New drug delivery system shows promise in treatment of life-threatening pregnancy condition
2023-07-25
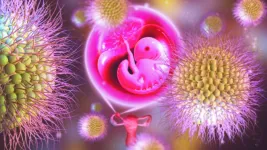
PORTLAND, Ore. – Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Pharmacy have developed a drug delivery system that shows promise for greatly enhancing the efficacy of the medicine given to women with the life-threatening condition of ectopic pregnancy, which occurs when a fertilized egg implants somewhere other than the lining of the uterus.
Olena Taratula of the OSU College of Pharmacy, and Maureen Baldwin and Leslie Myatt of Oregon Health & Science University led a team that used a mouse model to show ...
Experts call for independent inquiry into Canada’s COVID-19 response
2023-07-25
At first glance, Canada appears to have responded adequately to the covid-19 emergency, but beneath the surface lie major pandemic failures, warns a series of articles published by The BMJ today.
The BMJ Canada Covid Series provides a critical analysis of what worked and what didn’t in Canada’s covid-19 response and calls for a national independent review to learn lessons and ensure accountability for the past and future preparedness.
The articles, written by leading clinicians and researchers representing 13 institutions across Canada, highlight long-standing weaknesses ...
Bisexual people experience worse health outcomes than other adults in England – national study of more than 835,000 people
2023-07-25
Self-reported data from lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB) patients shows these groups have poorer health outcomes compared to those who identify as heterosexual, but bisexual people disproportionally experience the worst outcomes in England.
These new findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal The Journal of Sex Research, indicate that bisexual people face additional health disparities within an already marginalised community.
Experts, from the Brighton and Sussex Medical School and Anglia Ruskin University who led the analysis of more than 835,000 adults in England, suggests the disparities could result from unique prejudice and discrimination ...
Family loses child to necrotizing enterocolitis and publishes “Forever Our Little One,” a storybook for bereaved families
2023-07-25
Davis, CA – Mother-daughter duo Jennifer Canvasser and Leslie Napolitano have published Forever Our Little One, a storybook for bereaved families. Jennifer is the executive director of the Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Society, which she founded after her son Micah tragically died from complications of NEC. Leslie is an artist and illustrator who helped care for her grandson Micah during his time in the neonatal and pediatric intensive care units. Jennifer wrote the storybook for families ...
Curbing waste improves global food security but has limited environmental benefits
2023-07-24
Irvine, Calif., July 24, 2023 – Reducing waste is one way to help combat hunger around the world, but stricter control over food loss and waste does not lead to better environmental outcomes, according to researchers at the University of California, Irvine and the University of Colorado Boulder.
In a paper published recently in Nature Food, the scientists stress that curbing food spoilage increases the amount of produce in markets, which leads to lower costs. Cheaper food encourages people to buy and eat more, offsetting the lowering of greenhouse gas ...
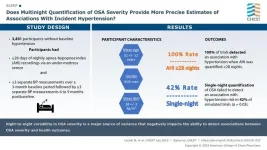
Highlights from the journal CHEST®, July 2023
2023-07-24
Glenview, Illinois – Published monthly, the journal CHEST® features peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research in chest medicine: Pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine and related disciplines. Journal topics include asthma, chest infections, COPD, critical care, diffuse lung disease, education and clinical practice, pulmonary vascular disease, sleep, thoracic oncology and the humanities.
The July issue of the CHEST journal contains 49 articles, including clinically relevant research, reviews, case series, commentary and more. Each month, the journal ...
New study reveals self-replicating RNA and novel vaccine delivery technology demonstrate enhanced safety and efficacy
2023-07-24
As the world continues to combat various infectious diseases, the development of novel vaccine technologies remains at the forefront of scientific research. mRNA-based vaccines and utilization of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for their delivery, have recently shown encouraging results in diseases such as COVID-19.
However, a critical concern revolves around the wide biodistribution of LNPs in the body, which, in some cases, may result in unintended side effects. A recent publication in the peer-reviewed ...
Often, consumers inadvertently give too much credit to products’ ‘scientifically studied’ claims
2023-07-24
Key takeaways
A new study finds that consumers often misremember if a product is labeled “scientifically studied” or “scientifically proven” — despite the significant difference in meaning between the two phrases.
UCLA psychologists conducted an experiment with one group of college students and another group of older adults to determine whether they would accurately recall which claim was made in an advertisement for a dietary supplement.
Only 26% of subjects correctly remembered which phrase was used, and the percentage who recalled the information ...
