New approach to fuel cell manufacturing could reduce cost, increase availability
2023-07-26
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A Penn State-led team of researchers developed a potentially promising approach to make fuel cells more affordable. The new method reduces the amount of platinum-group metal (PGM) loadings by replicating a process used in computer chip manufacturing.
They published their results this week (July 24) in JACS Au, an open-access journal of the American Chemical Society.
According to corresponding author Christopher Arges, an associate professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering and a faculty member in the Institutes ...
Study examines struggles of Haitian migrants self-managing diabetes on Dominican Republic sugar cane fields
2023-07-26
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- A new study from the University of Missouri Sinclair School of Nursing found that barriers, including poverty, low health literacy, cultural beliefs, lack of infrastructure and political issues, all work together to hinder diabetes self-management for Haitian migrants working in sugar cane fields in the Dominican Republic.
Rosalia Molina, a nurse who has taken previous medical missionary trips to the Dominican Republic to help impoverished individuals self-manage their diabetes, led the study as part of her doctoral studies at the MU Sinclair School of Nursing. She interviewed health care workers in the Dominican Republic about their challenges providing ...
Scientist discover protein required for an effective immune response to invading bacteria
2023-07-26
Key Takeaways
Researchers have discovered that the NLRP11 protein plays critical roles in alerting the body to a bacterial infection and initiating an immune response against it
NLRP11 is present in humans and other primates but absent in mice
The discovery could enable the development of mouse models that are more similar to humans for bacterial infection experiments
BOSTON – A team led by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has discovered a protein that plays critical roles in alerting the body to a bacterial ...
People with increased genetic risk of Alzheimer’s may lose sense of smell first
2023-07-26
MINNEAPOLIS – People who carry the gene variant associated with the strongest risk for Alzheimer’s disease may lose their ability to detect odors earlier than people who do not carry the gene variant, which may be an early sign of future memory and thinking problems, according to a study published in the July 26, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The gene variant associated with this increased risk of Alzheimer’s is called APOE e4.
“Testing a person’s ability to detect odors may be a useful way to predict future problems with cognition,” said study ...
RIT professor co-authors paper on new planetary formation findings
2023-07-26
Rochester Institute of Technology’s Joel Kastner, a professor in the Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science and School of Physics and Astronomy, and a team of researchers with the European Southern Observatory (ESO) have discovered new evidence of how planets as massive as Jupiter can form, using images from the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
The combination of VLT and ALMA imaging have yielded detections of dusty ...
Delaying methane mitigation increases risk of breaching Paris Agreement climate goal, study finds
2023-07-26
A new study by Simon Fraser University researchers shows that efforts to reduce methane emissions are needed immediately if we are to meet global climate change goals.
A key element of the 2015 Paris Agreement, a legally binding international treaty on climate change, is the commitment to limit average global temperatures increases to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, and pursue efforts to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. This requires reaching net-zero CO2 emissions by or around 2050—and deep reductions in methane and other ...
Lizards may miss out on mating opportunities and pick partners more hastily under warming temperatures
2023-07-26
Lizards may miss out on mating opportunities and pick partners more hastily under warming temperatures
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285656
Article Title: Behavioural plasticity in activity and sexual interactions in a social lizard at high environmental temperatures
Author Countries: Argentina
Funding: N.R. - Student Research Grant 2019 - Animal Behavior Society https://www.animalbehaviorsociety.org/web/index.php. M. C. - Consejo Nacional ...
Fungi which normally decay wood can effectively break down low density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic instead - and do so best in the absence of wood
2023-07-26
Fungi which normally decay wood can effectively break down low density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic instead - and do so best in the absence of wood
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288133
Article Title: Wood decay fungi show enhanced biodeterioration of low-density polyethylene in the absence of wood in culture media
Author Countries: Sri Lanka
Funding: 1. RNA: TWAS research grant 18-020 RG/BIO/AS_I The world academy of science https://twas.org/ 2. RNA, PW, HH: ICGEB research grant CRP/LKA18-03 https://www.icgeb.org/ International Center for genetic engineering and biotechnology 3. RNA, HH: t(NSF/RG/2019/BT/03). http://www.nsf.ac.lk/ ...
Fast electrical signals mapped in plants with new bioelectronic technology
2023-07-26
What happens inside the carnivorous plant Venus Flytrap when it catches an insect? New technology has led to discoveries about the electrical signalling that causes the trap to snap shut. Bioelectronic technology enables advanced research into how plants react to their surroundings, and to stress.
