BioIVT to discuss its pivotal role in liquid biopsy research at the AACC Annual Scientific Meeting and Clinical Lab Expo
2023-07-21
BioIVT, a global research partner and biospecimen solutions provider for drug and diagnostic development, today announced that it will highlight the integral role it is playing in liquid biopsy research at the American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC) Annual Scientific Meeting and Clinical Lab Expo. This conference will be held from July 23-27 at the Anaheim Convention Center in Anaheim, CA.
“Liquid biopsy research can revolutionize the way we detect, diagnose, and treat diseases. However, several issues need to be resolved before it can reach its full potential. They include adopting ...
Father’s psychiatric diagnosis increases risk of preterm birth, study reports
2023-07-21
Babies are more likely to be born prematurely when either their father or mother has had a psychiatric diagnosis, according to a study conducted by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Karolinska Institutet and published July 20 in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
The research shows, for the first time, that the risk of preterm birth is higher in infants whose father or mother has a psychiatric diagnosis than in those whose parents do not, and higher still when both parents have such diagnoses.
Preterm ...
Multi-society statement on US Supreme Court ruling on students for fair admissions
2023-07-21
ROCKVILLE, MD—JULY 19, 2023 – As organizations representing a wide range of scientific, engineering, and mathematical disciplines, we will not be deterred by the U.S. Supreme Court ruling on race considerations in college and university admissions.
America’s inherent strength and economic competitiveness among nations is its domestic and international talent across every race, ethnicity, gender, and geography. To meet current and emerging job demands and retain our research and development leadership globally, we must broaden who participates in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and medicine. Doing so will improve lives, advance our nation’s living standards, ...
Harnessing machine learning for early cancer detection in primary care
2023-07-21
“[Machine learning] has the potential to transform early cancer detection in primary care [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 21, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on June 9, 2023, entitled, “Transforming early cancer detection in primary care: harnessing the power of machine learning.”
Cancer remains a significant global health burden, and early detection plays a crucial role in improving patient outcomes. Primary care settings serve as frontline gatekeepers, providing an opportunity for early detection through symptom assessment and ...
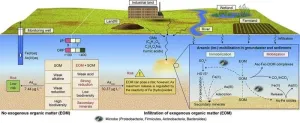
New study uncovers potential risk of arsenic release from sediment under organic matter influence
2023-07-21
Researchers from the Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences have conducted a study to assess the impact of environmental factors and microbial communities on the mobilization of arsenic (As). The findings, published in Volume 15 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, reveal important insights into the biogeochemical processes involved in As release. The study focused on processes such as desorption, reduction, complexation, and co-precipitation that affect the As behaviour in the environment. The interaction ...
$20 million awarded to lead next century of heart disease and stroke scientific research
2023-07-21
DALLAS, July 21, 2023 — More than 100 scientists from across the U.S. are receiving special grants to support their research work in finding innovative solutions to fight heart disease and stroke. The grants, totaling $20 million, are part of the Second Century of Science Initiative of the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization dedicated to a world of longer, healthier lives. The financial awards are announced as the Association, the largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S., prepares to celebrate ...
BESSY II: Surface analysis of catalyst particles in aqueous solutions
2023-07-21
Green hydrogen can be produced directly in a photoelectrochemical cell, splitting water with solar energy. However, this requires the development of super-efficient photoelectrodes that need to combine many talents at the same time: They must be excellent at converting sunlight into electricity, remain stable in acidic or basic water, act as catalysts to promote the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and be cheap, abundant and non-toxic. The large material class of metal oxides comes into question. However, it is difficult to find out what really happens at the interfaces ...
Study: How mother and infant sleep patterns interact during the first two years of life
2023-07-21
URBANA, Ill. — New mothers can expect sleep deprivation in the first few years of baby’s life. But too little sleep can take a toll on the health of both mother and child. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign looks at maternal and infant sleep patterns, identifying predictors and providing recommendations for instilling healthy habits.
“The first two years is a really critical period where a lot of development is going on, and sleep is important for health. We wanted to look at the association of mother and infant sleep and whether it changes over time,” said Tianying ...
Contribution of cultural heritage values to steppe conservation on ancient burial mounds of Eurasia
2023-07-21
During our history, ancient civilisations have considerably shaped the global ecosystems through a coevolution of landscape and local populations. In some cases, the legacy of the disappeared civilizations is still visible in the form of buildings and other monuments such as the Stonehenge, the buildings of the Roman and Hellenic Empires, and ancient burial places and fortresses built by several cultures. These monuments are invaluable parts of our history and cultural heritage. Although it is often not in the spotlight, they can also hold a considerable biodiversity conservation potential.
