Chemists develop new method to create chiral structures
2023-06-29
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Some molecules exist in two forms such that their structures and their mirror images are not superimposable, like our left and right hands. Called chirality, it is a property these molecules have due to their asymmetry. Chiral molecules tend to be optically active because of how they interact with light. Oftentimes, only one form of a chiral molecule exists in nature, for example, DNA. Interestingly, if a chiral molecule works well as a drug, its mirror image could be ineffective for therapy.
In ...
The first neutrino image of our galaxy
2023-06-29
For the first time, researchers have produced an image of the Milky Way using neutrinos, which were observed with the IceCube telescope in the Antarctic ice. The neutrino image suggests that cosmic ray interactions are more intense in the center of our galaxy than once thought. The results are published in an article in the journal Science.
For ages, the view of our Milky Way galaxy has inspired awe, visible with the naked eye as a hazy band of stars that stretches across the sky. Now IceCube researchers are able to see the Milky Way using neutrinos – tiny, ghostlike ...
DNA organization in real-time
2023-06-29
Performing cutting-edge science requires thinking outside the box and bringing together different scientific disciplines. Sometimes this even means being in the right place at the right time. For David Brückner, postdoctoral researcher and NOMIS fellow at ISTA, all the above-mentioned things came into effect as he attended an on-campus lecture by Professor Thomas Gregor from Princeton University. Inspired by the talk, Brückner reached out with an idea: to physically interpret the specific data sets Gregor presented. Now, the results of their collaboration are published ...
JDR Clinical & Translational Research receives first ever Impact Factor™
2023-06-29
Alexandria, VA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) and the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) announced today the JDR Clinical & Translational Research (JDR CTR) has received its first Journal Impact Factor™.
JDR CTR has earned a Journal Impact Factor of 3.0, with an Eigenfactor™ of 0.00148, an Immediacy Index of 0.5, and 786 total citations in 2022. This represents a significant achievement and a huge milestone in JDR CTR’s history, which was launched in 2016.
“JDR CTR’s new Impact Factor marks the culmination of years of commitment ...
Journal of Dental Research announces New Impact Factor™
2023-06-29
Alexandria, VA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research announced the Journal of Dental Research (JDR) 2-Year Journal Impact Factor™ is now 7.6, ranking it #3 of 91 journals in the “Dentistry, Oral Surgery & Medicine” category.
The JDR 5-year Journal Impact Factor™ is also 7.6, with an Immediacy Index of 1.1 and an article Influence score of 1.638. The JDR once again ranked #1 of 91 journals in total citations, with a total of 25,849 in 2022, and ranked #3 in Eigenfactor with a score of 0.01345.
The 2-year Journal Impact Factor™ is defined ...
NASA’s Webb identifies the earliest strands of the cosmic web
2023-06-29
Galaxies are not scattered randomly across the universe. They gather together not only into clusters, but into vast interconnected filamentary structures with gigantic barren voids in between. This “cosmic web” started out tenuous and became more distinct over time as gravity drew matter together.
Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have discovered a thread-like arrangement of 10 galaxies that existed just 830 million years after the big bang. The 3 million light-year-long structure is anchored by a luminous quasar – a galaxy with an active, supermassive black hole at ...
Improvement to CRISPR gene editing could make it more effective
2023-06-29
DURHAM, N.C. – CRISPR gene editing is a breakthrough that has been used to treat diseases such as sickle cell anemia, leukemia and genetic disorders, but it has challenges that limit its broad utility.
Identifying the root of those issues led a research team at Duke Health to find an improved approach to gene editing that expands its functionality.
In work appearing online June 29 in the journal Cell Chemical Biology, the researchers lay out a new way to identify diverse CRISPR RNA variants that can specifically home in on challenging areas of DNA to target for editing. The new approach opens up more of the genome for editing, ...
Water fasts can help you lose weight, but you might gain it back quickly
2023-06-29
Water fasts — where people consume nothing but water for several days — might help you lose weight, but it’s unclear how long you’ll keep it off, according to research from the University of Illinois Chicago. And the other metabolic benefits of water fasts, such as lower blood pressure and improved cholesterol, seem to disappear soon after the fast ends, the researchers found.
However, there do not appear to be any serious adverse effects for those who do a water fast or a similar kind of fast where people consume a very small number of calories a day, said Krista Varady, professor of kinesiology and nutrition, who led the research, ...