ACP says the US needs immediate action to prepare for future pandemics
2023-07-24
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 24 July 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Community health workers improved homebound care during pandemic
2023-07-24
SAN ANTONIO (July 24, 2023) — Staying healthy and connected was difficult for everyone during the COVID-19 pandemic, but especially so for homebound older patients and their caregivers. Fortunately, a program developed by the geriatrics and supportive care team of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio effectively integrated community health workers (promotores de salud in Spanish) into patient outreach to improve health. Thanks to the program, annual visits to older adults with type 2 diabetes, dementia and other health issues in underserved ...
Stretchy integrated electronics may be possible with sandwiched semiconductor
2023-07-24
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — There’s a barrier preventing the advent of truly elastic electronic systems, the kind needed for advanced human-machine interfaces, artificial skins, smart health care and more, but a Penn State-led research team may have found a way to stretch around it.
According to principal investigator Cunjiang Yu, who holds is the Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics and of Biomedical Engineering at Penn State, fully elastic electronic systems require flexibility and stretchability in every ...
Water-scarce cultures value long-term thinking more than their water-rich neighbors do
2023-07-24
Water is the world’s most valuable natural resource. Although a human can survive weeks or even months without food, going as little as three days without water could spell the end. The effects of water scarcity aren’t limited to immediate survival situations, however. Recently published research in Psychological Science suggests that cultures from water-scarce environments tend to be more likely than cultures from water-rich areas to value long-term thinking and to scorn short-term indulgence.
“Individuals from historically water-scarce climates tend to be ...
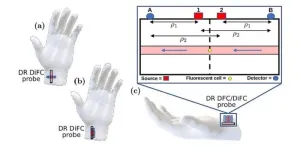
New method for noninvasive detection of circulating tumor cells in blood
2023-07-24
Metastasis occurs when cancer cells acquire the ability to spread and form new tumors in different places in the body, usually by traveling within blood or lymph vessels. Since metastasis is a hallmark of advanced cancer and severely complicates treatment, its early diagnosis is essential. One way to do this is by looking for circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in blood samples.
However, CTCs can be very rare, and they might be completely absent in small blood samples despite being present in a patient’s bloodstream. To address this problem, researchers have developed a technique called diffuse in-vivo flow cytometry (DiFC). It involves labeling CTCs with ...
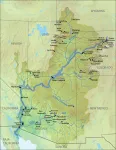
Colorado River Basin has lost water equal to Lake Mead due to climate change
2023-07-24
American Geophysical Union
Release No. 23-28
24 July 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/colorado-river-basin-has-lost-water-equal-to-lake-mead-due-to-climate-change/
Colorado River Basin has lost water equal to Lake Mead due to climate change
A rapid rate of reductions in runoff associated with the Colorado Basin’s snowpack region, quantified here for the first time, is largely responsible for the water loss.
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org +1 (202) 777-7492 (UTC-4 hours)
Contact ...
Beyond protected areas: Novel method shows promise for monitoring biodiversity on working lands
2023-07-24
New research led by Adam Dixon, a conservation scientist with the World Wildlife Fund, describes the successful pilot of a novel method to study how well grassland birds are faring on croplands. The study, published in Ecological Applications, looked at 44 pockets of non-crop vegetation in the gaps between crop rows and at the edges of fields on lands under intensive agricultural cultivation in Iowa. The study may serve as a model for monitoring wildlife on working lands more generally, which can include crop fields, cattle ranches, and logged forests.
The researchers analyzed satellite imagery data to determine each pocket's area and “texture,” ...
Is snacking bad for your health? It depends on what and when you eat
2023-07-24
Snacking is becoming increasingly popular, with more than 70% of people reporting they snack at least twice a day. In a new study involving more than 1,000 people, researchers examined whether snacking affects health and if the quality of snack foods matters.
“Our study showed that the quality of snacking is more important than the quantity or frequency of snacking, thus choosing high quality snacks over highly processed snacks is likely beneficial,” said Kate Bermingham, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at King's College London. “Timing is also important, with late night snacking being unfavorable for health.”
Bermingham ...
One way to reduce medical errors? Connect doctors with other doctors
2023-07-24
We trust our doctors with our lives, but the sad and scary fact is that doctors can get things wrong. Approximately 100,000 Americans die each year due to medical errors and recent studies have found that 10 to 15% of all clinical decisions regarding patient diagnosis and treatment are wrong.
A team of researchers led by Damon Centola, Professor and Director of the Network Dynamics Group at the Annenberg School for Communication at the University of Pennsylvania, has found a simple, effective way to reduce errors in patient diagnosis and treatment — use structured networks to connect clinicians with other clinicians.
