Treatment for opioid use disorder varies widely among states, study finds
2023-06-23
Despite a national opioid overdose epidemic supercharged by a surge of illicit fentanyl, new research from Oregon Health & Science University reveals wide discrepancies among U.S. states in effectively treating opioid use disorder among people covered by Medicaid.
The study, published today in the journal JAMA Health Forum, found that in many states, fewer than half of people diagnosed with opioid use disorder received proven medications to treat it.
“We fail people by not providing adequate treatment to people with opioid use disorder enrolled in Medicaid,” said lead author Stephan Lindner, Ph.D., associate professor in ...
Patterns, characteristics of nicotine dependence among adults with cigarette use
2023-06-23
About The Study: There were significant reductions in nicotine dependence prevalence from 2006 to 2019 among U.S. adults with cigarette use and all examined subgroups 26 years and older. Adults 50 years and older (especially those with major depressive episode and/or substance use disorder) had the highest nicotine dependence prevalence compared with other age groups, highlighting the importance of assisting with smoking cessation efforts and addressing nicotine dependence for this older population. Evidence-based tobacco cessation strategies tailored to age and comorbidities are ...
Characteristics of medical evacuation by train in Ukraine
2023-06-23
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that medical evacuation in a war zone by converted trains is possible and can improve access to health care for war-affected patients. The presence of intensive care capacity on board allows for transport of more severely ill or injured individuals. However, the target population should not be limited to trauma patients, as health care institutions affected host a much broader population whose needs and urgency for evacuation may change over time.
Authors: James ...
BU researcher receives NIH grant to study stress, depression
2023-06-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, June 23, 2023
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-3508-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Researcher Receives NIH Grant to Study Stress, Depression
(Boston)—Michael Wallace, PhD, assistant professor of anatomy & neurobiology at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, was awarded a $2.8 million from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Mental Health. The award will fund his project "Serotonergic modulation of the circuits and cell-types of the lateral habenula."
The award, which runs from 2023-2028, supports his research into the cellular and circuit impacts of serotonin on a brain region implicated in chronic stress and ...
Global warming accelerates CO2 emissions from soil microbes
2023-06-23
The rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration is a primary catalyst for global warming, and an estimated one fifth of the atmospheric CO2 originates from soil sources. This is partially attributed to the activity of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that decompose organic matter in the soil utilizing oxygen, such as deceased plant materials. During this process, CO2 is released into the atmosphere. Scientists refer to it as heterotrophic soil respiration.
Based on a recent study published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, a team of researchers from ...
UVA Health launches effort to improve HIV care across America
2023-06-23
A UVA Health doctor is launching an ambitious effort to assess and improve HIV care for people with low incomes across the nation, a campaign that could also help prevent transmission.
Kathleen McManus, MD, MS, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, and her collaborators plan to identify specific policies and programs that can increase the numbers of patients who keep the HIV virus in their blood at undetectable levels. This desirable state, known as being “undetectable” or having “sustained viral suppression,” is associated with better health outcomes for individuals ...
Young Editor recruitment for journal Space: Science & Technology
2023-06-23
Introduction
Science Partner Journal Space: Science & Technology is an online-only Open Access journal published in affiliation with Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT) and distributed by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). BIT cooperates with China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) in managing the journal. The mission of Space: Science & Technology is to promote the exploration and research of space worldwide, to lead the rapid integration and technological breakthroughs of interdisciplinary sciences in the space field, and to build a high-level academic platform for discussion, cooperation, technological progress and information dissemination ...
New type of computer memory could greatly reduce energy use and improve performance
2023-06-23
Researchers have developed a new design for computer memory that could both greatly improve performance and reduce the energy demands of internet and communications technologies, which are predicted to consume nearly a third of global electricity within the next ten years.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, developed a device that processes data in a similar way as the synapses in the human brain. The devices are based on hafnium oxide, a material already used in the semiconductor industry, and tiny self-assembled barriers, which can be raised or lowered ...
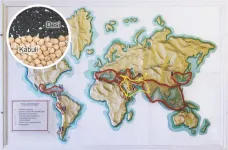
Study reveals genetic signatures of chickpea's cultural crossroads
2023-06-23
With its nutty flavor and dense nutrient profile, the humble chickpea has captivated palates and nourished civilizations for millennia. From its ancient origins to its widespread use in modern kitchens and restaurants around the world, this legume demonstrates both culinary versatility and cultural significance. Despite prominence in traditional cuisines across several continents, the origin, diversification, and spread of chickpeas throughout the Middle East, South Asia, Ethiopia, and the western Mediterranean have remained a mystery. A new study in Molecular Biology and Evolution titled “Historical ...
