Tracking ships’ icy paths amidst climate change
2023-07-05
There has been much buzz about the warming planet’s melting Arctic region opening shipping routes and lengthening travel seasons in ocean passageways that ice once blocked. Expanded fishing, trade and tourism is envisioned.
Operative word: Envisioned.
Scientists at Michigan State University (MSU), University of Waterloo, and University of Alaska Fairbanks report in Climatic Change where vessels are traveling in the ice-covered waters of the Arctic between Alaska and Russia, and what those reports may mean for important wildlife and communities in the region.
“Even with climate change, sea ice is still a substantial barrier to Arctic vessel traffic,” said Kelly Kapsar, ...
Study shines light on why companies use a variety of dark money strategies
2023-07-05
AUSTIN, Texas — As public concerns mount over lack of transparency in political giving, a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin is the first to illuminate how and why corporations choose to legally conceal their lobbying and campaign contributions.
U.S. companies are required to disclose the total amount they spend on political activity, but beyond that, the disclosure is incredibly vague, according to Tim Werner, associate professor of business, government and society at the McCombs ...
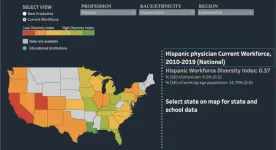
Health professions requiring advanced degrees have few Latinos
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON (July 5, 2023)--Although the situation is improving, Latinos and especially Mexican Americans, remain very underrepresented in U.S. health professions that require advanced degrees, according to a study published today in the journal Health Affairs. The study by George Washington University researchers is the first to examine the representation of the four largest Latino populations in the U.S. health workforce and the findings raise concerns about the lack of diversity in the U.S. health workforce.
The study ...
Fluctuating levels of cholesterol and triglycerides linked to increased risk of dementia
2023-07-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JULY 5, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Older people who have fluctuating levels of cholesterol and triglycerides may have a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias compared to people who have steady levels, according to new research published in the July 5, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. While the study found a link, it does not prove that fluctuating levels of cholesterol and triglycerides cause dementia.
“Prevention strategies for Alzheimer’s and related dementias are urgently needed,” ...
Study finds scant coverage for seniors’ mental health care
2023-07-05
Amid heightened demand for mental health care, a new study finds that nearly two-thirds of Medicare Advantage psychiatrist networks contain less than 25% of all psychiatrists in a given service area.
“This means that many people who have coverage through Medicare Advantage plans may not actually have access to psychiatrists, given how few are considered in-network,” said lead author Jane Zhu, M.D., assistant professor of medicine (general internal medicine and geriatrics) in the School of Medicine at Oregon Health & Science University.
The research published today in the July issue of the journal Health Affairs.
Medicare is the federal ...
New study shows Medicaid expansion associated with increase in palliative care for patients with advanced cancers
2023-07-05
ATLANTA, July 5, 2023 – More people with advanced cancers in the United States received critical palliative care services, according to new findings by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS). Palliative care includes supportive care managed by a healthcare team, such as relief from symptoms, pain, and stress. Researchers also found where a patient lives in the U.S. may determine their use of palliative care. Medicaid expansion under the ACA was associated with the largest increases in palliative care use. The study was published today in the July issue of the journal Health Affairs.
“Our findings are encouraging, especially with growing evidence of the important ...
Taking good care of your teeth may be good for your brain
2023-07-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JULY 5, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Taking good care of your teeth may be linked to better brain health, according to a study published in the July 5, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study found that gum disease and tooth loss were linked to brain shrinkage in the hippocampus, which plays a role in memory and Alzheimer’s disease. The study does not prove that gum disease or tooth loss causes Alzheimer’s disease; it only shows an association.
“Tooth ...
The time is right to attract new public health workers with evidence-based job descriptions and eye-catching job postings
2023-07-05
July 5, 2023-- Health departments have a historic opportunity to bolster their workforce due to new funding but often do not have accurate or updated job descriptions or short, attention-grabbing job postings to use as marketing tools for recruitment. New research by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health will help lead to evidence-based job descriptions and postings that health departments can now use.
The study is the first attempt to compile existing occupation-specific job task analyses, lists of competencies, and certifications across multiple job types within governmental public health that can allow comparisons of ...
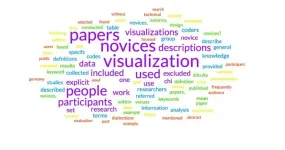
Know your audience: Why data communication needs to pay attention to novice users
2023-07-05
AMHERST, Mass. – Computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently found that data-visualization experts have no agreed-upon understanding of who makes up one of their largest audiences—novice users. The work, which recently won a coveted Best Paper Award at the Association for Computing Machinery’s conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI), is an important first step in ensuring more inclusive data visualizations, and thus data visualization that works for all users.
