Many children in rural areas receive high salt and sugar foods before age 2
2023-07-23
A study of over 10,000 children in rural Pennsylvania revealed that a large proportion of children were fed foods that are high in sugar and salt in their first years of life.
Over half (53%) of the children in the study received high-sodium meats such as hot dogs, 37% received salty snacks such as potato chips, and one-third (34%) received cakes, cookies, or pudding before age 2. In addition, over one-quarter (27%) of babies received juice before their first birthday.
“Given ...
The Lancet: People on ART with low but detectible levels of HIV viral load have almost zero risk of sexually transmitting the virus to others, in-depth review suggests
2023-07-23
Systematic review of 8 studies in more than 7,700 serodiscordant couples in 25 countries finds people living with HIV with viral loads less than 1,000 copies/mL have almost zero risk of transmitting the virus to their sexual partners. Previous studies have not been able to confirm a lack of transmission risk above 200 copies/mL.
Systematic review also consolidates and reinforces previous studies that have found there is zero risk of transmitting the virus to sexual partners when people living with HIV have an undetectable viral load.
Of the more than 320 documented sexual HIV transmissions ...
Researchers identify genes that directly influence what we eat
2023-07-22
In one of the first large-scale studies of genes related to diet, researchers have uncovered almost 500 genes that appear to directly influence the foods we eat. The findings represent an important step toward using a person’s genetics to develop precision nutrition strategies that help improve health or prevent disease.
“Some genes we identified are related to sensory pathways — including those for taste, smell, and texture — and may also increase the reward response in the brain,” said research team leader Joanne Cole, PhD, assistant professor in the Department ...
Scientists name top five foods rich in prebiotics
2023-07-22
There is growing evidence that consuming prebiotics — certain types of fiber often found in plants that stimulate beneficial bacteria in your gut — can help to maintain a healthy gut microbiome. In a new study, scientists estimated the prebiotic content of thousands of food types by using preexisting literature to find out which foods offer the highest prebiotic content.
According to the study, foods that pack the greatest prebiotic punch are dandelion greens, Jerusalem artichokes, garlic, leeks, and onions. In addition to supporting gut microbes, prebiotic rich ...
A defense against attacks on unmanned ground and aerial vehicles
2023-07-22
A University of Texas at Arlington engineering researcher is working on defenses that could thwart cyberattacks against networks of self-driving cars and unmanned aerial vehicles.
Animesh Chakravarthy, associate professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE), is the principal investigator on an approximately $800,000 U.S. Department of Defense grant titled “Resilient Multi-Vehicle Networks.” MAE Professor Kamesh Subbarao, and Bill Beksi, assistant professor ...
Renewable solar energy can help purify water, the environment
2023-07-22
Using electrochemistry to separate different particles within a solution (also known as electrochemical separation) is an energy-efficient strategy for environmental and water remediation: the process of purifying contaminated water. But while electrochemistry uses less energy than other, similar methods, the electric energy is largely derived from nonrenewable sources like fossil fuels.
Chemists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated that water remediation can be powered in part — and ...
Fly toolkit created for investigating COVID-19 infection mechanisms
2023-07-21
Millions of deaths and ongoing illnesses caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have prompted scientists to seek new ways of understanding how viruses so skillfully enter and reprogram human cells. Urgent innovations leading to the development of new therapies are needed since virologists predict that future deadly viruses and pandemics may again emerge from the coronavirus family.
One approach to developing new treatments for such coronaviruses, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19, is to block the mechanisms by which the virus reprograms our cells and forces them to produce more viral particles. But studies have identified nearly 1,000 human proteins ...
Novel targets identified for treatment of schistosomiasis
2023-07-21
The worms that cause schistosomiasis (Schistosoma mansoni) are unusual in several ways, especially the fact that male and female adults must stay paired together throughout their lives for reproduction to be successful. Females may produce as many as 3,000 eggs per day. Approximately half reach the host’s gut or bladder. The rest are swept away via the blood to the liver and spleen, where they cause severe inflammation and liver cirrhosis, the main cause of mortality.
Researchers at Butantan Institute ...
Researchers illuminate resilience of U.S. food supply chains
2023-07-21
Researchers have identified a number of chokepoints in U.S. agricultural and food supply chains through a study that improves our understanding of agri-food supply chain security and may aid policies aimed at enhancing its resilience. The work is presented in a paper published in the July 20, 2023, issue of the journal Nature Food, “Structural chokepoints determine the resilience of agri-food supply chains in the United States,” by authors including CEE Associate Professor Megan Konar and CEE Ph.D. student Deniz Berfin Karakoc.
