A step toward treating chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer
2023-07-12
Prostate cancer is a leading cause of death among American men, and it’s resistant to one of the most powerful chemotherapy medications — cisplatin. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed the first therapy of its kind that disrupts prostate cancer cells’ metabolism and releases cisplatin into the weakened cells, causing them to die. In mouse models, an orally administered version shrunk tumors substantially.
Cisplatin attacks testicular, breast, bladder, lung and ovarian cancer cells, damages their DNA and effectively destroys tumors. However, it’s not effective against prostate cancer ...
A new tactic to take on leprosy
2023-07-12
Leprosy has existed since at least Biblical times, yet scientists still don’t know exactly how Mycobacterium leprae causes the disease’s symptoms. Though antibiotics can treat the illness, researchers are concerned about the increase in drug-resistant strains. Now, a team reporting in ACS Central Science has begun to understand the unique role certain immune receptors play in leprosy infections in mice, which could lead to new types of treatments for this disease and others in humans.
Thousands of people are currently affected by leprosy — also known as Hansen’s disease — according to the World Health Organization. The disease can cause skin ...
Ohio train derailment, clean-up resulted in high levels of some gases, study shows
2023-07-12
A freight train carrying industrial chemicals derailed near East Palestine, Ohio, in February 2023, and to avoid explosions, authorities conducted a controlled release and burned the cars’ contents. Residents were worried about their health and the environment, so researchers have been assessing the local air quality with stationary and mobile sampling methods. Now, in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, they report that some gases, including acrolein, reached levels that could be hazardous.
After the derailment, disaster response teams ...
EMBARGOED: In preclinical study, Sylvester researchers target treatment-resistant prostate cancer with oral chemotherapy that works 2 ways
2023-07-12
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 12, 2023, AT 8AM ET) – Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have developed a first-of-its-kind, orally administered drug to disrupt prostate cancer cells’ metabolism and deliver the chemotherapy agent cisplatin directly into treatment-resistant prostate cancer cells.
They validated their targets in human prostate cancer biopsies, tested the new approach in human cancer cells and a mouse model ...
2018–2022 Southern Resident killer whale presence in the Salish Sea: continued shifts in habitat usage
2023-07-12
Monika Wieland Shields, Director of the Orca Behavior Institute, has observed orcas in the Salish Sea, a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington, since 2000. She has recently published an article in the peer-reviewed Open Access journal PeerJ Life & Environment that provides crucial insights into the changing habitat usage of the critically endangered Southern Resident killer whales (Orcinus orca), shedding light on historic trends and the current status of the population in the Salish Sea. ...
$3.9M grant funds e-cigarette flavoring research at Ohio State’s Center for Tobacco Research
2023-07-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new $3.9 million grant from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will allow researchers with the Center for Tobacco Research at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center to evaluate effects of e-cigarette flavors on the smoking behaviors of current adult smokers.
The study, co-led by Theodore Wagener, PhD, director of Ohio State’s Center for Tobacco Research, and Tracy Smith, PhD, of the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) Hollings Cancer Center, will be the first ...
Gut bacteria linked to fatty deposits in heart arteries
2023-07-12
In a major Swedish study, researchers have discovered a link between the levels of certain bacteria living in the gut and coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Such atherosclerotic plaques, which are formed by the build-up of fatty and cholesterol deposits, constitute a major cause of heart attacks. The study was led by researchers at Uppsala and Lund University and the findings have now been published in the scientific journal Circulation.
The new study was based on analyses of gut bacteria and cardiac imaging among 8,973 participants aged 50 to 65 from Uppsala and Malmö without previously known heart disease. They were all ...
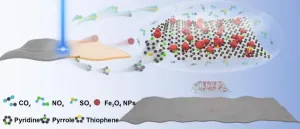
Study reveals new mechanism for rapid evolution of multi-drug resistant infections in patients
2023-07-12
Findings challenge the traditional view that antimicrobial resistance (AMR) emerges from pathogens that acquire new mutations
Samples from ICU patients suggest that instead, highly diverse pathogen communities harbour pre-existing resistant genotypes
The results suggest that interventions aimed at limiting the spread of bacteria between patients may provide a powerful approach to combat AMR.
A research study led by the University of Oxford provides a transformational new insight into how antimicrobial resistance (AMR) emerges in patients with bacterial infections. The findings, published today in the journal ...
Blood pressure patterns in the first half of pregnancy improve early prediction of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension
2023-07-12
Routine blood pressure readings recorded in the first half of pregnancy can be divided into 6 distinct patterns that can effectively stratify patients by their risk of developing preeclampsia and gestational hypertension later in pregnancy, Kaiser Permanente researchers found.