Data visualization is the representation of data in a ...
New genetic technology developed to halt malaria-spreading mosquitoes
2023-07-05
Malaria remains one of the world’s deadliest diseases. Each year malaria infections result in hundreds of thousands of deaths, with the majority of fatalities occurring in children under five. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently announced that five cases of mosquito-borne malaria were detected in the United States, the first reported spread in the country in two decades.
Fortunately, scientists are developing safe technologies to stop the transmission of malaria by genetically editing mosquitoes that spread the parasite that causes the disease. Researchers at the University of California San Diego led by Professor Omar Akbari’s laboratory have engineered ...
The Jackson Laboratory wins 2023 Plan Sponsor of the Year award in recognition of employee retirement plan
2023-07-05
The Jackson Laboratory has won the 2023 Plan Sponsor of the Year award in the “Nonprofit Defined Contribution Plans $300 Million and Greater” category. The annual Plan Sponsor of the Year award is presented by PLANSPONSOR magazine, a professional publication that focuses on retirement programs. The award recognizes retirement plan sponsors that show a commitment to their participants’ financial health and retirement success. Winners were announced at the PLANSPONSOR National Conference in Orlando, Fla. on June 21.
“Benefits such as ...
Children’s nature drawings reveal a focus on mammals and birds
2023-07-05
When asked to draw their local wildlife, 401 UK schoolchildren aged 7 to 11 most commonly drew mammals and birds, while amphibians and reptiles appeared in the fewest drawings, suggesting imbalances in children’s ecological awareness. Kate Howlett and Edgar Turner of the University of Cambridge, UK, present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 5, 2023.
Prior research has shown that, overall, European and North American children’s access to green space has declined in recent decades, and they are becoming increasingly disconnected from nature. Access ...
No increase in mortality for most overweight people, study finds
2023-07-05
Body mass index (BMI) may not increase mortality independently of other risk factors in adults, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Aayush Visaria and Soko Setoguchi of Rutgers University, US.
The prevalence of overweight and obesity has risen dramatically over the last 25 years, and it is well-established that elevated BMI can contribute to several cardio-metabolic conditions. However, studies that have analyzed the association between BMI and all-cause mortality have been inconsistent. Most US studies have used data from the 1960s through 1990s and have included predominantly non-Hispanic White adults.
In the new work, the researchers ...
Playing with kids could help improve the mental wellbeing of retirement home residents
2023-07-05
A study conducted at a retirement home in South Africa suggests that programs promoting interaction between residents and children may provide mental health benefits and could help manage common mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression. Elizabeth Jane Earl and Debbie Marais of Stellenbosch University, South Africa, present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 5, 2023.
Prior research suggests that common mental health conditions are often undiagnosed and untreated in retirement homes. Standard treatment for such conditions typically involves a combination of medication and non-pharmacological ...
Scent of a woman: Hand odor can reveal a person’s sex
2023-07-05
The profile of scent compounds from a person’s hand can be used to predict their sex, according to a new study led by Kenneth Furton of Florida International University, publishing July 5 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
In criminal investigations, dogs have long been used to reliably identify and track people based on their odor. But while human scent evidence from the field is well established, researchers have made little progress in analyzing human scent profiles in the lab.
In the new study, researchers used an analysis technique called mass spectrometry to analyze ...
A two-for-one approach to boost melanoma immunotherapy
2023-07-05
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – July 05, 2023 – New research from Sanford Burnham Prebys has helped explain how melanoma evades the immune system and may guide the discovery of future therapies for the disease. The study found that a protein known to be active in immune cells is also active inside melanoma cells, helping promote tumor growth. The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, suggest that targeting this protein with new drugs may deliver a powerful double hit to melanoma tumors.
“The ...
Depression after traumatic brain injury could represent a new, distinct disease
2023-07-05
A study of 273 people found that brain circuits associated with depression were different between people with traumatic brain injury and those without TBI.
The study suggests depression after TBI may not be the same as depression related to other causes.
A new study led by Shan Siddiqi, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, suggests that depression after traumatic brain injury (TBI) could be a clinically distinct disorder rather than traditional ...