In a study published today in the journal ...
Study finds new, unexpected mechanism of cancer cell spread
2023-07-24
A surprising finding from USC reveals key details about how cancer cells metastasize and suggests new therapeutic approaches for halting their spread.
The research, supported by the National Institutes of Health, centers on a cellular chaperone protein known as GRP78, which helps regulate the folding of other proteins inside cells. Previous studies from the same team, led by Amy S. Lee, PhD, professor of biochemistry and molecular medicine at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, have shown that when cells are under stress (due to COVID-19 or cancer), GRP78 gets hijacked, allowing viral invaders to replicate, ...
Sahara dust can enhance removal of methane
2023-07-24
The study by Maarten van Herpen et al., entitled “Photocatalytic Chlorine Atom Production on Mineral Dust-Sea Spray Aerosols over North Atlantic,” was funded in part by the NGO Spark Climate Solutions. It incorporates a proposed new mechanism whereby blowing mineral dust mixes with sea-spray to form Mineral Dust-Sea Spray Aerosol (MDSA).
The results suggest that MDSA is activated by sunlight to produce an abundance of chlorine atoms, which oxidize atmospheric methane and tropospheric ozone via photocatalysis. Largely composed of blowing dust from the Sahara Desert combined with sea salt aerosol from the ocean, MDSA is the dominant source of atmospheric ...
Unlocking secrets of the elusive ghost shark
2023-07-24
Researchers from the University of Florida and the Seattle Aquarium are exploring 100 meters underwater in the Pacific Northwest this summer to learn more about mysterious ghost sharks, one of the strangest beasts from the depths of the ocean.
Using remotely operated underwater vehicles, or ROVs, the scientists searched for nesting grounds of the Pacific spotted ratfish, Hydrolagus colliei, a ghostlike fish that lurks on the ocean floor.
“We know very little about these elusive relatives of sharks and even less about their spawning habits and embryonic development,” said ...
Risk of fatal heart attack may double in heat wave & high fine particulate pollution days
2023-07-24
Research Highlights:
An analysis of more than 202,000 heart attack deaths between 2015-2020 in a single Chinese province found that days that had extreme heat, extreme cold or high levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution were significantly associated with the risk of death from a heart attack, especially in women and older adults.
The greatest increase in the risk of death from heart attack was seen on days that had the combination of extreme heat and high levels of PM2.5.
The days with extreme heat were associated ...
Study shows positive outcomes for first three U.S. living HIV-to-HIV kidney transplant donors
2023-07-24
Based on findings from a study published today in the journal, The Lancet Regional Health – Americas, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine and three collaborating medical institutions suggest that people living with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who donate a kidney to other people living with HIV (PLWH) have a low risk of developing end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) or other kidney problems in the years following the donation.
“This new evidence is proof-of-concept that donating a kidney can be safe for people living with HIV,” says Christine Durand, M.D., associate professor of medicine at Johns ...
Webb detects water vapor in rocky planet-forming zone
2023-07-24
Water is essential for life as we know it. However, scientists debate how it reached the Earth and whether the same processes could seed rocky exoplanets orbiting distant stars. New insights may come from the planetary system PDS 70, located 370 light-years away. The star hosts both an inner disk and outer disk of gas and dust, separated by a 5 billion-mile-wide (8 billion kilometer) gap, and within that gap are two known gas-giant planets.
New measurements by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) have detected water vapor in the system’s inner disk, at distances ...
Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis often missed or delayed, especially in non-White infants
2023-07-24
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is leading an awareness campaign that aims to reduce missed or delayed diagnosis of cystic fibrosis after newborn screening, especially in non-White infants. In its first phase, the campaign targets primary care providers and public health officials, so that treatment can start earlier, which is linked to better outcomes for people with cystic fibrosis. The general public phase is expected to follow within the year.
Funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ...
Potent anti-cancer therapy created using ‘click chemistry’
2023-07-24
A potent anti-cancer therapy has been created using Nobel prize-winning “click chemistry”, where molecules click together like LEGO bricks, in a new study by UCL and Stanford University researchers.
The study, published in Nature Chemistry, opens up new possibilities for how cutting-edge cancer immunotherapies might be built in future.
The research team created an anti-cancer therapy with three components: one targeting the cancer cell, another recruiting a white blood cell called a T cell to attack the cancer cell, and a third knocking out part of the cancer cell’s defences.
Previously, ...
[1] ... [1790]
[1791]
[1792]
[1793]
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
1798
[1799]
[1800]
[1801]
[1802]
[1803]
[1804]
[1805]
[1806]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.