Supermarket trolleys set to help diagnose common heart rhythm disorder and prevent stroke
2023-06-23
Edinburgh, UK – 23 June 2023: It could be the shopping trip that saves your life: supermarket trolleys are helping to diagnose atrial fibrillation which can then be treated to prevent disabling or fatal strokes. The research is presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“This study shows the potential of taking health checks to the masses without disrupting daily routines,” said study author Professor Ian Jones of Liverpool John Moores University, UK. “Over ...
BU researchers shed light on signaling pathway responsible for head and neck cancers
2023-06-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, June 23, 2023
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
(Boston)—Despite advances in defining the genomic characteristics of head and neck cancers, these malignancies continue to rank among the deadliest cancers with few targeted therapies available. An important challenge in designing effective treatments is intratumor heterogeneity, the presence of multiple subpopulations of cells with distinct genomic and molecular alterations, with some cells inherently more resistant to certain ...
New EIC project to improve CAR T therapies in solid tumors
2023-06-23
Partners in the international consortium CAR T-REX announce the awarding of a highly competitive EIC Pathfinder Open grant, following the positive evaluation of their project entitled ‘CAR T Cells Rewired to Prevent EXhaustion in the Tumour Microenvironment’. One of 57 projects selected amongst 858 submissions, with a total funding of €2.7M, CAR T-REX was recognised for its radical and ambitious vision to improve the efficacy and safety of CAR T-based solid tumour-targeted cell therapies.
By ...
Magdeburg researchers discover a new mechanism of cancer immune defense
2023-06-23
Modern immunotherapies boost the body's own defenses against cancer. They activate killer T cells of the immune system that can specifically recognize and destroy cancer cells. In many patients, however, cancer cells adapt and become invisible to killer T cells so that the treatment is no longer effective. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Magdeburg has now discovered a new mechanism that enables the immune system to also eliminate such invisible cancer cells. These findings open up new possibilities ...
City buildings could blow air taxi future off course
2023-06-23
The air taxi market is almost ready for take off, with companies such as Boeing, Hyundai, Airbus and Toyota building fleets to have commuters flitting through the sky. Europe and the US have both drafted new rules to pave the way for air taxis to begin operations within the decade, with Australia’s Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA) to follow suit.
Increasingly sophisticated studies over recent years, including a recent paper by RMIT University’s Uncrewed Aircraft Systems (UAS) Research Team, have measured how sudden wind gusts form around city buildings and destabilise aircraft.
Lead researcher and aerospace engineer, Dr Abdulghani Mohamed, who’s ...
Customized treatment for heart failure patients through the use of AI, Amsterdam UMC launches a global consortium
2023-06-23
Heart failure is the leading cause of hospitalisation in those over 65 and research predicts that the condition will increase in global prevalence by almost 50% by 2030. Currently heart failure affects more 64 million people worldwide. In order to reduce the burden of disease on both health systems and patients, Amsterdam UMC is launching, thanks to a Horizon Europe grant of almost 6 million euros, a consortium to look for an AI-powered solution.
Consortium leader and Professor of Precision Medicine at Amsterdam UMC, Folkert Asselbergs explains ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces cultivated meat spinout company
2023-06-23
(LOS ANGELES) – June 23, 2023 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is excited to unveil their first spinout company, Omeat, an organization dedicated to technology for the sustainable production of beef and other meats on a global scale. Omeat produces cultivated meat, using cost-effective, humane, and efficient methods to collect regenerative factors for cell cultivation from healthy, living cows.
The Omeat technology was initially conceived and developed by TIBI scientists four years ago, under the leadership of TIBI Director ...
A new species of early toothed whale
2023-06-23
Have you ever wondered what the earliest ancestors of today’s dolphins looked like? Then look no further, meet Olympicetus thalassodon, a new species of early odontocete, or toothed whale, that swam along the North Pacific coastline around 28 million years ago. This new species is one of several that are helping us understand the early history and diversification of modern dolphins, porpoises and other toothed whales. The new species is described in a new study published in the open access journal ...
Yearly re-scanning not needed for common brain tumor detected in 1 in 10 people
2023-06-23
People with a common type of benign brain tumour detected in around 1 in 10 don’t require annual scans, a new national study has found.
