Early peanut introduction gaining traction among US parents, but more work needed
2023-07-21
Peanut introduction is not well known among those with less access to health-care information
Having a pediatrician recommend early peanut introduction was best way for parents/caregivers to be informed
Fear of an allergic reaction is the main reason parents decline, but only 1% infants had a reaction, which was mild
CHICAGO --- In 2017, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) announced a dramatic reversal in its approach to peanut-allergy prevention, recommending parents expose their infants as young as four months old to peanuts to prevent peanut allergy.
In the five years since, early introduction ...
Digital pathology set to be a game changer in the medical industry
2023-07-21
Patients will receive faster and more accurate pathology results following a decade-long research project that is set to transform medical diagnosis.
The University of Queensland and Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology (SNP) have automated a microscope scanning and analysis system in Brisbane that has been tested, implemented and accredited ready for rollout around the world.
UQ Professor of AI Brian Lovell said the system significantly improved tests in terms of cost, quality and speed.
“This digital pathology technology processes thousands of tests a day and has been ...
A ‘toolbox of biocatalysts’ improves control over free radicals
2023-07-21
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — One of the central challenges for synthetic chemists is to impose control over free radicals. Highly reactive molecules with an unpaired electron, free radicals may be familiar to you; these are the type of molecules we take antioxidant supplements for, in an effort to tame oxidative stress.
In the world of synthetic chemistry, however, free radicals hold a lot of promise.
“Free radical chemistry is very useful for the synthesis of both bioactive small molecules and everyday polymers,” said UC Santa Barbara chemistry professor Yang Yang, an author of a paper on the matter that appears in Nature Catalysis. “However, ...
Experts alarmed as free Barbies given to UK primary schools to teach social skills
2023-07-21
Toy company Mattel has been criticised for “stealth marketing” after giving away free Barbie and Ken dolls to schools as part of a programme to teach empathy to children, finds an investigation published by The BMJ today.
Investigative journalist Hristio Boytchev reports that Mattell’s “Barbie School of Friendship” programme, in which free dolls are given for children to carry out role play exercises, has been rolled out to 700 schools across the UK, "with the potential to ...
Impacts of climate change on animals will be “multi-faceted,” study in CABI Reviews reveals
2023-07-21
A new study published in CABI Reviews suggests that the impact of climate change on animals will be “multi-faceted” with “cascading effects” across five welfare domains including nutrition, environment, behaviour, physical and mental health.
The research, highlights how researchers need to carefully consider which domains are immediate and future priority to safeguard the welfare and longevity of animals for food, as domestic pets and those for conservation in nature reserves and zoos.
Animals at risk from the impacts of climate change highlighted ...
Center for Open Science welcomes Yvette Seger to its Board of Directors
2023-07-20
Charlottesville, VA –The Center for Open Science (COS) is delighted to announce the appointment of Yvette Seger, PhD to its Board of Directors. Seger brings impressive experience and strategic leadership across a range of areas that aligns well with COS’s mission, vision, and activities, including policy analysis, advocacy, and implementation.
Seger holds multiple roles as Director of Science Policy, Deputy Director of the Office of Public Affairs, and Director of Strategic Scientific Program ...
Fueled by new chemistry, algorithm mines fungi for useful molecules
2023-07-20
A newly described type of chemistry in fungi is both surprisingly common and likely to involve highly reactive enzymes, two traits that make the genes involved useful signposts pointing to a potential treasure trove of biological compounds with medical and chemical applications.
It was also nearly invisible to scientists until now.
In the last 15 years, the hunt for molecules from living organisms — many with promise as drugs, antimicrobial agents, chemical catalysts and even food additives — has relied on computer algorithms trained to search the DNA of bacteria, ...
Streets recognized by CMS as legitimate locale to deliver health care
2023-07-20
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) officially recognized that medical care can be delivered on the street, making it possible for providers like USC’s Street Medicine team to be reimbursed for services provided to people who are currently unhoused.