Most people know that the nervous system in humans and other animals sends electric impulses. But do plants also have electrical signals even though they lack a nervous system? Yes, plants have electrical signals that are generated in response to touch and stress factors, such as wounds caused by herbivores and attacks on their roots. As opposed to animals, who can move out of the ...
Aphids make tropical milkweed less inviting to monarch butterflies, study finds
2023-07-26
Many gardeners will tell you that aphids are the bane of their existence. According to a new study from the University of Florida, these tiny pests also pose problems for the iconic monarch butterfly. The study found that when oleander aphids infested tropical milkweed — a nonnative milkweed species commonly used across southern portions of the U.S. stretching from California to Florida — the butterflies laid fewer eggs on the plants, and caterpillars developing on those plants were slower to mature.
Monarch butterflies depend on milkweed and its close relatives to complete their life ...
Climate change threatens 771 endangered plant and lichen species
2023-07-26
All plants and lichens listed as endangered under the Endangered Species Act are sensitive to climate change but there are few plans in place to address this threat directly, according to a new study by Amy Casandra Wrobleski of Pennsylvania State University and colleagues, published July 26, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate.
Climate change is expected to have a major impact on species around the world, especially endangered species, which are already rare. A majority of the organisms listed under the Endangered Species Act are ...
Increased step count linked to better health for people with heart failure
2023-07-26
More often, people are turning to consumer wearable devices, such as smartwatches, to monitor their health and physical activity.
Using these wearable devices, a study led by Michigan Medicine and the University of Missouri with Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute finds that taking more daily steps is associated improved health, including fewer symptoms and physical limitations, for people with heart failure. The results are published in JACC: Heart Failure.
Clinicians are increasingly presented with their patients’ wearable device data, ...
NIH spent $950M for basic or applied research leading to patents providing market exclusivity for drugs approved 2010-19
2023-07-26
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
A new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry demonstrates that the National Institutes of Health (NIH) spent $950 million on basic or applied research associated with patents that provided manufacturers with market exclusivity. This amount represents <1% (0.59%) of the $164 billion in total NIH funding for research contributing to the approval of these products.
The article in PLOS ONE titled “NIH funding for patents that contribute ...
People with heart failure can step their way to better health
2023-07-26
People with heart failure who increase their daily step count also saw improvements in their health status over a 12-week period, according to a study published today in JACC: Heart Failure. The study suggests that physical data from wearable devices, such as step count, can be clinically significant and has the potential to inform future clinical trials and clinical care.
Consumer wearable devices to track health status and progress are commonly used and part of a growing trend of mobile health technology. However, how to interpret data from wearable devices, including step count, is at times ...
Ancient DNA reveals diverse community in “Lost City of the Incas”
2023-07-26
Who lived at Machu Picchu at its height? A new study, published today in Science Advances, used ancient DNA to find out for the first time where workers buried more than 500 years ago came from within the lost Inca Empire.
Researchers, including Jason Nesbitt, associate professor of archaeology at Tulane University School of Liberal Arts, performed genetic testing on individuals buried at Machu Picchu in order to learn more about the people who lived and worked there.
Machu Picchu is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Cusco ...
Essential cell death-regulating mechanisms important for recovery from SARS-CoV infection and skin injury discovered
2023-07-26
Programmed cell death, a fundamental biological process that facilitates the elimination of old, damaged, infected, and non-functional cells, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance between health and disease in the human body. Research by the team of Dr Alessandro Annibaldi from the Center for Molecular Medicine Cologne (CMMC) at the University of Cologne has uncovered a novel mechanism of cell death regulation, shedding light on its significance during conditions such as SARS-CoV infection and skin injury. The study ‘Cleavage ...
DNA analysis offers new insights into diverse community at Machu Picchu
2023-07-26
New Haven, Conn. — A genetic analysis suggests that the servants and retainers who lived, worked, and died at Machu Picchu, the renowned 15th century Inca palace in southern Peru, were a diverse community representing many different ethnic groups from across the Inca empire.
The genomic data, described in a new study in Science Advances, is the first investigation of the genomic diversity of individuals buried at Machu Picchu and adjacent places around Cusco, the Inca capital. It builds upon previous archeological and bio-archaeological research, including a 2021 Yale-led study which found that Machu Picchu (AD 1420-1530) is older than was previously believed.
“The ...
