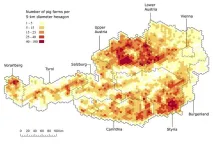
Researchers map Austria's pig trade network for the first time
2023-07-05
The transfer of pigs from one place to another poses the risk of spreading infectious diseases. Knowing how holdings (e.g., farms, markets, etc.) are connected is therefore of crucial importance. In a study by the Complexity Science Hub, the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, and the Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety (AGES), researchers are now drawing a map of the Austrian pig trade for the first time.
Every year, around 250,000 transfers of pigs take place in Austria. Each of these transfers carries a certain risk of spreading swine infectious diseases. To identify possible risks of disease spread and ...
Migrant orangutans learn which foods are good to eat by watching the locals
2023-07-05
Orangutans are dependent on their mothers longer than any other non-human animal, nursing until they are at least six years old and living with her for up to three years more, learning how to find, choose, and process the exceedingly varied range of foods they eat. But how do orangutans that have left their mothers and now live far from their natal ranges, where the available foods may be very different, decide what to eat and figure out how to eat it? Now, an international team of authors has shown that in such cases, migrants follow the rule ‘observe, and do as the locals do’. The results are published in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
“Here we ...
Pure capped mRNA vaccine opens the door to more effective vaccines with lower chances of inflammation
2023-07-05
A research group from Japan has developed a method to produce highly active mRNA vaccines at high purity using a unique cap to easily separate the desired capped mRNA. This ‘Purecap’ technique extracted up to 100% pure Cap2-type mRNA, which showed 3-4 times better production of the protein that stimulates the immune system. These results open up the possibility of purer vaccines with a lower risk of inflammation caused by impurities. Their findings were published in Nature Communications.
mRNA vaccines have been used successfully as therapy against variants ...
New understanding of how the brain processes and stores words we hear
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON – Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists say the brain’s auditory lexicon, a catalog of verbal language, is actually located in the front of the primary auditory cortex, not in back of it -- a finding that upends a century-long understanding of this area of the brain. The new understanding matters because it may impact recovery and rehabilitation following a brain injury such as a stroke.
The findings appear in Neurobiology of Language on July 5, 2023.
Riesenhuber’s lab showed the existence of a lexicon for written words at the base of the brain’s left hemisphere in a region ...
Similar to humans, elephants also vary what they eat for dinner every night
2023-07-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Elephants eat plants. That’s common knowledge to biologists and animal-loving schoolchildren alike. Yet figuring out exactly what kind of plants the iconic herbivores eat is more complicated.
A new study from a global team that included Brown conservation biologists used innovative methods to efficiently and precisely analyze the dietary habits of two groups of elephants in Kenya, down to the specific types of plants eaten by which animals in the group. Their findings on the habits of ...
Endometriosis linked to reduction in live births before diagnosis of the disease
2023-07-05
Endometriosis is linked to a reduction in fertility in the years preceding a definitive surgical diagnosis of the condition, according to new research published today (Wednesday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals.
In the first study to look at birth rates in a large group of women who eventually received a surgical verification of endometriosis, researchers in Finland found that the number of first live births in the period before diagnosis was half that of women without the painful condition. ...
[1] ... [1830]
[1831]
[1832]
[1833]
[1834]
[1835]
[1836]
[1837]
1838
[1839]
[1840]
[1841]
[1842]
[1843]
[1844]
[1845]
[1846]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.