The decision, which was announced on June 28, 2023, was the result of a multi-year effort on the part of leaders of USC Street Medicine and the Street Medicine Institute to have CMS create a place of service (POS) code for the street. As a result of this designation, street medicine providers nationwide will be able ...
Can prehabilitation improve inflammatory biomarkers in American Indian cancer patients?
2023-07-20
A University of Arizona Cancer Center researcher was awarded a $1.3 million grant from the National Cancer Institute to study the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions in American Indian patients with obesity-related solid tumor cancers who are preparing for surgery.
According to principal investigator Jennifer Erdrich, MD, MPH, there are 13 cancer subtypes linked to obesity that account for 40% of all cancers diagnosed annually in the United States.
American Indian and Alaska Native populations are more than 1.5 times more likely to be obese than the general population and have some of the lowest cancer survival rates in the nation. Many factors ...
Hardship affects the gut microbiome across generations
2023-07-20
Key takeaways
A UCLA-led study has shown that hardship experienced by mothers during their own childhood or during pregnancy is reflected in the composition of their 2-year-old children’s gut microbiome.
It was previously understood that in rodents, prenatal stress affects microbiomes into adulthood, but how long after birth the effects lasted in humans was unknown.
The changes to this community of microorganisms are likely among the ways that hardship affects a child’s socioemotional development.
Hardship experienced by mothers during their own childhood or during pregnancy is reflected ...
Department of Energy releases draft request for proposals for the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory Management and Operating Contract Competition
2023-07-20
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the release of a Draft Request for Proposals (RFP) for the selection of a management and operating (M&O) contractor for the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL).
DOE is soliciting public feedback on the draft RFP. Interested parties are encouraged to take advantage of this opportunity to provide comments regarding the draft contract performance requirements. The draft RFP will be open for public comment until August ...
WFSJ presents WCSJ2025 and WCSJ2027!
2023-07-20
“It’s a great privilege to host the World Conference of Science Journalists 2025,” says Mandi Smallhorne, president of SASJA. “As it is the first time the conference has ever been held on African soil, this is truly a historic event, we’re delighted to be the pioneers! We look forward to welcoming the science journalists of the world to our home; we are sure it will be an eye-opening and rewarding experience. Our beautiful country has a lot to share, and that includes some fascinating scientific experiences, from the Square Kilometre Array, to cutting edge genomic sequencing, to the Cradle of Humankind. We are brewing ...
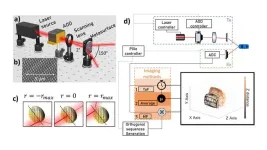
Wide field-of-view metasurface-enhanced scanning lidar technology
2023-07-20
Pulsed laser scanning lidar is a core technology for autonomous driving and robotic mobility. Herein, a directional light pulse is backscattered by a reflective object and the elapsed time between emission and detection of the pulse is used to calculate depth. These direct time-of-flight (d-ToF) measurements of returning light pulses enable the three-dimensional imaging of complex scenes.
At present, lidar technology requires numerous developments, including enhancement of the observation field of view (FoV) with high angular resolution, improvement of the imaging frame rate, extension of the ambiguity range by reducing the signal-to-noise ...
Powerhouse proteins protect heart cells from chemotherapy damage
2023-07-20
Researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have identified a process by which enzymes can help prevent heart damage in chemotherapy patients.
The enzymes are normally found in a cell’s mitochondria, the powerhouse that produces energy. But when heart cells are put under stress from certain types of chemotherapy drugs, the enzymes move into the cell’s nucleus, where they are able to keep the cells alive. The paper is published in Nature Communications.
“As chemotherapy has become more and more effective, we have more and more cancer survivors. But the tragic ...
New theory better explains how the brain stores memories
2023-07-20
How useful a memory is for future situations determines where it resides in the brain, according to a new theory proposed by researchers at HHMI"s Janelia Research Campus and collaborators at UCL.
