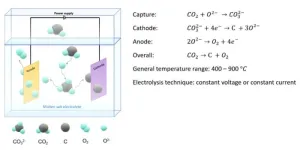
Overview of CO2 capture and electrolysis technology in molten salts: operational parameters and their effects
2023-06-26
Carbon dioxide capture, storage, and utilization have been widely researched to achieve CO2 zero emission and resolve climate change issues. Molten salt electrolysis is one promising method to simultaneously capture and convert CO2 into valuable carbon materials and oxygen with high current efficiencies, to provide a promisingly positive cash flow. However, this method still requires investigation for future scale-up applications. A team of scientists reviews the molten salt CO2 electrolysis’s ...
Researchers urge caution in gene editing early human embryos following findings that it could have unexpected and dangerous consequences Further research to refine gene editing technology is needed
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: Scientists have discovered that the cells of early human embryos are often unable to repair damage to their DNA. The researchers say that this has important implications for the proposed use of gene editing techniques to remove serious inherited diseases from embryos, as well as for IVF in general.
Presenting the research to the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1], Dr Nada Kubikova from the University of Oxford (UK), said: “Gene editing has the potential to correct defective genes, a process that usually involves first breaking and then ...
New sensor chip advances rapid, cost-effective disease diagnostics
2023-06-26
Media Inquiries to Laura Muntean, laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu, 6012481891
Written by Gabe Saldana, 956-408-5040, gabe.saldana@ag.tamu.edu
Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientists and collaborators at Iowa State University have developed a sensor chip that can detect many disease pathogens with 10 times the sensitivity of currently available methods.
The chip also eliminates the need for chemical dye reagents typically used in the diagnostic process. The new technology shows promise for rapid, low-cost point-of-care diagnostic capabilities in plants, foods, animals and humans, including detecting foodborne pathogens, bird flu and COVID-19.
An ...
Opting to freeze eggs can help women have babies when they are older, but many do not use their frozen eggs
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: More than 40% of women who chose to freeze their eggs in their 30s were able to have babies later in life when they returned to the fertility clinic, according to research presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
However, many of the women in the study who had frozen their eggs (known as elective oocyte cryopreservation) had not returned to the fertility clinic and many who did return chose fertility treatments that did not involve their frozen eggs.
The research was presented by Dr Ezgi Darici, a clinical fellow at the Centre for Reproductive Medicine at ...
Fertility may decline early in women treated for Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood, but most who try for babies when they are young are successful
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: Women treated for childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may face declining fertility at a younger age, according to research presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
The research also found that women treated for Hodgkin lymphoma may have to try for longer to become pregnant; however, the majority of women in the study who had tried to become pregnant were ultimately successful.
The research was presented by Dr Katja Drechsel from the Princess Máxima Centre for Paediatric Oncology, ...
NSF invests $162 million in research centers to accelerate materials science from lab to factory
2023-06-26
A $162 million investment from the U.S. National Science Foundation will drive the creation of advanced materials capable of remarkable things — from being tough enough to withstand the heat of a fusion reactor to processing information at the quantum level. Nine Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSECs) will each receive $18 million over six years. The centers aim to transform fundamental scientific breakthroughs into tangible benefits for multiple sectors of the U.S. economy and innovations ...
Towards synthesis of phenanthridine-based pharmaceutical compounds
2023-06-26
Phenanthridines are heterocyclic compounds consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused to a six-membered ring containing nitrogen. They are found in many naturally occurring organic compounds known for their anticancer and antitumor properties. Due to their potential medicinal applications, there is a significant interest in synthesizing phenanthridine derivatives in laboratories. A promising synthesis approach involves radical isonitrile insertion to produce imidoyl radical intermediates, which then cyclize to form phenanthridine. However, the exact mechanism of isonitrile insertion is not well understood.
Recently, a team of researchers, led by Associate Professor ...
Arsenic levels decline for most highly exposed U.S. communities served by public water systems following final arsenic ruling
2023-06-26
June 26, 2023-- Reductions in arsenic exposure among the U.S. population were reported for users of public water systems in the South and West, and among Mexican American participants, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Differences in change over time were reported by educational attainment in addition to by region, race/ethnicity, and public water arsenic level. The full findings are published in the journal Environmental Pollution.
The Final Arsenic Rule, first enforced since 2006, reduced the arsenic maximum contaminant level to 10 μg/L in public water systems.
“We ...