The study, published July 12 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, showed that 6 pregnancy blood pressure trajectories seen within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy along with clinical, social, and behavioral risk factors can accurately predict and stratify risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension in low- to moderate-risk patients. ...
Gulf War illness caused by mitochondrial dysfunction, not inflammation
2023-07-12
Gulf War Illness (GWI) is a chronic multisymptom health condition affecting one-third of all veterans who served in the 1991 Gulf War, most of whom remain afflicted more than 30 years later. Common symptoms include fatigue, headaches, muscle aches, joint pain, diarrhea, insomnia and cognitive impairment.
The condition is believed to have been triggered by veterans’ exposure to environmental toxins. However, its exact mechanism in the body continues to be debated, making it difficult to diagnose and treat. The prevailing ...
Queen Mary-led research uncovers why people who have Down’s Syndrome age prematurely
2023-07-12
An overdosed gene on chromosome 21 causes people with Down’s Syndrome to age faster than the general population.
The molecular processes responsible for natural ageing of cells are poorly understood. Studying conditions in humans where ageing is accelerated due to genetic causes presents opportunities to learn about the mechanisms that control ageing and devise strategies to slow down the ageing process.
Adults who have Down’s Syndrome (DS) show earlier signs of ageing-related conditions: reduction in tissue regenerative capacity, alopecia, dry skin, ...
Scientists find evidence of world’s oldest glaciers
2023-07-12
Scientists have discovered the traces of the world’s oldest known glaciers, dating from 2.9 billion years ago, in rocks sitting under the world’s largest gold deposits in South Africa. This suggests the presence of continental ice caps at that time and that either the area was closer to the poles, or that parts of the Earth may have been frozen in a previously unknown “snowball Earth” period of extreme cold weather. This work is presented for the first time at the Goldschmidt geochemistry conference in Lyon, after recent peer-reviewed ...
Sea snakes may have evolved to see colors again
2023-07-12
A new paper in Genome Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, finds that the annulated sea snake, a species of venomous snake found in ocean waters around Australia and Asia, appears to have evolved to see an extended palette of colors after its ancestors lost that ability in response to changing environments.
Color vision in animals is primarily determined by genes called visual opsins. While there have been multiple losses of opsin genes during the evolution of tetrapods (the group including amphibians, reptiles, and mammals), the emergence of new opsin genes is extremely ...
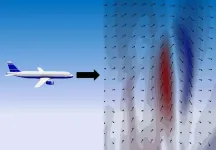
Supercomputer used to simulate winds that cause clear air turbulence
2023-07-12
A research group from Nagoya University has accurately simulated air turbulence occurring on clear days around Tokyo using Japan’s fastest supercomputer. They then compared their findings with flight data to create a more accurate predictive model. The research was reported in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Although air turbulence is usually associated with bad weather, an airplane cabin can shake violently even on a sunny and cloudless day. Known as clear air turbulence (CAT), these turbulent ...
Sea snake vision evolved to regain color
2023-07-12
An international team of scientists examining the genetic history of sea snakes have found that the species has enhanced their colour vision in response to living in brighter and more colourful marine environments.
“Our research has found that the annulated sea snake possesses four intact copies of the opsin gene SWS1,” said PhD candidate Isaac Rossetto, from the University of Adelaide’s School of Biological Sciences who led the study.
“Two of these genes have the ancestral ultraviolet sensitivity, and two have evolved a new sensitivity to the longer wavelengths that dominate ocean habitats.
“The earliest ...
Scientists developed 180% relative bandwidth microwave absorber by ultrafast UV laser
2023-07-12
Scientists from Chinese Academy of Sciences Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, National Physical Laboratory (UK), The University of Manchester (UK) and National University of Singapore have developed a new approach, published in International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing (IF: 14.7), to fabricate a specifically designed wideband microwave absorption metamaterial with well-controlled electrical and magnetic characteristics on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate using ultraviolet (UV) laser irradiation.
The process involves using a UV laser to precisely control the characteristics of 2-D pattern on a specially formulated donor ...
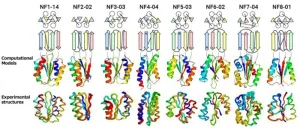
Beyond nature's imagination: Scientists discover extensive array of protein folds unexplored in nature
2023-07-12
A groundbreaking study has shed new light on the astonishing diversity of protein structures and their folds in nature. Researchers set out to reveal the extent to which nature has explored the vast landscape of possible protein topologies. The results have unveiled an astounding array of unexplored protein folds, expanding our understanding and uncovering the depth of the protein universe.