In the vast steppes of Eurasia (and probably ...
NIH grant to facilitate high-speed bioprinting of bones, tracheas, organs
2023-07-21
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Developing technology to quickly and efficiently bioprint human tissues at scale is the goal of a new project led by Penn State researchers. When fully developed, the technology will be the first to enable the fabrication of scalable, native tissues such as bones, tracheas and organs.
The National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Engineering at the National Institute of Health has awarded over $2 million in support of the project, led by Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, professor of engineering science and mechanics, biomedical engineering, and neurosurgery at Penn State.
“This will be a platform technology, which can be used for multiple purposes,” ...
Penn State researchers examine how environmental chemicals affect gut microbiome
2023-07-21
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Worldwide, high rates of obesity and other inflammatory conditions are associated with increased risk for cancer, cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Investigating how environmental chemical exposure impacts the gut microbiome to exacerbate these conditions is the goal of a new $7 million grant awarded to Andrew Patterson, professor of molecular toxicology and the John T. and Paige S. Smith Professor in the College of Agricultural Sciences.
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, part of the National ...
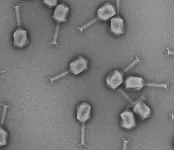
Treating bladder infections with viruses
2023-07-21
About one in two women are affected by cystitis during her lifetime, and many suffer from recurrent urinary tract infections. Bladder infections are not only painful and potentially dangerous, but they also pose a significant dilemma for physicians. With antibiotic resistance becoming widespread in urinary tract infections and continually increasing, physicians are often forced to blindly prescribe antibiotics without knowing their effectiveness against the pathogen causing the infection. This is because it takes several days to identify a specific ...
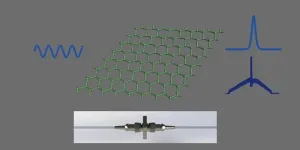
Two types of ultrafast mode-locking operations generation from an Er-doped fiber laser based on germanene nanosheets
2023-07-21
Saturable absorbers as passive modulators in passively mode-locked fiber lasers play a crucial role in the generation of ultrashort pulses. Germanene, a graphene-like two-dimensional material with fast carrier relaxation time and large nonlinear absorption coefficient comparable to that of graphene, is a saturable absorber material with very fast response.
Researchers led by Prof. Wei Xia at University of Jinan (UJN), are interested in modulation switches in fiber lasers, and two-dimensional material saturable absorbers have been a hot research topic in recent years. Two-dimensional materials make up for the disadvantages of ...
Trends in the prevalence of hepatitis C infection during pregnancy and maternal-infant outcomeTrends in the prevalence of hepatitis C infection during pregnancy and maternal-infant outcomes
2023-07-21
About The Study: This study of more than 70 million births or spontaneous abortions showed the prevalence of hepatitis C (HCV)-positive pregnancies in the U.S. increased 16-fold between 1998 and 2018. Maternal HCV infection was associated with increased odds of preterm labor, poor fetal growth, or fetal distress. These data may support recent recommendations for universal HCV screening with each pregnancy.
Authors: Po-Hung Chen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, ...
Association between cervical cancer screening guidelines and preterm delivery
2023-07-21
About The Study: The findings of this study of births to females ages 18 to 24 suggest that additional recommended cervical cancer screenings before birth were associated with an increased risk of preterm delivery. Cervical cancer screening guidelines should consider the downstream implications for preterm delivery risk when weighing the population-level costs of screenings against the benefits of reduced cervical cancer mortality.
Authors: Rebecca Bromley-Dulfano, M.S., of Harvard University Medical School in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To ...
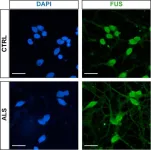
Research reveals the scale of disorder underpinning Motor Neurone Disease
2023-07-21
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 21 July 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Cells
Research reveals the scale of disorder underpinning Motor Neurone Disease
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL have shown that hundreds of proteins and mRNA molecules are found in the wrong place in nerve cells affected by Motor Neuron Disease (MND), also known as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).
ALS is a rapidly progressing and devastating condition that causes paralysis by affecting ...