Earth formed from dry, rocky building blocks
2023-07-05
Billions of years ago, in the giant disk of dust, gas, and rocky material that orbited our young sun, larger and larger bodies coalesced to eventually give rise to the planets, moons, and asteroids we see today. Scientists are still trying to understand the processes by which planets, including our home planet, were formed. One way researchers can study how Earth formed is to examine the magmas that flow up from deep within the planet’s interior. The chemical signatures from these samples contain a record of the timing and the nature of the materials that came together to form ...
Lasering lava to forecast volcanic eruptions
2023-07-05
University of Queensland researchers have optimised a new technique to help forecast how volcanoes will behave, which could save lives and property around the world.
Dr Teresa Ubide from UQ’s School of the Environment and a team of international collaborators have trialled a new application of the tongue-twisting approach: laser ablation inductively coupled plasma quadruple mass spectrometry.
“It’s a mouthful, but this high-resolution technique offers clearer data on what’s chemically occurring within a volcano’s magma, which is fundamental to forecasting eruption patterns and changes,” Dr Ubide said.
She described magma ...
Dissolving cardiac device monitors, treats heart disease
2023-07-05
New device shows promise in small animal studies
Not only can it restore normal heart rhythms, it also can show which areas of the heart are functioning well and which areas are not
After the device is no longer needed, it harmlessly dissolves inside the body, bypassing the need for extraction
EVANSTON, Ill. — Nearly 700,000 people in the United States die from heart disease every year, and one-third of those deaths result from complications in the first weeks or months following a traumatic heart-related event.
To help prevent those deaths, researchers at Northwestern ...
Why the day is 24 hours long: Astrophysicists reveal why Earth’s day was a constant 19.5 hours for over a billion years
2023-07-05
A team of astrophysicists at the University of Toronto (U of T) has revealed how the slow and steady lengthening of Earth’s day caused by the tidal pull of the moon was halted for over a billion years.
They show that from approximately two billion years ago until 600 million years ago, an atmospheric tide driven by the sun countered the effect of the moon, keeping Earth’s rotational rate steady and the length of day at a constant 19.5 hours.
Without this billion-year pause in the slowing of our planet’s rotation, our current 24-hour day would stretch to over 60 hours.
The ...
Black Americans may face relatively accelerated biological aging because they tend to experience lower socioeconomic status, more neighborhood deprivation and higher air pollution than White Americans
2023-07-05
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287112
Article Title: Contributions of neighborhood social environment and air pollution exposure to Black-White disparities in epigenetic aging
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This work was supported by National Institute on Aging: R01-AG066152 (CM), R01- AG070885 (RB), P30-AG072979 (CM). Additional support includes Pennsylvania Department of Health (2019NF4100087335; CM), and Penn Institute on Aging (CM). National Institute on Aging: https://www.nia.nih.gov Pennsylvania Department of Health: https://www.health.pa.gov/Pages/default.aspx Penn Institute on Aging: https://www.med.upenn.edu/aging/. ...
Memories of childhood abuse and neglect has greater impact on mental health than the experience itself
2023-07-05
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London and City University New York, published today (Wednesday 5 July) in JAMA Psychiatry, has found that the way childhood abuse and/or neglect is remembered and processed has a greater impact on later mental health than the experience itself. The authors suggest that, even in the absence of documented evidence, clinicians can use patients’ self-reported experiences of abuse and neglect to identify those at risk of developing mental health difficulties ...
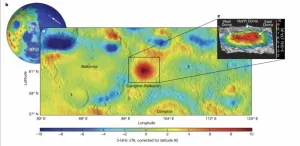
Large sub-surface granite formation signals ancient volcanic activity on Moon's dark side
2023-07-05
DALLAS (SMU) – A large formation of granite discovered below the lunar surface likely was formed from the cooling of molten lava that fed a volcano or volcanoes that erupted early in the Moon’s history – as long as 3.5 billion years ago.
A team of scientists led by Matthew Siegler, an SMU research professor and research scientist with the Planetary Science Institute, has published a study in Nature that used microwave frequency data to measure heat below the surface of a suspected volcanic ...
Finding the flux of quantum technology
2023-07-05
We interact with bits and bytes everyday – whether that’s through sending a text message or receiving an email.
There’s also quantum bits, or qubits, that have critical differences from common bits and bytes. These photons – particles of light – can carry quantum information and offer exceptional capabilities that can’t be achieved any other way. Unlike binary computing, where bits can only represent a 0 or 1, qubit behavior exists in the realm of quantum mechanics. Through “superpositioning,” a qubit can represent a 0, ...
[1] ... [1811]
[1812]
[1813]
[1814]
[1815]
[1816]
[1817]
[1818]
1819
[1820]
[1821]
[1822]
[1823]
[1824]
[1825]
[1826]
[1827]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.