Claire K. Ankuda, MD, MPH (Mount Sinai Health System) recognized with AFAR 2023 Rising Star Award in Health Services and Aging Research
2023-07-24
New York, NY – The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), a national non-profit organization whose mission is to support and advance healthy aging through biomedical research, is proud to recognize the outstanding contributions of Claire K. Ankuda, MD, MPH, MSc with the 2023 Terrie Fox Wetle Rising Star Award in Health Services and Aging Research.
This award honors a health services researcher in an early or middle phase of his/her career who has already made important contributions with work that respects the value of multidisciplinary health services ...
Ming Xu, PhD (UConn) receives AFAR 2023 Vincent Cristofalo Rising Star Award in Aging Research
2023-07-24
New York, NY – The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), a national non-profit organization whose mission is to support and advance healthy aging through biomedical research, is pleased to recognize the exemplary contributions of Ming Xu, PhD, to the field of aging research through the 2023 Vincent Cristofalo Rising Star Award in Aging Research.
This award is named in honor of the late Dr. Cristofalo, who dedicated his career to aging research and to encouraging young scientists to investigate important problems in the biology of aging. Established in 2008, the award is a ...
NIH researcher Rafael de Cabo, PhD receives AFAR 2023 Irving S. Wright Award of Distinction
2023-07-24
The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), a national non-profit organization whose mission is to support and advance healthy aging through biomedical research, is pleased to recognize the exemplary contributions of Rafael de Cabo, PhD, to the field of aging research through the 2023 Irving S. Wright Award of Distinction.
This award is named in honor of AFAR’s founder and recognizes exceptional contributions to basic or clinical research in the field of aging. Established in 1982, the award is a framed citation and carries a cash prize of $5,000.
Dr. de Cabo is Senior Investigator of the ...
Muscadine wine shows promise in improving aging skin
2023-07-24
Could muscadine wine help perk up sagging skin? According to a new study, women who drank two glasses of dealcoholized muscadine wine daily showed significant improvements in the elasticity and water retention of their skin compared with those who consumed a placebo.
The study is the first time scientists have studied the impacts of nonalcoholic wine consumption on skin health in a randomized clinical trial. Researchers attribute the beneficial effects to chemical compounds called polyphenols that naturally occur in many plants.
“Muscadine grapes have been found to have a unique polyphenolic profile in comparison to other red wine varieties,” ...
Study explores how often children diagnosed with flu experience serious neuropsychiatric side effects
2023-07-24
While the incidence of influenza-associated neuropsychiatric events in children in the United States is unknown, the controversy over the use of a common antiviral medication typically administered to treat flu in children has sparked concern among parents and medical professionals alike.
The dilemma about whether the treatment causes neuropsychiatric events or if the infection itself is the culprit, led a group of pediatric researchers at Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt to study the question.
“Population-Based ...
Hebrew SeniorLife and Duke University receive $10.5 million award to study osteoporosis care in fracture patients
2023-07-24
Broken bones in later life are a leading cause of disability, recurrent fracture, nursing home placement, and death.
Prior studies have shown that health care providers can prevent poor outcomes, including death, by treating patients with bone-strengthening medications and by stopping risky medications that cause falls. However, few patients receive this high-quality care because it is time consuming and requires specialized knowledge that primary care providers may not have.
Researchers from Hebrew SeniorLife and Duke University will undertake a 5.5-year study that will compare two care models that have previously ...
A multiplex assay to assess activated p300/CBP in circulating prostate tumor cells
2023-07-24
“The results from this initial cohort support the integration of these biomarkers into prospective clinical trials.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 24, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 20, 2023, entitled, “Development of a multiplex assay to assess activated p300/CBP in circulating prostate tumor cells.”
Reduced SIRT2 deacetylation and increased p300 acetylation activity leads to a concerted mechanism of hyperacetylation at specific histone lysine sites (H3K9, H3K14, and H3K18) in castration-resistant ...
UPMC and Pitt researchers identify link between cancer-causing gene and aging
2023-07-24
A gene called Myc (pronounced “mick”) that is among the most important drivers of cancer in both mice and humans also plays a newly discovered crucial role in aging, according to a new Cell Reports study by researchers at UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
The research, led by Edward V. Prochownik, M.D., Ph.D., the Paul C. Gaffney Professor of Pediatrics in the Division of Hematology/Oncology at UPMC Children’s and professor in the Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, has implications for newer forms of cancer therapy.
Myc has traditionally been ...