Scripps Research scientists develop AI-based tracking and early-warning system for viral pandemics
2023-07-21
LA JOLLA, CA — Scripps Research scientists have developed a machine-learning system—a type of artificial intelligence (AI) application—that can track the detailed evolution of epidemic viruses and predict the emergence of viral variants with important new properties.
In a paper in Cell Patterns on July 21, 2023, the scientists demonstrated the system by using data on recorded SARS-CoV-2 variants and COVID-19 mortality rates. They showed that the system could have predicted the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 “variants of concern” (VOCs) ahead of their official designations by the World Health Organization (WHO). Their ...
University of Liverpool scientists make promising discovery in fight against breast cancer
2023-07-21
Researchers from the University of Liverpool have created a biomedical compound that has the potential to stop the spread of breast cancer. A recently published paper details these early findings.
Scientists from the Chemistry and Biochemistry Departments at the University of Liverpool and Nanjing Medical School in China have discovered a possible way to block proteins produced in the body when a patient has cancer and which causes its spread to other parts of the body. This process, called metastasis, is largely responsible for patient deaths.
The major problem hindering the successful treatment of commonly occurring cancers is not the primary tumour which can usually be removed by ...
Male crickets court females in unison – unless rivals get too close
2023-07-21
Male crickets sing in unison to attract females – but stop singing if a rival gets too close, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists watched more than 100 male field crickets, and measured how often they chirped at the same time (called “singing overlap”).
Singing by males one to five metres away from a listening male had a “stimulatory effect”, leading to a chorus of crickets singing together.
However, males were less likely to sing if another cricket chirped within one metre – possibly because the territorial insects instead chose to fight ...
Some people’s brain function still affected by Long COVID years after infection
2023-07-21
Some people’s brain function still affected by Long COVID years after infection
UK researchers have found that people with longer-term COVID-19 symptoms including brain fog showed reduced performance in tasks testing different mental processes up to two years after infection with the virus.
Researchers from King’s College London looked at whether infection with COVID-19 affected performance in two rounds of online cognitive testing that took place in 2021 and 2022. Data was collected for over 3,000 participants of the COVID Symptom Study Biobank study, across 12 tasks that tested memory, attention, reasoning, processing speed and ...
MASER technology scientist awarded funding for new research
2023-07-21
A scientist from Northumbria University has been awarded almost half a million pounds to develop a new technology which could transform deep-space communication, radio astronomy, medical imaging and airport security scanning.
Dr Juna Sathian has received a grant from the government’s Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to develop a new type of MASER (Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) device.
The forerunner to LASERs, MASERs were first discovered in the 1950s. But there has been ...
Researchers decipher the secrets of Benjamin Franklin’s paper money
2023-07-21
Benjamin Franklin may be best known as the creator of bifocals and the lightning rod, but a group of University of Notre Dame researchers suggest he should also be known for his innovative ways of making (literal) money.
During his career, Franklin printed nearly 2,500,000 money notes for the American Colonies using what the researchers have identified as highly original techniques, as reported in a study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research team, led by Khachatur Manukyan, an associate research professor ...
KIPA potentially predicts chemotherapy response in triple negative breast cancer
2023-07-21
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions are developing a strategy to predict the response of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) to chemotherapy, which would be a valuable tool for physicians deciding on the treatment with better probability of success on an individual basis. The study appears in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Multiple research innovations in cancer diagnostics are on display in this work,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Matthew Ellis, member of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center and the Dan ...
On the hunt for strangeness
2023-07-21
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Peter Hurck has been searching for strange particles, named such because they contain strange quarks, since beginning work on his Ph.D. As the 2023 Jefferson Science Associates (JSA) Postdoctoral Prize winner, he’ll continue conducting data analyses to identify strange particles and learn about their properties.
Many of these experiments that contribute to the data Hurck is analyzing are conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, which is managed and operated by JSA.
“Strangeness hasn't been studied as much because it's quite ...
ASBMB expresses concerns on proposed NIH budget cuts
2023-07-21
On July 19, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology released a statement expressing concerns on the National Institutes of Health budget proposed in the House Labor, Health and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies funding bill. The bill allocates only $44.7 billion for NIH, which represents a 6.4% decrease from fiscal year 2023 levels and would have detrimental repercussions for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke, the National Cancer Institute and the National Institute ...
[1] ... [1782]
[1783]
[1784]
[1785]
[1786]
[1787]
[1788]
[1789]
1790
[1791]
[1792]
[1793]
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
[1798]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.