This research has been published in the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology on July 3, 2023.
Proteins, ...
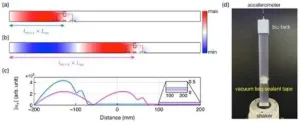
Bound states in the continuum is possible in the acoustoelastic coupling
2023-07-12
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario where two individuals are gripping a rope, each holding one end. Person A proceeds to shake the rope in an up-and-down motion, thus generating a propagating wave that travels towards person B. Now, if person C, positioned between person A and B, engages in a comparable frequency of waving motion as that of the rope’s wave, could the wave be redirected back to person A rather than reaching person B? Initially, this situation appears implausible, as person C does not physically ...
Pre-operative exercise substantially helps with recovery – study
2023-07-12
Policy-makers are being urged to take notice of a University of Otago study that confirms that undertaking a short programme of high intensity interval training before surgery can substantially help with recovery.
The study, published in the journal Surgery, reviewed and analysed 12 studies including 832 patients who had undertaken preoperative high-intensity interval training. Such training involves repeated aerobic high-intensity intervals at about 80 per cent of the maximum heart rate followed by active recovery.
Lead investigator Dr Kari Clifford says the study included all types of major surgeries – those expected ...
Scientists developing way to make cheaper Lithium batteries
2023-07-12
Lyon, France: Lithium is becoming the new gold, with rocketing use in lithium-ion batteries in electric cars, computers, and portable devices driving up the price and affecting the supply of the relatively rare metal. Scientists are on the verge of developing a way of using sodium to replace some of the lithium, so driving down costs and guaranteeing the supply.
Recently scientists have looked at dispensing with lithium altogether and instead using sodium or other elements in high quality batteries. Sodium is cheaper and more available (it’s found in seawater, as sodium chloride), but they have ...
Plant Biology 2023 plenary closeup: Connecting the dots
2023-07-12
This year’s Presidential Symposium places plant science within a larger context, spotlighting the connections between plants and humanity. Accordingly, ASPB President Gustavo MacIntosh selected speakers with a broad array of backgrounds and expertise. Yet when the Presidential Symposium takes place Saturday, August 5, at 1:30 pm, you’ll find they agree on critical fundamentals.
“Humans are totally dependent on plants for food,” began Barbara Schaal of Washington University.
“When it comes to agriculture, plants and people are really ...
Tiny fish surprise scientists in ‘volunteer’s dilemma’
2023-07-12
Tiny fish called Trinidadian guppies have surprised scientists when faced with the so-called “volunteer’s dilemma”.
The idea of the dilemma is that individuals are less likely to cooperate if they are in a large group.
Various studies have demonstrated this in humans – but guppies appear to buck the trend.
In the new study, by the University of Exeter, guppies in larger groups were more likely to risk approaching a predator to gather information for the shoal.
“When faced with a possible predator, guppies have to balance risks,” said Rebecca Padget, from Exeter’s Centre for Research in Animal Behaviour.
“At least one ...
Six research centers will lead innovation towards a fully sustainable energy sector
2023-07-12
An investment of £53 million in six research centres will drive forward change in the energy system and help to meet the UK’s net zero target by 2050.
The energy research centres will boost knowledge, create innovative green technologies and reduce demand for energy to achieve greener, cleaner domestic, industrial and transport energy systems.
UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) has awarded:
£15 million for a new Energy Demand Research Centre that will provide solutions for energy demand reduction, understand the impact on consumers, and enable equitable policy decision-making.
£17.5 ...
Training robots how to learn, make decisions on the fly
2023-07-12
Mars rovers have teams of human experts on Earth telling them what to do. But robots on lander missions to moons orbiting Saturn or Jupiter are too far away to receive timely commands from Earth. Researchers in the Departments of Aerospace Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign developed a novel learning-based method so robots on extraterrestrial bodies can make decisions on their own about where and how to scoop up terrain samples.
“Rather than simulating how to scoop every possible type of rock or granular material, ...
Substance use linked to long-lasting brain changes, cognitive decline
2023-07-12
An estimated 50 million individuals in the United States struggle with the challenges of cocaine or alcohol use disorders, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Beyond the well-documented health risks, addiction to these substances detrimentally affects our cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to adapt and switch between different tasks or strategies. Although previous research has hinted at this connection, the underlying reasons for this cognitive impairment remain elusive.
Cognitive flexibility is a crucial element in various domains of our life, including ...
[1] ... [1816]
[1817]
[1818]
[1819]
[1820]
[1821]
[1822]
[1823]
1824
[1825]
[1826]
[1827]
[1828]
[1829]
[1830]
[1831]
[1832]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.