Ocean animals vacate areas both around and outside deep-sea mining operations
2023-07-14
In 2020, Japan performed the first successful test extracting cobalt crusts from the top of deep-sea mountains to mine cobalt—a mineral used in electric vehicle batteries. Not only do directly mined areas become less habitable for ocean animals, but mining also creates a plume of sediment that can spread through the surrounding water. An investigation on the environmental impact of this first test, published July 14th in the journal Current Biology, reports a decrease in ocean animals both in and around the mining zone.
The International ...
Our favorite vintages and their precarious mountainside homes are at risk due to climate change, environmental scientists warn
2023-07-14
Tucked into the hillsides of Italy, Portugal, and Spain, some of the world’s most famous—and most difficult to maintain—vineyards are heralded for their unique flavor profiles and centuries of tradition. But as extreme weather and changing socioeconomic conditions make this so-called “heroic viticulture” even more challenging, scientists worry these grapes and their cultural histories are at risk. In a Backstory publishing on July 14 in the journal iScience, researchers argue that farmers and scientists must work together to protect ...
One, two, many, lots: Fruit flies can discriminate between numerical quantities
2023-07-14
In the animal world, you don't need to learn a numeral system – such as the ten-digit Indo-Arabic system we commonly use – to be able to count. Animals constantly use numerical information from their environment to make decisions. Estimating the number of conspecifics in a competing group before engaging in conflict, the amount of food available in a difficult-to-reach location, or the number of potential sexual partners in a new territory is essential for survival and reproduction. This skill can reach an astonishing level of refinement; for example, certain species of ants orient themselves ...
Effects of meditation training and non-native language training on cognition in older adults
2023-07-14
About The Study: In this secondary analysis of an 18-month randomized trial that included 135 older adults, meditation and non-native language training did not confer salutary cognitive effects. Although further analyses are needed to explore the effects of these interventions on other relevant outcomes related to aging and well-being, these findings did not support the use of these interventions for enhancing cognition in cognitively healthy older adults.
Authors: Natalie L. Marchant, Ph.D., of University College London, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.17848)
Editor’s ...
Associations between neighborhood-level racial residential segregation, socioeconomic factors, and life expectancy
2023-07-14
About The Study: This nationwide cross-sectional study demonstrated that residing in a highly segregated neighborhood was associated with a statistically significantly lower life expectancy by four years, which was partially mediated by neighborhood-level socioeconomic factors. These findings help to quantify the contribution of residential segregation as a key structural driver of racial inequities.
Authors: Sadiya S. Khan, M.D., M.Sc., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1805)
Editor’s ...
Lifestyle enrichment in later life and its association with dementia risk
2023-07-14
About The Study: In this study of 10,000 older individuals in Australia, more frequent participation in adult literacy activities (taking education classes, using a computer, and writing letters or journals) and in active mental activities (playing games, cards, or chess and doing crosswords or puzzles) was associated with reduced dementia risk over 10 years. However, social outings and interactions were not associated with dementia risk.
Authors: Joanne Ryan, Ph.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is ...
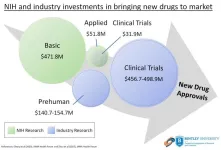
NIH spent $8.1B for phased clinical trials of drugs approved 2010-19, ~10% of reported industry spending
2023-07-14
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) contributed $8.1 billion in project funding for phased clinical trials involving drugs approved by the FDA from 2010-2019, according to a new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry. The study, published in JAMA Health Forum, shows that NIH funding for clinical trials represents <3.5% of total NIH spending for basic or applied research related to these products and was significantly less than reported industry spending on clinical development. ...
Coordination could spare billions in grid upgrade costs and accelerate electrification
2023-07-14
The electric grids of the future will need to handle much bigger loads due to electrification of transportation and other sectors. This could mean expensive infrastructure upgrades to ensure their reliable operation, but a new study from Stanford University says most of those upgrades may be unnecessary.
Better grid reliability could be achieved instead by installing software in homes and businesses that coordinates various consumer demands and resources. Such coordination not only improves reliability of the electric grid, but also ...
Conditional cash transfer programs have prevented 739,919 child deaths in Latin America
2023-07-14
Over the past two decades, conditional cash transfer programmes have led to a 24% reduction in child mortality in Brazil, Mexico and Ecuador, equivalent to more than 700,000 child deaths averted, according to an impact evaluation study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The results, published in JAMA Network Open, also show that expanding these programmes could save more than 150,ooo lives by mitigating the effects of the ...