The agricultural and food ...
Spallation Neutron Source accelerator achieves world-record 1.7-megawatt power level to enable more scientific discoveries
2023-07-21
The Spallation Neutron Source at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory set a world record when its particle accelerator beam operating power reached 1.7 megawatts, substantially improving on the facility’s original design capability.
The accelerator’s higher power provides more neutrons for researchers who use the facility to study and improve a wide range of materials for more efficient solar panels, longer–lasting batteries and stronger, lighter materials for transportation. The achievement marks a new operational milestone for ...
NIH awards will fund post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome research
2023-07-21
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded five projects for research to better understand Post-treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS), which is a collection of symptoms, such as pain, fatigue, and difficulty thinking or “brain fog,” which linger following standard treatment for Lyme disease. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 476,000 people in the United States are infected with Lyme disease each year. Between 10 and 20% of ...
House Appropriations bill would slash life-saving medical research, disease prevention and treatment
2023-07-21
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society opposes severe funding cuts proposed in the House Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies (Labor-HHS) funding bill that would put life-saving endocrine research, disease prevention, and treatment at risk.
The House Appropriations Committee is planning to mark up the Labor-HHS funding bill before Congress leaves for its August recess.
The proposed funding levels in the Labor-HHS bill would harm America’s public health infrastructure and restrict research investments needed to develop next-generation cures. Cutting funding will reduce or eliminate services ...
Mayo Clinic researchers pave the way for individualized obesity therapy, tailoring interventions to a person’s needs
2023-07-21
ROCHESTER, Minn. — In a pilot study of 165 people, Mayo Clinic researchers looked at the effectiveness of two different approaches to weight loss: a standard lifestyle intervention and individualized therapy. The standard lifestyle intervention included a reduced diet, exercise and behavior therapy. The individualized approach was based on phenotypes and included different interventions depending on the person's predominant underlying cause of obesity. A diet based on phenotypes considers a person's ...
Deep-dive into one state's telehealth use shows key trends and policy opportunities
2023-07-21
In just three years, millions of people across Michigan’s two huge peninsulas have taken advantage of their newfound ability to connect with their doctors, nurses and therapists through a computer or phone, a new report shows.
Between 11% and 17% of all appointments to evaluate symptoms or discuss treatment now take place virtually, depending on the type of insurance, the analysis shows.
That’s up from less than 1% of such visits before the COVID-19 pandemic suddenly spurred temporary flexibility in health insurance rules for telehealth, according to the report by a team from the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare ...
Bodybuilding supplement may help stave off Alzheimer’s
2023-07-21
The secret to protecting your memory may be a staple of a bodybuilder’s diet. RUSH researchers recently discovered that a muscle-building supplement called beta-hydroxy beta-methylbutyrate, also called HMB, may help protect memory, reduce plaques and ultimately help prevent the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
HMB is not a prescription drug or a steroid, but an over-the-counter supplement that is available in sports and fitness stores. Bodybuilders regularly use HMB to increase exercise-induced gains in muscle size and strength while improving exercise performance. HMB is considered safe even after long-term ...
IU team contributes six research papers to Human BioMolecular Atlas Program collection in Nature
2023-07-21
Katy Börner’s team from the Luddy School of Informatics, Computing, and Engineering’s Cyberinfrastructure for Network Science Center has made significant contributions to constructing a Human Reference Atlas and has led or co-authored six research articles in a just-released HuBMAP package in Nature.
Börner, Victor H. Yngve distinguished professor of engineering and information science, and CNS director, leads one of the two mapping components within the NIH-funded Human BioMolecular Atlas Program. Her team includes ...
Research supporting increased crop growth published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
2023-07-21
NORMAN, OKLA. – An article describing research conducted by John Peters, Ph.D., chair of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences at the University of Oklahoma, and fellow researchers, has been published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The article “Structural insights into redox signal transduction mechanisms in the control of nitrogen fixation by the NifLA system” explores the way bacteria regulate the expression of genes related to nitrogen fixation ­– the conversion of nitrogen in the air into ammonia that can help plants grow.
“Using small angle X-ray scattering ...