The largest study of its kind has been published in the European Journal of Endocrinology and looks at clinical data on a type of tumour growth in the pituitary gland in the brain. The common growth, called a non-functioning pituitary microadenoma (NFPA), is less than 1cm across, is predicted to affect around 10% of the population and usually doesn’t cause any symptoms.
In the ...
Women with common heart rhythm disorder have faster cognitive decline than men
2023-06-23
Edinburgh, UK – 23 June 2023: Women with atrial fibrillation progress more rapidly to cognitive impairment and dementia than men with the heart rhythm condition, according to research presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)1 and published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
“Symptoms of atrial fibrillation in women are often ignored by healthcare providers or attributed to stress or anxiety so it can go undiagnosed for long period of time, while men are more likely to be diagnosed and ...
Race-neutral testing could have given access to life-saving lung transplants for more black patients
2023-06-23
June 21, 2023 – NEW YORK, NY— Race-neutral lung function interpretation could increase access to lung transplants for Black patients with respiratory disease, according to new research published in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society online ahead of print.
In “Race-Specific Interpretation of Spirometry: Impact on the Lung Allocation Score,” lead researcher J. Henry Brems, MD, MBE of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and colleagues investigated how race-specific versus race-neutral equations alter the lung allocation score (LAS) and the priority for lung transplant across races. The lung allocation score determines ...
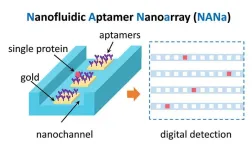
Bridging the gap for precision medicine: nanofluidic aptamer nanoarray measures individual proteins
2023-06-23
In the evolving world of precision medicine, the need for methods that can measure biomolecules with supreme accuracy and specificity is paramount. Recognizing this, Associate Professor Yan Xu of the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University and his international research team have made a great stride in this direction. They have developed an innovative nanofluidic device capable of capturing single proteins stochastically and detecting them digitally at their naturally high concentrations. This breakthrough could potentially ...
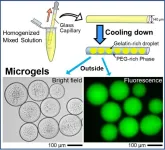
Smart yet simple – creating uniform DNA-encapsulating microgels that mimic a living cell
2023-06-23
The living cell harbors physiologically relevant components such as the genetic material (DNA) and proteins in a ‘self-organized’ setting. Understanding this process of self-assembly can reveal the underlying mechanism of self-organization of living matter. Water/oil (w/o) or water/water (w/w) droplets may be used as prototypes or “models” that mimic cells and can be used to study cellular self-assembly. These models also have major implications in the field of biomedical research. Although cell mimetics can be generated using complicated and high-cost equipment, the associated methods are costly, ...
Even a modest reduction in kidney function increases health risks in young adults
2023-06-23
A study of more than 8 million adults in Ontario, Canada suggests that even a modest loss of kidney function is associated with increased health risks. The study, published in The BMJ, could lead to better approaches to prevent chronic kidney disease and related conditions, particularly in younger adults.
“The dogma is that healthy, young adults don’t need to worry about kidney function unless it drops to around 50% of the normal level, but our research suggests that even a more modest 20-30% drop may have consequences and we may want to have earlier conversations ...
Forensic bitemark analysis for court trials is not supported by sufficient data and “is leading to wrongful convictions”
2023-06-23
The commonly-used evidence in trials, bitemark analysis, is not backed up by scientific research – an analysis of current literature, and 12 new studies, shows.
Published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the California Dental Association, the research suggests 26 people have been wrongfully convicted, and some even sentenced to death, from the use of this forensic science.
“The scientific community does not uphold the underlying premises that human teeth are unique and their unique features transfer to human skin,” states lead author Mary Bush, Associate Professor at the State University of New York in Buffalo, NY.
“We find bitemark transfer ...
COVID-19's impact on socioeconomic inequality in health behaviors among Japanese adolescents
2023-06-23
Key Findings
This study is the first worldwide to investigate time trend in socioeconomic inequality in various health behaviors among adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study found widening socioeconomic inequality among Japanese adolescents in achieving recommended physical activity levels before and during the pandemic, alongside narrowing inequality in breakfast intake. Specifically, despite no observed differences in physical activity by income in 2019, by 2021, adolescents from families with lower equivalent household incomes were less likely to engage in physical activity.
Research is needed to continue monitoring the impact these phenomena will have ...
[1] ... [1831]
[1832]
[1833]
[1834]
[1835]
[1836]
[1837]
[1838]
1839
[1840]
[1841]
[1842]
[1843]
[1844]
[1845]
[1846]
[1847]
... [8817]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.