Energy insecurity is an underappreciated social and environmental determinant of health
2023-06-29
In light of climate change and the impending transition to clean energy, many long-standing programs to address energy insecurity need to be refreshed. A new paper published online in the journal Health Affairs provides growing documentation of the connections between energy insecurity and poor health. The paper, by Diana Hernandez, PhD, associate professor of sociomedical sciences at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, also offers an overview of current policy initiatives and discusses ways that current policies can be improved upon.
The average U.S. household allocates 3.1 percent of its income to energy expenses but for low-income households, ...
Current developments in nutrition debuts strong with its first impact factor
2023-06-29
Rockville, MD – The latest journal impact factors and rankings reflect the high-quality research that is published each year by the American Society for Nutrition (ASN).
Scopus recently ranked Advances in Nutrition the number one journal in the Nutrition and Dietetics field. The Society’s newest journal, Current Developments in Nutrition, surpassed expectations with an excellent inaugural impact factor of 4.8 confirming its promising future.
“I am delighted to receive such a superb first impact factor,” stated Jack Odle, PhD, William Neal Reynolds Distinguished Professor at North Carolina State University and Editor-in-Chief of Current ...
CHEST releases clinical practice guideline on antithrombotic therapy in arterial thrombosis and thromboembolism in COVID-19
2023-06-29
Glenview, Illinois – The American College of Chest Physicians® (CHEST) recently released a new clinical guideline on antithrombotic therapy in arterial thrombosis andthromboembolism in COVID-19. Published in the journal CHEST®, the guideline contains 11 evidence-based recommendations to improve risk-evaluation and to assist in determining the course of treatment.
While there are guidelines for the management of COVID-19-related coagulopathy for venous thromboembolism (VTE), a recent large cohort study showed ...
UTHSC College of Pharmacy rises to No. 6 in research funding from National Institutes of Health
2023-06-29
The College of Pharmacy at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center is now ranked No. 6 in annual research funding from the National Institutes of Health, according to a new listing published by the American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy of its approximately 140 member institutions.
“The ranking of No. 6 in NIH funding for federal fiscal year 2022 is external validation for the UTHSC College of Pharmacy’s standing as one of the leading institutions in research among the 142 U.S. pharmacy schools,” said Bernd Meibohm, ...
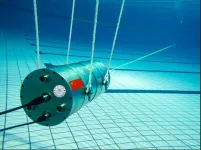
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks
2023-06-29
WASHINGTON — Researchers report a new single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances. They also show that the new system can detect the thickness of the oil underwater up to 12 m away, which could be useful for detecting oil spills.
“Differentiating substances in water and detecting their distribution characteristics in the ocean are of great significance for marine monitoring and scientific research,” said research team leader Mingjia Shangguan from Xiamen University in China. “For instance, the remote sensing of underwater oil that we ...
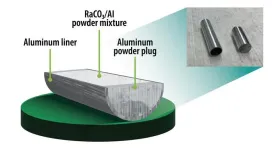
Faster, safer target prep
2023-06-29
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have developed a method to simplify one step of radioisotope production — and it’s faster and safer.
ORNL produces several radionuclides from irradiated radium-226 targets, including actinium-227 and thorium-228, both used in cancer treatments. Continuously improving isotopes for human health is one of the lab’s missions.
Currently, it takes workers two weeks to prepare radium-226 targets for irradiation in the High Flux Isotope Reactor. The targets are exposed to radiation throughout the process, which involves pressing radium carbonate aluminum composite into 10 pellets — one each day — and sealing ...
Health care utilization following interventions to improve social well-being
2023-06-29
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis including 41 studies and 7,800 participants found that psychosocial interventions were associated with decreased health care use in most health services and increased use of outpatient care. The greatest health care decrease was among caregivers and individuals with mental illnesses and in interventions delivered 1-on-1 by health professionals.
Authors: Neta HaGani, M.S.W., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
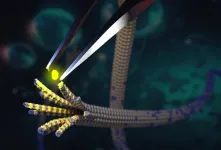
Transferring data with many colors of light simultaneously
2023-06-29
New York, NY—June 29, 2023—The data centers and high-performance computers that run artificial intelligence programs, such as large language models, aren’t limited by the sheer computational power of their individual nodes. It’s another problem — the amount of data they can transfer among the nodes — that underlies the “bandwidth bottleneck” that currently limits the performance and scaling of these systems.
The nodes in these systems can be separated by more than one kilometer. Since metal wires dissipate electrical signals as heat when transferring data at high speeds, these systems transfer data via fiber-optic ...
