Unraveling the molecular basis of Dmc1 filament assembly in homologous recombination
2023-07-19
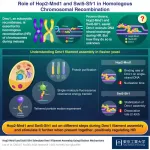
Homologous recombination (HR) is an important process that plays multiple crucial roles during meiosis, a type of cell cycle dedicated to sexual reproduction. During HR, homologous DNA molecules exchange their genetic material. During the meiotic prophase, DNA are clipped throughout the genome, forming numerous DNA double-strand breaks. Such DNA breaks attract homologous recombination enzymes, which promote pairing of homologous chromosomes.
Dmc1 is one such meiosis-specific recombinase in eukaryotes (organisms that have a clearly defined nucleus), ...
Simultaneous synthesis and fixing of covalent organic frameworks
2023-07-19
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are versatile materials composed of interconnected organic molecules held together by covalent bonds. These frameworks can be constructed in two-dimensional or three-dimensional (3D) forms which possess a unique combination of low density, high surface area, and easily tunable properties. Among the various types of COFs, imine-linked COFs have garnered considerable attention owing to their exceptional thermal and chemical stability as well as their broad scope of monomeric starting materials.
However, traditional bulk synthetic methods for COFs often yield powders that are insoluble ...
A cool way to keep things cool: the electrocaloric effect
2023-07-19
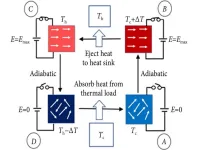
As necessary as cooling technologies are, we’re still operating on an outdated technology that can be considered a significant contributor to global warming and greenhouse gas emissions. Currently, vapor compression cycle-based cooling (VCC) is the standard for reliable cooling of air conditioning and refrigeration, but by switching to electrocaloric cooling (EC) researchers are hoping to create a more environmentally friendly, scalable and compressor-free method of cooling to benefit businesses, families and the environment.
The researchers published their work in iEnergy on ...
JMIR Publications acquires the Online Journal of Public Health Informatics, broadening its prestigious open access portfolio
2023-07-19
(Toronto July 19, 2023) Fully open access publisher JMIR Publications has acquired the Online Journal of Public Health Informatics (OJPHI), expanding its portfolio to 35 gold open access journals. This acquisition marks an open access milestone in JMIR Publications’ continued mission to keep openness at the heart of what it does.
Indexed in PubMed Central, OJPHI has been delivering the latest developments in the emerging field of public health informatics since 2009. The journal publishes research articles, book reviews, technology reviews, working papers, interviews, commentaries, and handpicked student capstone projects.
All ...
Call for Papers: Theme Issue on “Responsible Design, Integration, and Use of Generative AI in Mental Health”
2023-07-19
JMIR Medical Education (2023 Impact Factor 5.2) and Guest Editors: Amir Tal, PhD, and Oren Asman, LLD welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Responsible Design, Integration, and Use of Generative AI in Mental Health"
This special theme issue aims to unite various stakeholders in exploring the responsible use of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) within the mental health domain. The goal is to curate a collection of articles that examine the advantages, challenges, and potential risks associated with deploying GAI models ...
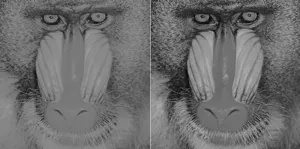
Light quality enhances contrast vision
2023-07-19
Prof Sei-ichi Tsujimura of the Nagoya City University and Prof Su-Ling Yeh of National Taiwan University and Kagoshima University, have discovered that our visual acuity (contrast sensitivity) can be improved by using a light with a special spectrum that can selectively stimulate melanopsin cells in the retina.
Background
The retina of our eye contains cone photoreceptor cells, which identify colors in bright environment, and rod photoreceptor cells, which work in the dark. It has long been thought that humans see and identify objects by these two types of photoreceptor cells alone. ...
Monitoring often excludes crucial river ecosystems; Can citizen science fill the gap?
2023-07-19
Intermittent rivers and ephemeral streams are the world's dominant river ecosystem, yet monitoring and management typically focus on rivers that flow year round. Writing in BioScience, Amélie Truchy of the French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food, and the Environment (INRAE) and colleagues describe the problem, as well as a potential solution: citizen science.
The authors discuss the results from a new app, DRYRivERS, which allows scientist and nonscientist users alike to record data on ephemeral streams and intermittent ...
Cardiac rehabilitation reduces risk of death years after heart surgery, still underutilized
2023-07-19
For millions of Americans who have heart surgery or experience cardiovascular complications, like heart attack or heart failure, they may be encouraged to participate in cardiac rehabilitation. The medically supervised program combines lifestyle changes, education and physical activity to help patients recover and reduce their risk of future problems.