No simple answer for why people believe in conspiracy theories
2023-06-26
People can be prone to believe in conspiracy theories due to a combination of personality traits and motivations, including relying strongly on their intuition, feeling a sense of antagonism and superiority toward others, and perceiving threats in their environment, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
The results of the study paint a nuanced picture of what drives conspiracy theorists, according to lead author Shauna Bowes, a doctoral student in clinical psychology at Emory ...
Wiley and the European College of Sport Science announce partnership
2023-06-26
HOBOKEN, N.J. – June 26, 2023 – Wiley, a knowledge company and global leader in research, publishing and knowledge solutions, today announced that it will publish the European Journal of Sport Science (EJSS) on behalf of the European College of Sport Science (ECSS) beginning in January 2024, spearheading the journal’s transition to open access.
“EJSS is one of the preeminent multidisciplinary sport science journals,” said Allyn Molina, Vice President for Life Sciences at Wiley. “As a publisher at the forefront ...
A potential breakthrough treatment for cystic fibrosis enters clinical trial led by CI Med and U of Iowa researchers
2023-06-26
URBANA, Ill. – Clinical testing is underway for a potentially groundbreaking new treatment for cystic fibrosis. Pioneered by scientists at Carle Illinois College of Medicine at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the Carver College of Medicine at the University of Iowa in partnership with the spin-out biotechnology company, cystetic Medicines, this promising inhalable molecular prosthetic is intended to improve lung function in people with CF who cannot benefit from current therapies.
The launch of this clinical trial is an important ...
Ataxias: International Award for Bonn Patient Care and Research
2023-06-26
The Ataxia Center at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and DZNE have been awarded the title “Ataxia Center of Excellence” by the US National Ataxia Foundation (NAF) for their patient care and research – as the only organization in Europe. The foundation represents patient interests and is one of the world’s major non-governmental funders of ataxia research. These rare brain diseases are characterized by progressive loss of balance and coordination, accompanied by slurred speech. It is estimated that this condition affects around 16,000 women and men in Germany.
The NAF awarded the title “Ataxia ...
Men experience a long-term drop in semen quality after COVID infection – even if the infection was mild
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: More than three months after suffering from mild COVID infection, men have lower sperm concentrations and fewer sperm that are able to swim, according to new findings presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
Professor Rocio Núñez-Calonge, scientific advisor at UR International Group at the Scientific Reproduction Unit, Madrid (Spain), said that after an average of 100 days following SARS-CoV-2 infection there appeared to be no improvement in sperm quality ...
Cheap and safe hormone treatment shows promise for couples with unexplained infertility
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: A small study with couples experiencing unexplained infertility suggests that a hormone treatment could increase the chances of having a baby.
The trial, presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1], compared couples trying to conceive naturally with couples where the woman used a vaginal progesterone treatment during the second half of her menstrual cycle.
The researchers say a larger trial is now warranted but, given the treatment is safe and low-cost, it could ultimately benefit many people living with infertility around the world.
The study ...
50-million-year-old katydid fossil reveals muscles, digestive tract, glands and a testicle
2023-06-26
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — 50 million years ago in what is now northwestern Colorado, a katydid died, sank to the bottom of a lake and was quickly buried in fine sediments, where it remained until its compressed fossil was recovered in recent years. When researchers examined the fossil under a microscope, they saw that not only had many of the insect’s hard structures been preserved in the compressed shale, so had several internal organs and tissues, which are not normally fossilized.
They describe their findings in the journal Palaeoentomology.
“Katydids ...
Are more babies born if embryos are cultured for three or five days in the lab? Largest randomised clinical trial to date suggests that age matters
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: Women are just as likely to give birth to live babies after fertility treatment if embryos are transferred to their wombs three days after fertilisation in the laboratory rather than five. However, the women’s age can affect the outcomes, according to new research presented to the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
Dr Simone Cornelisse, a researcher and resident in obstetrics and gynaecology at Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen (The Netherlands), told the conference that among 1202 women from 21 Dutch fertility centres who were randomly assigned to have embryos transferred to their wombs ...
Cancer risk among women with polycystic ovary syndrome doubles after menopause
2023-06-26
Copenhagen, Denmark: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are not at any greater risk of ovarian cancer than those without the common hormone condition, say researchers. However, those with PCOS who have been through the menopause are more than twice as likely to be diagnosed with ovarian cancer.
The data based on nearly two million women is presented today (Monday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1]. The research is also published simultaneously in the International Journal of Cancer [2].
This ...