Neighborhood racial segregation linked to shorter life spans by four years
2023-07-14
New nationwide study is first to examine implications of racial segregation on life expectancy by neighborhood
Findings quantify how neighborhood segregation contributes to racial inequities in life expectancy
Black residents living in heavily segregated areas experienced higher rates of poverty and unemployment and less education
CHICAGO --- Black residents living in highly segregated neighborhoods have significantly shortened life expectancies, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Compared to residents living in less segregated predominantly ...
Fintetuning for antibodies
2023-07-14
Antibodies are crucial, not only for treating tumors and infections. Sometimes, however, the immune reaction they trigger can be too strong and end up causing more damage, for example in the case of people infected with Covid-19. Problems such as these can often be avoided by finetuning antibodies, as Prof. Dr. Falk Nimmerjahn from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and two of his colleagues in the Netherlands and in the UK have now reported in the journal Nature Immunology.
In his laboratories, the FAU researcher is carrying out research into immunoglobulin ...
Single-end hybrid Rayleigh Brillouin and Raman distributed fibre-optic sensing system
2023-07-14
The real-time monitoring of facilities, particularly large facilities (such as rail transit systems, large bridges, and buildings), can provide information regarding their surrounding environment and allow their health conditions to be assessed, which is essential for establishing the current concept of smart cities based on the Internet of Things. As a precise real-time monitoring technique, distributed fiber-optic sensing (DFOS) systems, which require long-distance simultaneous measurements along a sensing fiber, are in high demand for various industrial applications. However, ...
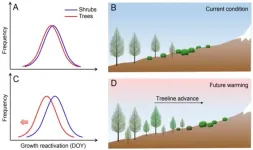
Why trees outcompete shrubs to shift upward?
2023-07-14
The findings from this study, led by Professor Eryuan Liang (Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), were published as a research article in the journal National Science Review. The study also involved researchers from, CREAF, CSIC, Global Ecology Unit CREAF-CSIC-UAB, Instituto Pirenaico de Ecología (IPE-CSIC), Spain and Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Canada.
Climatic warming is altering the structure and function of alpine ecosystems, including shifts of vegetation boundaries. The upward shift of alpine treelines, the uppermost limit of tree growth forming the boundary between montane forest and alpine communities, ...
New fossil flying reptile ‘Elvis’ takes flight
2023-07-14
A new 145-million-year-old pterosaur (extinct flying reptiles that lived alongside the dinosaurs) was named today by a team of British, American and German researchers. The animal was nicknamed ‘Elvis’ when the fossil was first unearthed in Bavaria, Germany because of the giant pompadour-like bony crest on its skull.
Now the animal has been given a formal scientific name of Petrodactyle wellnhoferi. The name translates as ‘Wellnhofer’s stone-finger’ honouring legendary German palaeontologist ...
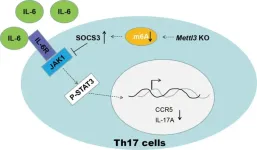
m6A mRNA modification potentiates Th17 functions to inflame autoimmunity
2023-07-14
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most extensive studied RNA modification across various species, and the important effect of m6A modification in immune system has been revealed in distinct contexts, including mRNA metabolism, cell differentiation, proliferation and response to stimulation. Previous studies from Hua-Bing Li group demonstrated that m6A methyltransferase METTL3 control T cells homeostasis and sustain the suppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, the role of m6A methyltransferase in other subtype of T cells remains unknown.
T helper cells 17 ...
Exercise during dialysis has positive health impact
2023-07-14
Patients who engage in light exercise while undergoing dialysis are physically fitter and are admitted to hospital less frequently than those who do not. These are the findings of a large-scale study conducted by a consortium led by the Technical University of Munich (TUM). The researchers believe that exercise programs should be offered to dialysis patients as standard.
Around 558,000 people in the United States have such severely impaired kidney function that they require dialysis several times per week. In Germany, about 80,000 people regularly undergo ...
Link between oropharyngeal cancer and sexual behavior
2023-07-14
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a ubiquitous virus, and most people are infected at some point in their lives. HPV can infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucosa at various sites. There are more than 100 known HPV subtypes, most of which cause only benign lesions such as warts and condyloma. Thanks to a well-functioning immune response, most people who are infected don’t develop serious symptoms. However, some HPV subtypes are not so harmless. These subtypes, and especially subtype HPV16, can transform infected cells to become neoplastic, and these malignant transformed cells then develop into precancerous ...
