New catalyst could dramatically cut methane pollution from millions of engines
2023-07-20
Individual palladium atoms attached to the surface of a catalyst can remove 90% of unburned methane from natural-gas engine exhaust at low temperatures, scientists reported today in the journal Nature Catalysis.
While more research needs to be done, they said, the advance in single atom catalysis has the potential to lower exhaust emissions of methane, one of the worst greenhouse gases, which traps heat at about 25 times the rate of carbon dioxide.
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Washington State University ...
New resources to improve patient and public involvement in health research
2023-07-20
Patients and members of the public will be able to more easily take part in impactful research thanks to a new tool developed by the University of Birmingham’s work on Long COVID.
These resources are detailed in a paper published today in Nature Medicine from researchers working within the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Applied Health Research, the NIHR Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) and NIHR Applied Research Collaboration West Midlands, reporting the evaluation ...
(How) cells talk to each other
2023-07-20
Like us, cells communicate. Well, in their own special way. Using waves as their common language, cells tell one another where and when to move. They talk, they share information, and they work together – much like the interdisciplinary team of researchers from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) and the National University of Singapore (NUS). They conducted research on how cells communicate – and how that matters to future projects, e.g. application to wound healing.
What comes to your mind when you think of biology? Animals, plants, theoretical computer models? The last one, you might not associate with it right away, although ...
Volunteering in late life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia
2023-07-20
Key Takeaways:
Volunteering later in life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia.
New study of older adults found better memory and executive function among those who volunteered.
Watch the video.
(Sacramento) Volunteering in late life is associated with better cognitive function — specifically, better executive function and episodic memory. Those are the findings of a new study from UC Davis Health presented today (July 20) at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2023 in Amsterdam.
“We ...
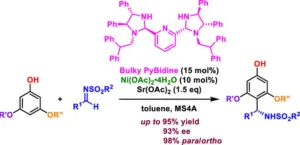
New study expands the scope of aza-friedel−crafts reactions
2023-07-20
From life-saving drugs and synthetic polymers to diverse advanced materials, the products containing organic compounds seem endless, thanks in part to regioselectivity, a feature in chemical reactions where a substituent is selectively added to a specific position of an organic compound. This favors the formation of desired products with specific functionalities. One notable regioselective reaction used for the precise design of organic compounds is the Friedel−Crafts reaction, which enables the addition of substituents to specific positions on aromatic compounds ...
Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health
2023-07-20
Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health
NIH-funded study supports new role for nutrient found in fish, dietary supplements
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are abundant in fish and fish oil supplements, appear promising for maintaining lung health, according to new evidence from a large, multi-faceted study in healthy adults supported by the National Institutes of Health. The study provides the strongest evidence to date of this association and underscores the importance of including omega-3 fatty acids in the diet, especially given that many Americans do not meet current guidelines. Funded largely by the National Heart, ...
Engineering plants for a changing climate
2023-07-20
Climate change is affecting the types of plant varieties we can cultivate, as well as how and where we can do so. A new collection of articles in the open access journal PLOS Biology explores the twin challenges of engineering plants for resilience to climate change and enhancing their carbon-capture potential. PLOS Biology Editors Pamela Ronald & Joanna Clarke provide a summary editorial, and details regarding the other papers may be found below.
To meet the agricultural challenges caused by climate change and a growing population, we need to improve crop production. This Perspective from industry leaders including Catherine Feuillet calls for more and better ...
Precision measurement of polarization
2023-07-20
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – A doctoral dissertation examining the most precise measurement of electron beam polarization ever made was just awarded the prestigious 2022 Jefferson Science Associates (JSA) Thesis Prize. Since 2017, award-winner Allison Zec has been part of a collaboration that ran experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
The goal of both the CREX and PREX-II experiments was to run an experiment and its mirror opposite simultaneously to determine ...
New study shows Black cancer survivors face increased mortality from heart disease; neighborhood socioeconomic status and insurance contributing factors
2023-07-20
ATLANTA, July 20, 2023 – A new study from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) found that Black cancer survivors in the United States experience a higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease (CVD) compared with White cancer survivors. The research showed Black cancer survivors carry from 30% up to a three-fold higher mortality risk from CVD, depending on the type of cancer that was diagnosed. Differences in neighborhood socioeconomic status and health insurance between Black and White cancer survivors explained the disparities in cardiovascular death rates between populations, according to the study authors. ...