A Michigan Medicine study now finds that people who participate in cardiac rehabilitation have a decreased risk of death years after surgery, with a trend towards better outcomes in patients who attend more sessions.
“Time and time again, cardiac rehabilitation has been shown to ...
A quick and inexpensive test for osteoporosis risk
2023-07-19
As life expectancy increases worldwide, age-associated diseases such as osteoporosis are having an increasing impact. Although early detection could help physicians intervene as soon as possible — when treatment might offer the greatest benefit — this type of detection is not yet possible with current osteoporosis diagnostic tests. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a biosensor that could someday help identify those most at risk for osteoporosis using less than a drop of blood.
Early intervention is critical to reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with osteoporosis, a condition characterized by an elevated ...
Espresso can prevent Alzheimer’s protein clumping in lab tests
2023-07-19
Whether enjoyed on its own or mixed into a latte, Americano or even a martini, espresso provides an ultra-concentrated jolt of caffeine to coffee lovers. But it might do more than just wake you up. Research now published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows that, in preliminary in vitro laboratory tests, espresso compounds can inhibit tau protein aggregation — a process that is believed to be involved in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Roughly half of all Americans drink coffee every day, and espresso is a popular way to consume ...
A vegan way to stop damage from excessive ice build-up and freezer burn
2023-07-19
Almost everyone has a bag of veggies shoved into the dark recesses of their freezer that’s now essentially an unrecognizable block of ice crystals. And when thawed, foods damaged by excessive ice lose their texture and become mushy. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have shown that broken-down soy proteins can prevent ice crystal growth and could be especially useful for preserving frozen vegan foods or biological samples.
Some animals that ...
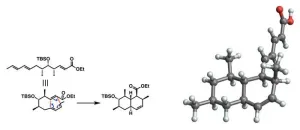
Towards new antibiotics with the first artificial synthesis of tanzawaic acid b
2023-07-19
The discovery of antibiotics in 1928 was a major turning point in the history of medicine. For the first time since the dawn of human civilization, doctors had gained access to an extremely powerful and effective tool to fight against a wide variety of bacterial infections. Today, bacterial diseases that were previously a death sentence can be cured, and infections following surgery or chemotherapy can be prevented or treated more effectively.
Unfortunately, the worldwide use (and abuse) of antibiotics led to the emergence of drug-resistant bacterial strains. Over time, bacteria that could normally be killed by ...
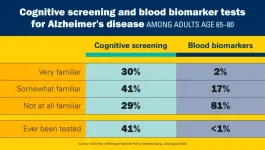
Early signs of Alzheimer’s: Most older adults see the value of screening but haven’t been tested
2023-07-19
Eighty percent of older adults see the benefit of tests that can give an early warning that a person’s memory and thinking abilities have started to decline, a new poll of people age 65 to 80 finds. And 60% think that health care providers should offer cognitive screening, in the form of brief memory tests, to all older adults every year.
If they had a cognitive screening test and it showed signs of trouble, the vast majority of those polled said it would spur them to take action to protect their brain health (96%) and adjust their financial and health ...
Does this exoplanet have a sibling sharing the same orbit?
2023-07-19
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have found the possible ‘sibling’ of a planet orbiting a distant star. The team has detected a cloud of debris that might be sharing this planet’s orbit and which, they believe, could be the building blocks of a new planet or the remnants of one already formed. If confirmed, this discovery would be the strongest evidence yet that two exoplanets can share one orbit.
“Two decades ago it was predicted in theory that pairs of planets of similar mass may share the same orbit around their star, the so-called Trojan or co-orbital planets. For the first time, we have found evidence ...
Michael Wong named fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry
2023-07-19
HOUSTON – (July 19, 2023) – Rice University’s Michael Wong was named a fellow to the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC), the oldest chemical society in the world, whose mission is to “advance excellence in the chemical sciences.” More than 180 years old, the United Kingdom-based chemical society has over 54,000 members worldwide.
“It’s a confirmation that the work we do in our group is something that people appreciate and is making a meaningful contribution ...
From nature, a solution to save coral from climate change
2023-07-19
Genoa (Italy), 19 July 2023 – Researchers at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology - IIT) and Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca (University of Milan-Bicocca), in cooperation with Acquario di Genova (Genoa Aquarium) in Italy, have recently published a study in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, which demonstrates the efficacy of curcumin, a natural antioxidant substance extracted from turmeric, in reducing coral bleaching, a phenomenon caused primarily by climate change. The research group developed a biodegradable biomaterial to deliver the molecule without ...