Scientists use Insilico Medicine’s generative AI platform to predict drug targets for rare lysosomal storage disease
2023-07-14
A team led by researchers at the Mechanisms of Inherited Kidney Disorders (MIKADO) group at the University of Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland) has used Insilico Medicine’s generative artificial intelligence (AI) target discovery engine, PandaOmics, to identify actionable drug targets for the lysosomal storage disease cystinosis and to validate them in preclinical models of the disease. These results, which open new therapeutic possibilities for this devastating disease, were published June 14 in the journal Nature Communications. Collaborators include scientists from Microsoft Research-University of Trento Centre for Computational ...
Lipid test can reveal risk of preeclampsia, a potentially deadly pregnancy complication
2023-07-14
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a way to identify pregnant women at risk of preeclampsia, a serious disorder characterized by high blood pressure and kidney dysfunction which can result in premature delivery, seizures and even death. Complications from the condition are the second-leading cause of maternal death around the world.
The UVA scientists, led by Charles E. Chalfant, PhD, found that they could predict the risk of preeclampsia by examining lipids (fats) ...
Stellar cradles and graves seen in farthest galaxy ever
2023-07-14
New observations using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have distinguished the sites of star formation and a possible site of star death from the surrounding nebula in a galaxy 13.2 billion light-years away. This is the farthest that such structures have been observed.
A team led by Yoichi Tamura, an astronomer at Nagoya University, attempted high-resolution observations of MACS0416_Y1, located 13.2 billion light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. Previous observations of this galaxy by the same team had detected radio waves emitted by both oxygen and dust, two components of interstellar nebulae. Detailed observations of the ...
Liquid crystals that mimic beetle shell coloration units used to create more secure type of QR code
2023-07-14
A research group led by Dr. Jialei He of Nagoya University's Graduate School of Engineering has developed a method for processing cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) into micrometer-sized spherical particles. CLCs are a type of liquid crystal that possess a helical structure, giving them unique optical properties and the ability to selectively reflect light. By combining spherical CLC particles with commercially available pigments, the researchers developed a unique anti-counterfeiting QR code that can only be displayed under a specific circular polarizer. The results were published in the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
CLCs are an example of how nature can be ...
ROSE: a revolutionary, nature-inspired soft embracing robotic gripper
2023-07-14
Ishikawa, Japan -- Although grasping objects is a relatively straightforward task for us humans, there is a lot of mechanics involved in this simple task. Picking up an object requires fine control of the fingers, of their positioning, and of the pressure each finger applies, which in turn necessitates intricate sensing capabilities. It’s no wonder that robotic grasping and manipulation is a very active research area within the field of robotics.
Today, industrial robotic hands have replaced humans in various complex and hazardous ...
Study shows surprisingly low use of COVID antiviral treatments in nursing homes
2023-07-14
Nursing homes were a key battleground during the COVID pandemic and prioritized for distribution of PPE, vaccines, and COVID testing kits. However, new research shows that monoclonal antibodies and oral antiviral drugs were not used in these facilities as much as would be expected given the high-risk of resident populations.
Brian McGarry, PhD, with the University of Rochester Medical Center, and collaborators at Harvard University, authored the new study, which appears today in JAMA. The authors examined data compiled ...
This eight-armed octopus-like pore detects taste
2023-07-14
The neurons in our bodies are dotted with tiny pores that let essential molecules pass in and out of our cells. Neurons need these channels to send the signals that allow us to move, think, and perceive the world around us. Now, structural biologists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have captured never-before-seen images of one of the largest pores in human neurons. It’s called calcium homeostasis modulator protein 1, or CALHM1 for short.
Previous studies have shown that mutations in the Cahlm1 gene may be a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. CSHL’s new ...
New study demonstrates the potential of diseased coral parents in restoring stony coral tissue loss disease-affected species
2023-07-14
Stony Coral Tissue Loss Disease (SCTLD) has wreaked havoc on coral reefs across the Caribbean, resulting in significant mortality of various coral species, including Pseudodiploria strigosa, which has been particularly affected in the Mexican Caribbean. In response to the decreased abundance and colony density caused by SCTLD, scientists have explored larval-based restoration methods, despite concerns about disease transmission. A new PeerJ Life & Environment study reveals that even colonies affected by SCTLD can play a vital role in the assisted sexual reproduction for the restoration of SCTLD-susceptible species.
The ...
[1] ... [1805]
[1806]
[1807]
[1808]
[1809]
[1810]
[1811]
[1812]
1813
[1814]
[1815]
[1816]
[1817]
[1818]
[1819]
[1820]
[1821]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.