Fiber optic sensing tracks seismicity from injected carbon dioxide at Australian site
2023-07-21
Researchers at a field site in Victoria, Australia are among the first to use fiber optic distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) for high-precision tracking of induced seismicity from a small carbon dioxide (CO2) injection, according to a new study published in Seismological Research Letters.
The CO2CRC Otway Project in Victoria is a research test site for the subsurface storage of carbon dioxide, as one possible way to reduce the impacts of climate-warming carbon emissions. However, there is a risk of induced earthquakes after gigatons of carbon dioxide will be injected within the same geologic ...
Biosurfactants might offer an environmentally friendly solution for tackling oil spills
2023-07-21
Can biosurfactants increase microbiological oil degradation in North Sea seawater? An international research team from the universities of Stuttgart und Tübingen, together with the China West Normal University and the University of Georgia, have been exploring this question and the results have revealed the potential for a more effective and environmentally friendly oil spill response.
Oil leaks into the oceans are estimated at approximately 1500 million liters annually worldwide. This leads to globally significant environmental pollution, as oil contains hazardous compounds ...
Revealing HIV drug-resistance mechanisms through protein structures
2023-07-21
LA JOLLA (July 21, 2023)—Salk Institute researchers, in collaboration with the National Institutes of Health, have discovered the molecular mechanisms by which the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) becomes resistant to Dolutegravir, one of the most effective, clinically used antiviral drugs for treating HIV.
The new study, published July 21, 2023 in Science Advances, reveals how changes to the 3D structures of integrase, an HIV protein, can lead to Dolutegravir resistance and how other compounds may be able to overcome this resistance.
“With HIV, one must think two steps ahead of the virus,” says ...
New sensor mimics cell membrane functions
2023-07-21
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Drawing inspiration from natural sensory systems, an MIT-led team has designed a novel sensor that could detect the same molecules that naturally occurring cell receptors can identify.
In work that combines several new technologies, the researchers created a prototype sensor that can detect an immune molecule called CXCL12, down to tens or hundreds of parts per billion. This is an important first step to developing a system that could be used to perform routine screens for hard-to-diagnose cancers or metastatic tumors, or as a highly biomimetic electronic “nose,” ...
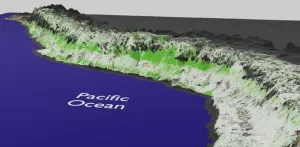
The Pacific slope of Peru is greening, and this is not good news
2023-07-21
Analysing satellite data spanning the past 20 years, the research team based at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge examined how vegetation has been changing along the Pacific coast of Peru and northern Chile. This area is known for its unique and delicate arid and semi-arid environments.
The analysis revealed that certain areas experienced positive vegetation growth, known as greening, while others displayed negative trends, referred to as browning. Unsurprisingly, the changes in vegetation are influenced by things like farming and urban development or change in ...
Dark SRF experiment at Fermilab demonstrates ultra-sensitivity for dark photon searches
2023-07-21
Scientists working on the Dark SRF experiment at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory have demonstrated unprecedented sensitivity in an experimental setup used to search for theorized particles called dark photons.
Researchers trapped ordinary, massless photons in devices called superconducting radio frequency cavities to look for the transition of those photons into their hypothesized dark sector counterparts. The experiment has put the world’s best constraint on the dark photon existence in a specific mass range, as ...
Extracellular vesicles could aid spread of scleroderma-caused fibrosis throughout body
2023-07-21
Extracellular vesicles, responsible for cell-to-cell communication, might be a driver of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis, according to a recent paper in Arthritis and Rheumatology.
Characterized by stiff and hardening tissue known as fibrosis, systemic sclerosis – also known as scleroderma – can affect the skin as well as other organs. Most research has focused on the pathology and starting point of fibrosis, but researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina are focusing ...
Ricardo Valerdi named Head of Systems and Industrial Engineering at the University of Arizona
2023-07-21
Ricardo Valerdi was selected as head of the Department of Systems and Industrial Engineering after a national search that yielded a highly competitive pool of candidates after serving as interim head for the 2022-2023 academic year.
“When I joined SIE 12 years ago, it looked very different,” said Valerdi. “Today we have a new generation of talented and ambitious faculty who are impacting our society’s Grand Challenges in manufacturing, transportation, aerospace ...
[1] ... [1793]
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
[1798]
[1799]
[1800]
1801
[1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
[1807]
[1808]
[1809]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.