Dance and the state: Research explores ballet training in Ukraine
2023-07-24
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Ballet training centers of Ukraine successfully resist co-optation by both neo-imperial and nationalist ideologies, forming robust and inclusive dancing communities that in many ways mirror structures of modern Ukrainian society, according to research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The signature Vaganova style of Soviet ballet can be described in a number of ways: exacting, athletic, classical, Russian. It’s also uniform across post-Soviet training academies, including those based in now-independent Ukraine.
Training shapes bodies, and post-Soviet dancers still begin ...
New study reveals why defense against brain corrosion declines in people with Alzheimer’s disease
2023-07-24
A new study by researchers at Case Western Reserve University revealed that the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD) can be slowed by suppressing a specific protein in the brain that causes corrosion.
A main pathogenic initiator of AD and related dementias is oxidative stress, which corrodes the brain, called oxidative damage.
David E. Kang, the Howard T. Karsner Professor in Pathology at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine and the study’s lead researcher, said they’ve identified for the first time a cause ...
Key to preventing HIV progression lies in the gut
2023-07-24
Restoring and improving gut health may be key to slowing HIV progression to AIDS, according to a new study by University of Pittsburgh infectious diseases scientists published today in the journal JCI Insight.
The animal study, which was performed with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), the monkey form of HIV, revealed that tackling only systemic immune activation and inflammation when attempting to control disease progression and comorbidities isn’t effective. Instead, treatments should target the root cause of those problems and focus on healing the gut.
“It ...
New studies show daily prune consumption supports cardiovascular health in aging population
2023-07-24
ROSEVILLE, CALIF. – July 24, 2023 – A pair of new studies presented as abstracts today at the American Society of Nutrition (ASN) annual meeting report that daily prune consumption has promising effects on several biomarkers related to cardiovascular health. Conducted in postmenopausal women and men 55 years and older, the studies reveal:
In men, long-term prune consumption improved HDL cholesterol and the total cholesterol to HDL ratio, while decreasing oxidative stress and the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein ...
Novel thermal sensor could help drive down the heat
2023-07-24
Excess heat from electronic or mechanical devices is a sign or cause of inefficient performance. In many cases, embedded sensors to monitor the flow of heat could help engineers alter device behavior or designs to improve their efficiency. For the first time, researchers exploit a novel thermoelectric phenomenon to build a thin sensor that can visualize heat flow in real time. The sensor could be built deep inside devices where other kinds of sensors are impractical. It is also quick, cheap and easy to manufacture using well-established methods.
According ...
Risk of forced labor is widespread in U.S. food supply, study finds
2023-07-24
Eliminating forced labor is a vital starting point for creating a just and sustainable food supply, but most of us don’t know much about the labor conditions involved in producing our food. It’s possible that the people who picked and processed some of the items on our dinner table worked in conditions that involved force, fraud, coercion, or debt bondage.
In a study published July 24 in Nature Food, researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University and the University of Nottingham Rights Lab calculated the risk of forced labor across all aspects of the U.S. food supply, excluding seafood. They found that the majority of forced ...
Association of early-, middle-, and late-life depression with incident dementia
2023-07-24
About The Study: The results of this study of more than 1.4 million adult Danish citizens followed up from 1977 to 2018 suggest that the risk of dementia was more than doubled for both men and women with diagnosed depression. The persistent association between dementia and depression diagnosed in early and middle life suggests that depression may increase dementia risk.
Authors: Holly Elser, M.D., Ph.D., of the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2309)
Editor’s ...
Study improves understanding of how bacteria benefit plant growth
2023-07-24
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Plants form alliances with microbes in the soil in which they grow. Legumes, for example, benefit from a symbiotic relationship with microbes that inhabit nodules in their roots and “fix” nitrogen in the atmosphere to make it available to promote the legumes’ growth. But are microbes always beneficial to plants? Or does competition between strains for plant access degrade the service the bacteria ultimately provide?
A team led by scientists at the University of California, Riverside, set up experiments to answer these questions and better understand the competition process. The researchers used a native ...
Association of social isolation with hospitalization and nursing home entry among older adults
2023-07-24
About The Study: Social isolation was significantly associated with higher odds of skilled nursing facility stays and nursing home placement during two years, but not with hospitalization, in this nationally representative study of 11,000 older adults. Efforts to deter or delay nursing home entry should seek to enhance social contact at home or in community settings.
Authors: Mary Louise Pomeroy, Ph.D., M.P.H., of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3064)
Editor’s ...