Dementia risk and disadvantaged neighborhoods
2023-07-19
About The Study: The results of this study of 1.6 million patients suggest that residence within more disadvantaged neighborhoods was associated with higher risk of dementia among older veterans integrated in a national health care system.
Authors: Christina S. Dintica, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2120)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
Does cognitive function after retirement differ across race and sex?
2023-07-19
A study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that immediately after retirement, white adults tended to experience a significant decline in cognitive function, whereas Black adults experienced minimal cognitive decline. White men showed the steepest post-retirement cognitive decline across sex/race combinations, whereas Black women showed the least decline.
White women performed better cognitively at retirement than other race/sex subgroups, and after retirement, their cognitive functioning declined at a rate that was slightly ...
Can parents’ Disability Insurance boost children’s economic mobility?
2023-07-19
New research published in Contemporary Economic Policy indicates that Disability Insurance (DI) may improve economic opportunities for children whose parents have health conditions that limit work.
The study included 52,575 parent-child pairs in the United States. When investigators examined economic mobility patterns for children whose parents reported work-limiting disability, they found that children had less upward economic mobility and more downward mobility relative to children of non-limited parents. Children of parents ...
Nurse-home visiting program may boost child language and mental health
2023-07-19
A randomized controlled trial conducted in Canada and published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry found that Nurse-Family Partnership (NFP), a nurse-home visiting program, improved child language and mental health at age 2 years when compared with existing services. Rates of child injuries and maternal subsequent pregnancies were similar in the two groups.
This real-world effectiveness trial involved sustained research-policy-practice collaborations from 2011–2022. Investigators successfully reached/enrolled and sustained engagement with 739 participants (368 NFP, 371 comparison) and their 737 children for ...
How effective is Functional Family Therapy for addressing youth behavior problems?
2023-07-19
Functional Family Therapy is a family-based intervention for youth with behavior problems, and although it’s been implemented in 45 states in the U.S and in nine other high-income countries, a recent analysis of published and unpublished studies found that the therapy is not consistently more or less effective than other treatments, including various forms of individual, family, and group interventions.
The authors of the analysis, which is published in Campbell Systematic Reviews and included 20 studies, also noted that there is insufficient evidence ...
Developing NMR method for drug structure elucidation
2023-07-19
In the late 1950s and 1960s, more than 12,000 malformed babies with short arms and legs were born as a side effect of thalidomide, a drug sold to pregnant women to prevent morning sickness. The tragedy was caused by the drug's side effect, which exists in a racemic mixture of two mirror-image forms. Research to determine the molecular structure of various compounds is essential for understanding biological phenomena and developing drugs to treat diseases and is mainly based on the interpretation ...
Concentration of cell membrane components with nanocarbon materials
2023-07-19
Overview
A research team from the Department of Applied Chemistry and Life Science at the Toyohashi University of Technology (Professor Ryugo Tero et al.) discovered a phenomenon in which specific lipids were concentrated on graphene oxide in a multicomponent lipid bilayer membrane serving as a cell membrane model. This research team also clarified the mechanism by which the components of “lipid rafts" (where important cell membrane reactions such as neurotransmission and metabolism occur) gather owing to the surface characteristics of graphene oxide. This discovery is ...
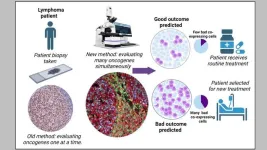
NUS researchers develop novel approach for predicting resistance against cancer therapy
2023-07-19
A team of researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS), led by Assistant Professor Anand Jeyasekharan, has discovered a unique combination of oncogenes that could predict treatment resistance, and hence unfavourable outcomes, of patients with Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common type of blood cancer in Singapore and globally.
This unique oncogenic combination, serving as an indicator of treatment resistance, can be detected through state-of-the-art technology. The researchers, however, went a step ...
Singapore scientists find that a special omega-3 lipid might prevent fatty liver disease
2023-07-19
SINGAPORE, XX July 2023 – Long-running research by Duke-NUS Medical School into the omega-3 transporter protein Mfsd2a has shown that it plays a key role in a specific mechanism that prevents the liver from storing too much fat from food. Published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, this latest study by Duke-NUS and collaborators from Singapore General Hospital (SGH) signals the possibility that a dietary supplement could be developed to help prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Eating too much fatty food increases the risk of many health problems, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes and NAFLD. The excess fat that accumulates in the ...
[1] ... [1801]
[1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
[1807]
[1808]
1809
[1810]
[1811]
[1812]
[1813]
[1814]
[1815]
[1816]
[1817]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.