Humans’ evolutionary relatives butchered one another 1.45 million years ago
2023-06-26
Researchers from the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History have identified the oldest decisive evidence of humans’ close evolutionary relatives butchering and likely eating one another.
In a new study published today, June 26, in Scientific Reports, National Museum of Natural History paleoanthropologist Briana Pobiner and her co-authors describe nine cut marks on a 1.45 million-year-old left shin bone from a relative of Homo sapiens found in northern Kenya. Analysis of 3D models of the fossil’s surface revealed ...
Childhood cancer: Vulnerability in the immune response against metastases discovered
2023-06-26
Scientists led by Sabine Taschner-Mandl, PhD, St. Anna Children's Cancer Research Institute, and Nikolaus Fortelny, PhD, Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, are the first to analyze bone marrow metastases from childhood tumors of the nervous system using modern single-cell sequencing analysis. It turns out that cancer cells prevent cells in their environment from fighting the tumor – a process that could be reversed with medication. The findings were published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Neuroblastoma is the most ...
Novel study deepens knowledge of treatment-resistant hypertension
2023-06-26
For many patients with hypertension—an elevated blood pressure that can lead to stroke or heart attack—medication keeps the condition at bay. But what happens when medication that physicians usually prescribe doesn’t work? Known as apparent resistant hypertension (aRH), this form of high blood pressure requires more medication and medical management.
Novel research from investigators in the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Hypertension, found that aRH prevalence was lower in ...
Progesterone decreases night sweats & improves sleep in perimenopausal women
2023-06-26
New controlled trial research documents that Progesterone (micronized, oral) is effective at decreasing night sweats and improving sleep in perimenopausal women who have menstruated in the last 1-year. Perimenopausal women most want treatment for these two symptoms.
Current guidelines prescribe Menopausal Hormone Therapy (MHT) for disturbing hot flushes/flashes or night sweats (vasomotor symptoms, VMS) in all women younger than 60 years.
“This guideline assumes that hormone levels and symptoms are the same in the early years of ...
What are the endometrial cancer risks and trends among different African descent populations?
2023-06-26
Study reveals some distinctions between Black women in the US and the French Caribbean but increasing trends for aggressive forms in both regions.
Compared with white women, Black women have elevated risks of being diagnosed with advanced uterine cancer—also known as endometrial cancer—and of developing aggressive tumors. Researchers recently compared the incidence and trends for endometrial cancer, both overall and by subtype, between African descent women in Florida and women in the French Caribbean—specifically, the islands of Martinique and Guadeloupe. The findings are published by Wiley online ...
Endometrial cancer risk and trends among distinct African-descent populations
2023-06-26
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL 3:01 AM ET Monday, June 26, 2023) – Current evidence indicates Black women in the U.S. are at greater risk of developing advanced uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, and of developing its more aggressive form – non-endometroid cancer – than white women.
But research to date has mostly studied Black women as a homogenous group, and there is limited data about specific African-descent subpopulations worldwide. That is until now.
A new study by researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine compared both the overall incidence and trends for endometrial ...
New Orleans infection preventionists adapt adult protocols to reduce infections in babies
2023-06-26
Orlando, Fla., June 26, 2023 – Facing persistent cases of hospital-onset Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) during the pandemic, the infection prevention and control (IPC) team at Children’s Hospital New Orleans developed an inexpensive nasal decolonization regimen previously used only in their adult patients that decreased rates of MRSA by 50 percent. Their results are being presented at the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology’s (APIC’s) Annual Conference in Orlando Florida, June 26-28.
Without a lot of scientific literature on nasal decolonization in the pediatric population to guide them, Infection Preventionist ...
Neurosurgical infections drop more than 80% in two years at Pittsburgh hospital
2023-06-26
Neurosurgical Infections Drop More Than 80% in Two Years at Pittsburgh Hospital
Readmissions, patient satisfaction scores improve through infection preventionist-led, multidisciplinary collaboration
Orlando, Fla. June 26, 2023 – When excess surgical site infections (SSIs) were detected among neurosurgery patients at University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) Mercy in 2019, infection preventionist Katie Palladino, MPH, CPH, CIC, partnered with a hospital neurosurgeon on a multidisciplinary quality and process improvement initiative that ...
[1] ... [1827]
[1828]
[1829]
[1830]
[1831]
[1832]
[1833]
[1834]
1835
[1836]
[1837]
[1838]
[1839]
[1840]
[1841]
[1842]
[1843]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.