High body temperature increases resistance to pathogenic viral infections, new study finds
2023-07-20
Researchers from The University of Tokyo unravel the connection between high body temperature and increased viral resistance.
Clinical evidence suggests that elderly individuals are at a higher risk of contracting viral infections. Quite notably, the older people also have lower mean body temperatures. However, the effects of increased body temperature on fighting viral infections remain largely unexplored. A team of Japanese researchers has now been able to bridge the gap by linking higher body temperature with an increased infection-fighting capability of the gut microorganisms or "microbiota." Their study was published in Volume 14 ...
New research sheds light on factors influencing trust and bias in societies
2023-07-20
People with more positive perceptions of their nation’s institutions are more likely to show favoritism toward fellow citizens, according to new research in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research suggests that support for national institutions could pose a challenge for establishing trust across borders.
Researchers also found that people who identify strongly with their own nation are likely to favor their fellow citizens, which aligns with previous studies. The possible role of trust in national institutions, however, was an unexpected development for researchers.
“We observed greater favoritism in trust toward fellow citizens ...
Mark Hauber to lead the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center
2023-07-20
New York, NY – The City University of New York Graduate Center is pleased to announce the appointment of Mark Hauber as the executive director of its Advanced Science Research Center (CUNY ASRC).
Established in 2014, the CUNY ASRC is a world-class STEM research and education institution dedicated to interdisciplinary science that addresses global challenges and develops innovative technologies that will advance the economies of New York State and the nation. Its five research initiatives center on nanoscience, photonics, structural ...
New advances in integrating mechanisms of multiple stress response in conifers
2023-07-20
The proper response to various abiotic stresses is essential for plants’ survival to overcome their sessile nature, especially for perennial trees with very long-life cycles. However, in conifers, the molecular mechanisms that coordinate multiple abiotic stress responses remain elusive.
This article has been published on Horticulture Research with title: An ethylene-induced NAC transcription factor acts as a multiple abiotic stress responsor in conifer.
Here, the transcriptome response to various abiotic stresses like salt, cold, drought, heat shock and osmotic were systematically detected in Pinus tabuliformis (P. ...
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers
2023-07-20
The fastest way to heat food and drink might also rank as the fastest route to ingesting massive quantities of minuscule plastic particles, says new research from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Experiments have shown that microwaving plastic baby food containers available on the shelves of U.S. stores can release huge numbers of plastic particles — in some cases, more than 2 billion nanoplastics and 4 million microplastics for every square centimeter of container.
Though the health effects of consuming micro- and nanoplastics remain unclear, the Nebraska team further found that three-quarters of cultured embryonic ...
Researchers design multiclass cancer diagnostic tool using AI, MicroRNA
2023-07-20
Cancer is one of the most devastating diseases in the world. In 2023, more than 1.9 million new cancer cases and 609,820 deaths are projected to occur in the United States alone. As efforts are underway to improve diagnostic tools, microRNAs are at the forefront biomedical research.
MicroRNAs, or miRNAs, are a class of small non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs), which are essential for all biological functions. The main role of miRNA in the human body is gene regulation. As such, they regulate a variety of biological and pathological processes, including the formation and development of cancer. In fact, many cancers are closely associated with ...
Majority of older adults with cognitive impairment still drive
2023-07-20
The majority of older adults with cognitive impairment are still driving, despite concerns raised by caregivers and others, a Michigan Medicine study in a South Texas community finds.
Researchers assessed more than 600 adults over 65 years old in Nueces County, Texas, who had cognitive assessment scores that indicated a likelihood of impairment.
Of those people with cognitive impairment, 61.4% were current drivers, and around one-third of all caregivers had concerns about their care-recipient driving. The results are published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
“It is likely appropriate that some with mild cognitive impairment are ...
Study finds European breeding birds respond only slowly to recent climate change
2023-07-20
-With pictures-
Over the last 30 years European breeding birds have shifted their range by, on average, 2.4km per year, according to new research.
However, these changes were significantly different from expectations based on changing climate and landcover during that period.
Based on climate alone, the researchers predicted that the average range shifts by species should have been around 50% faster.
The study led by experts from Durham University, UK, used survey data collected as part of two Europe-wide ...