Consumption of soft drinks and overweight and obesity among adolescents in 107 countries and regions
2023-07-24
About The Study: The prevalence of daily consumption of soft drinks was associated with the prevalence of overweight and obesity among adolescent students in this study of 107 countries and regions. These results, in conjunction with other evidence, suggest that reducing soft drink consumption should be a priority in combating adolescent overweight and obesity.
Authors: Huan Hu, Ph.D., of the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health in Kanagawa, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Excess death rates for Republican and Democratic registered voters in Florida and Ohio during pandemic
2023-07-24
About The Study: In this study evaluating 538,000 deaths in individuals ages 25 and older in Florida and Ohio between March 2020 and December 2021, excess mortality was significantly higher for Republican voters than Democratic voters after COVID-19 vaccines were available to all adults, but not before. These findings suggest that differences in vaccination attitudes and reported uptake between Republican and Democratic voters may have been factors in the severity and trajectory of the pandemic in the U.S.
Authors: Jacob Wallace, Ph.D., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Community health worker home visiting and birth outcomes among Medicaid recipients
2023-07-24
About The Study: Participation in a home visiting program provided by community health workers working with nurses and social workers, compared with usual care, was associated with reduced risk for adverse birth outcomes, improved prenatal and postnatal care, and reductions in disparities, among birthing individuals with Medicaid. The risk reductions in adverse birth outcomes were greater among Black individuals.
Authors: Cristian I. Meghea, Ph.D., of Michigan State University in East Lansing, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Why we lose fat and muscle during infection
2023-07-24
LA JOLLA (July 24, 2023)—Although infections can present with many different symptoms, one common symptom is the loss of fat and muscle, a process called wasting. Salk scientists wanted to know whether wasting was beneficial in fighting infections.
Researchers in Professor Janelle Ayres’ lab discovered the wasting response to T. brucei infection in mice occurs in two phases, each regulated by different immune cells. While fat loss did not benefit the fight against infection, muscle loss did—a surprising clue that some wasting may help manage illness.
The findings, published in Cell Reports on July 24, 2023, can inform the development of more effective ...
Dementia becomes an emergency 1.4 million times a year
2023-07-24
A busy, crowded, confusing emergency room is not an ideal place for a person living with dementia.
But 1.4 million times a year, people with Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia end up in emergency care, a new study shows.
Together, they make up nearly 7% of all emergency visits for any reason by people over age 65, according to a University of Michigan team’s findings published in JAMA Neurology.
And compared with their peers who don’t have dementia, these patients have twice the rate of seeking emergency care after an accident or a behavioral or ...
Study: Inflation Reduction Act’s cap on insulin out-of-pocket costs boosts prescription fills
2023-07-24
LOS ANGELES – The Inflation Reduction Act’s policy capping out-of-pocket costs for insulin to $35 for a month’s supply led to increases in the total number of insulin fills for Medicare beneficiaries, according to a new study from the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics and University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Following the cap’s enactment in January 2023, the number of insulin fills among Medicare Part D enrollees increased from 519,588 to 523,564 per month. In contrast, the number of insulin fills decreased among older adults without Medicare during the same period. The study was published today in the Journal of ...
FASEB joins Society Publishers to recommend diversity initiatives for publications
2023-07-24
ROCKVILLE, Md. — The Federation of American Society for Experimental Biology (FASEB) recently co-authored a report to provide guidance to society publishers on how to address diversity and inclusivity matters within their journal programs. Titled Recommendations for Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion Initiatives for Society Publishers, the report was published by the Society Publishers’ Coalition, of which FASEB is a member. Darla P. Henderson, PhD, FASEB Director of Open Science and Research Integrity and Director of Publications, represented FASEB and was among the report’s ...
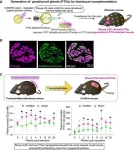
Successful generation of functional parathyroid glands from mouse embryonic stem cells
2023-07-24
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) show that it is possible to generate functional parathyroid glands using mouse embryonic stem cells using blastocyst complementation
Tokyo, Japan – Regenerative medicine has opened up exciting possibilities in the world of medicine. Now, researchers in Japan are searching for ways to recreate and rebuild body tissues and organs, which may be an alternative cure for diseases.
In a recently published study in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), researchers from Tokyo Medical ...
[1] ... [1791]
[1792]
[1793]
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
[1798]
1799
[1800]
[1801]
[1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
[1807]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.