Lost metabolic fitness of CAR NK cells is key mechanism of tumor resistance
2023-07-26
A new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center discovered loss of metabolic fitness in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) natural killer (NK) cells is a critical mechanism of resistance, with infused cells gradually losing the ability to compete with tumor cells for nutrients, leading to tumor relapse.
The study, published today in Science Advances, demonstrates that engineering CAR NK cells to express interleukin-15 (IL-15) enhances the cells’ metabolic fitness and provides a longer-lasting ...
Researchers develop machine learning models that could improve suicide-risk prediction among children
2023-07-26
A new study from UCLA Health researchers finds that the typical ways health systems store and track data on children receiving emergency care miss a sizable portion of those who are having self-injurious thoughts or behaviors. The researchers also found that several machine learning models they designed were significantly better at identifying those children at risk of self-harm.
Amid a nationwide youth mental health crisis, mental health providers are trying to improve their understanding of which children are at-risk of suicide or self-harm so providers can intervene earlier. However, health systems often ...
DOE announces $33 million to advance energy research across America
2023-07-26
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $33 million to support 14 clean-energy research projects as part of a program to ensure the Department’s research funding is reaching pockets of the country that traditionally have received disproportionally low amounts of Federal scientific funding. The projects will cover a range of topics—including grid integration, renewable solar and wind energy, and advanced manufacturing. Today’s funding will help ensure all regions of the country share in the ownership of priority research that advances science and addresses energy ...
Predicting lifespan-extending chemical compounds for C. elegans with machine learning
2023-07-26
“We created datasets for predicting whether or not a compound extends the lifespan of C. elegans [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 13, entitled, “Predicting lifespan-extending chemical compounds for C. elegans with machine learning and biologically interpretable features.”
Recently, there has been a growing interest in the development of pharmacological interventions targeting ...
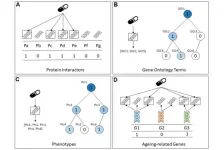
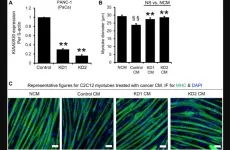
KIAA0930: A cachexic phenotype inducer in cancer cells
2023-07-26
“We believe that KIAA0930 would be a novel cachexia therapeutic target.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 20, 2023, entitled, “The uncharacterized transcript KIAA0930 confers a cachexic phenotype on cancer cells.”
Patients with cancer cachexia have a poor prognosis and impaired quality of life. Numerous studies using preclinical models have shown that inflammatory cytokines play an important role in the development of cancer cachexia; however, no clinical trial targeting cytokines has been successful. Therefore, ...
Lifespan of ageing science’s model organism driven by reproductive self-destruction
2023-07-26
The lifespan of a small roundworm that has been used as a key model organism in ageing research is limited by how it self-sacrifices to feed its young, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The authors of the new Nature Communications paper say their findings raise questions about how well insights from the Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) worm can be translated to human ageing advances.
C. elegans is widely used as a laboratory animal, and has been central to ageing research for 40 years thanks to discoveries of genes that can be supressed to produce up to a tenfold increase in ...
A study outlines the optimal strategy for accelerating the energy transition in China
2023-07-26
China has set itself the goal of reaching its peak of carbon dioxide emissions in 2030 and thereafter to reduce emissions to reach carbon neutrality by 2060. To achieve this, it needs to increase photovoltaic (PV) and wind power to 10-15 petawatt hours (PWh) by 2060.
However, according to historical installation rates and a recent high-resolution energy-system-model and forecasts based on China's 14th Five-Year Energy Development Programme (CFEDP), the capacity of China for producing non-fossil-fuel energy will reach a maximum of only 9.5 PWh per year by 2060.
Now, an international study with the participation ...
How eavesdropping viruses battle it out to infect us
2023-07-26
Viruses, like movie villains, operate in one of two ways: chill or kill.
They can lay low, quietly infiltrating the body’s defenses, or go on the attack, exploding out of hiding and firing in all directions. Viral attacks are almost always suicide missions, ripping apart the cell that the virus has been depending on. The attack can only succeed if enough other healthy cells are around to infect. If the barrage of viral particles hits nothing, the virus cannot sustain itself. It doesn’t die, since viruses aren’t technically alive, but it ceases to function.
So for a virus, the key challenge is deciding when to flip from chill mode into kill mode.
Four years ago, Princeton ...
[1] ... [1784]
[1785]
[1786]
[1787]
[1788]
[1789]
[1790]
[1791]
1792
[1793]
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
[1798]
[1799]
[1800]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.