Researchers aim for rapid biomarker diagnostic test for stroke, using saliva
2023-07-20
Birmingham researchers are to set to collaborate on a study that could result in a rapid non-invasive diagnostic test to quickly and accurately identify stroke patients who need time-critical treatment before irreversible brain damage occurs.
Funded by the Stroke Association, the Golden HOur for STroke (GHoST) study will involve the West Midlands Ambulance Service University NHS Foundation Trust, Midlands Air Ambulance Charity, and University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Trust and industry partner Marker Diagnostics. A successful outcome could also revolutionise ...
Give more people with learning disabilities the chance to work, Cambridge historian argues
2023-07-20
Employment levels for people with learning disabilities in the UK are 5 to 10 times lower than they were a hundred years ago. And the experiences of workers from the 1910s–50s offer inspiration as well as lessons about safeguarding.
A new study by Cambridge historian Professor Lucy Delap (Murray Edwards College) argues that loud voices in the 20th-century eugenics movement have hidden a much bigger picture of inclusion in British workplaces that puts today’s low rates to shame.
Professor Delap found that in some parts of Britain, up to 70% of people variously labelled ‘defective’, ...
Use of law enforcement strategies to curb underage drinking has decreased over past decade: Study
2023-07-20
By Kimberly Flynn
PISCATAWAY, NJ — Despite the harm that excessive alcohol consumption can cause in a community, use of some alcohol-related enforcement strategies remained low or decreased from 2010 to 2019, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs. In particular, researchers found a drop in enforcement of underage drinking laws.
Researchers at the University of Minnesota first surveyed 1,028 county and municipal law enforcement agencies throughout the United States in 2010 about their practices regarding three factors to alcohol harms in communities: underage drinking, impaired ...
The malnutrition paradox: Adolescent obesity in Zimbabwe
2023-07-20
In some African countries that have traditionally faced issues such as undernourishment and hunger, being overweight is perceived as a good sign of health and prosperity. However, in most of these countries, a malnutrition paradox is evident. Obesity, a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide, is increasing at an alarming rate in countries like Zimbabwe, where the consumption of processed, energy-dense foods associated with western lifestyles, has been adopted.
An insightful study led by graduate student Ashleigh Pencil, from the Graduate School of Human Life ...
Dreaming in technicolor
2023-07-20
A team of computer scientists and designers based out of the University of Waterloo have developed a tool to help people use colour better in graphic design.
The tool, De-Stijl, uses powerful machine learning technology to suggest intuitive colour palettes for novice designers and inexperienced users. The software combines and improves on the functionalities of existing tools like Figma, Pixlr, and Coolor, allowing users to select important theme colors and quickly visualize how they’ll impact a design.
“You put your graphical ...
NIH renews UC Davis MIND Institute grant to study fragile X-associated syndromes for 24th year
2023-07-20
It’s been 22 years since UC Davis MIND Institute Medical Director Randi Hagerman and her husband, researcher Paul Hagerman, discovered the neurodegenerative condition called FXTAS (fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome). Hagerman, a pediatrician known for her enthusiasm for her work and patients, has been studying FXTAS ever since, seeking to develop treatments for it.
She was recently awarded her 24th consecutive year of funding from the National Institutes of Health for her fragile X-related work, a ...
AI must not worsen health inequalities for ethnic minority populations
2023-07-20
Scientists are urging caution before artificial intelligence (AI) models such as ChatGPT are used in healthcare for ethnic minority populations. Writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, epidemiologists at the University of Leicester and University of Cambridge say that existing inequalities for ethnic minorities may become more entrenched due to systemic biases in the data used by healthcare AI tools.
AI models need to be ‘trained’ using data scraped from different sources such as healthcare websites and scientific research. However, evidence shows ...
Monitoring T cells may allow prevention of type 1 diabetes
2023-07-20
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research scientists have shown that analyzing a certain type of immune cell in the blood can help identify people at risk of developing type 1 diabetes, a life-threatening autoimmune disease. The new approach, if validated in further studies, could be used to select suitable patients for treatment that stops the autoimmune process—making type 1 diabetes a preventable condition.
In the study, which appeared in Science Translational Medicine on July 5, 2023, the researchers ...
[1] ... [1785]
[1786]
[1787]
[1788]
[1789]
[1790]
[1791]
[1792]
1793
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
[1798]
[1799]
[1800]
[1801]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.