An early predictor of cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease
2023-06-29
Have you ever felt the strong sensation that someone is behind you, so intense that you turn around, only to see that no-one is there? This is a 'presence hallucination’. Presence hallucinations are particularly frequent but underreported in patients with Parkinson’s disease and may appear early on in the course of the disease. They are sometimes ignored by the patient, by clinicians, or brushed off as a simple side-effect of medication.
Now, EPFL scientists have found that patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and who have early hallucinations are ...
Cracking the tubulin code
2023-06-29
Tubulin is a protein that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of cells. It is the main component of microtubules, which are long, hollow fibers that provide structural support, help the cell divide, give it its shape, and act as tracks for moving molecular cargo around inside the cell.
There are two types of tubulin: alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin. Together, they form dimeric (two-part) building blocks, spontaneously assembling into microtubules that undergo further continuous cycles of assembly and disassembly.
The tubulin code
To fine-tune microtubules, the dimers undergo various post-translational modifications (PTMs), which are chemical modifications that occur ...
Amander T. Clark takes on new role as President of the ISSCR
2023-06-29
Skokie, IL – The ISSCR is pleased to announce Amander T. Clark, PhD, Professor of Molecular, Cell and Developmental Biology, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), USA, as its President. Dr. Clark’s one-year term of office leading the global society begins 1 July 2023.
“I will work to ensure that the society continues to defend stem cell science and the researchers working to transform lives,” Dr. Clark said at the ISSCR 2023 Annual Meeting in Boston this month. “We will expand our engagement with the public ...
New AI tool beats standard approaches for detecting heart attacks
2023-06-29
A new machine learning model uses electrocardiogram (ECG) readings to diagnose and classify heart attacks faster and more accurately than current approaches, according to a study led by University of Pittsburgh researchers that published today in Nature Medicine.
“When a patient comes into the hospital with chest pain, the first question we ask is whether the patient is having a heart attack or not. It seems like that should be straightforward, but when it’s not clear from the ECG, it can take ...
Proteins predict significant step toward development of diabetes
2023-06-29
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scientists have taken an important step forward in predicting who will develop Type 1 diabetes months before symptoms appear.
In a paper published online on June 29 in Cell Reports Medicine, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and their colleagues identify a set of altered proteins that predict a condition known as islet autoimmunity, a precursor for everyone who will ultimately develop Type 1 diabetes.
The scientists caution that the work marks a beginning, not the end, of a search for a way to predict who will develop the disease. More work needs to be done ...
Sociogenomics: The intricate science of how genetics influences sociology
2023-06-29
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Humans contain multitudes. Each person on the planet contains enough DNA to stretch to Pluto – several times.
Studying how all this genetic material works, and especially how genes influence human behavior, is an enormously complicated undertaking – one that’s being made easier by the emergence of massive banks of genetic data and complex data science analysis techniques to parse that data.
Robbee Wedow, an assistant professor of sociology and data science in Purdue University’s College of Liberal Arts, an adjunct assistant professor of ...
City of Hope appoints David W. Craig, Ph.D., as founding chair of its new Department of Integrative Translational Sciences within its Beckman Research Institute
2023-06-29
LOS ANGELES — City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, today announced that effective June 30, David W. Craig, Ph.D., will be professor and founding chair of its newly created Department of Integrative Translational Sciences within Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope. Craig also will serve as deputy director of translational sciences at Beckman Research Institute and associate ...
A seed survival story: How trees keep ‘friends’ close and ‘enemies’ guessing
2023-06-29
UNIVERSITY PARK — Around the globe, forests are facing unprecedented challenges. They're grappling with wildfires, diseases, droughts and deforestation. The survival of these great forests hinges on their ability to regrow — and for many trees, a process called "masting" is key to this regeneration.
Masting — the unpredictable boom-and-bust cycle of seed production — can have profound consequences for plant populations and the food webs that are built on their seeds. But the complex relationship between seed-production cycles and seed consumers ...
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices
2023-06-29
Overheating of wearable skin-like electronic devices increases the risk of skin burning and results in performance degradation. A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) invented a photonic material-based “soft, ultrathin, radiative-cooling interface” that greatly enhances heat dissipation in devices, with temperature drops more than 56°C, offering an alternative for effective thermal management in advanced wearable electronics.
“Skin-like electronics are an emerging development in wearable devices,” said Dr Yu Xinge, Associate Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME) at CityU, who co-led the research. “Effective thermal ...
[1] ... [1819]
[1820]
[1821]
[1822]
[1823]
[1824]
[1825]
[1826]
1827
[1828]
[1829]
[1830]
[1831]
[1832]
[1833]
[1834]
[1835]
... [8819]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.