The theory offers a new way of understanding systems consolidation, a process that transfers certain memories from the hippocampus – where they are initially stored – to the neocortex -- where they reside long term.
Under the classical view of systems consolidation, all memories move from the hippocampus to the neocortex over time. But this view doesn’t always hold up; research shows some memories permanently reside ...
Draining 401(k) accounts when changing jobs: the hidden time bomb undermining retirement savings
2023-07-20
Key Takeaways:
At job separation, 41.4% of employees cash out 401(k) savings, most draining their entire accounts.
Cashing out increases with the proportion of the 401(k) balance contributed by employers. The “account composition effect” is most likely driven by behavioral rather than economic explanations.
The cash-out option was presented to terminating employees in a salient way, unintentionally nudging them to withdraw their 401(k) savings.
BALTIMORE, MD, July 17, 2023 – When researchers set out to study 401(k) retirement savings ...
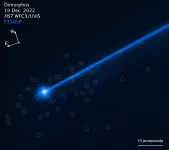
Hubble sees boulders escaping from asteroid dimorphos
2023-07-20
The popular 1954 rock song "Shake, Rattle and Roll," could be the theme music for the Hubble Space Telescope's latest discovery about what is happening to the asteroid Dimorphos in the aftermath of NASA's DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) experiment. DART intentionally impacted Dimorphos on September 26, 2022, slightly changing the trajectory of its orbit around the larger asteroid Didymos.
Astronomers using Hubble's extraordinary sensitivity have discovered a swarm of boulders that were possibly shaken off the asteroid when NASA deliberately slammed the half-ton DART impactor spacecraft into Dimorphos ...
The American Society for Nutrition appoints Xingen Lei, Ph as next editor-in-chief of The Journal of Nutrition
2023-07-20
Rockville, MD (July 20, 2023) Xingen Lei, PhD, professor of molecular nutrition and associate dean of research and innovation at Cornell University’s College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, has been named the next editor-in-chief of The Journal of Nutrition, effective January 1, 2024. Established in 1928, The Journal of Nutrition is the oldest journal devoted to publishing influential original research, reviews, and perspectives of molecular, cellular, animal, human, and population nutrition and mechanisms.
Dr. Lei has published extensively in The Journal of Nutrition ...
Sending the shoes back? How about this lovely gift card? Cross-selling can help retailers avoid lost revenue from returns
2023-07-20
https://www.rotman.utoronto.ca/Connect/MediaCentre/NewsReleases/20230720
Toronto - It’s become so darn easy to order stuff thanks to the miracles of online shopping. But it’s not so simple on the retailer end, especially when more than 16 per cent of those sales are later sent back. In the U.S., that adds up to a staggering $816 billion in lost revenue.
Cross-selling can help, say a pair of researchers. Their experiments show that once we’ve chosen to buy something, we tend to consider that money as already spent or gone, also called ...
ECOG-ACRIN adds a new treatment trial to the ComboMATCH precision medicine initiative
2023-07-20
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) has enrolled the first patient in a new treatment trial to evaluate the effectiveness of adding nilotinib to standard paclitaxel chemotherapy. The trial (EAY191-E4) is for the treatment of adults with cancers that are getting worse after being treated with taxane-based chemotherapy. It is a new addition to the recently launched ComboMATCH precision medicine initiative, which uses tumor biology as a guiding point for testing new combinations of cancer drugs.
James M. Ford, MD, the ECOG-ACRIN Chair for ComboMATCH and Professor of Medicine (Oncology) and Genetics at Stanford University, ...
Climate science is catching up to climate change with predictions that could improve proactive response
2023-07-20
In Africa, climate change impacts are experienced as extreme events like drought and floods. Through the Famine Early Warning Systems Network (which leverages expertise from USG science agencies, universities, and the private sector) and the IGAD Climate Prediction and Applications Center, it has been possible to predict and monitor these climatic events, providing early warning of their impacts on agriculture to support humanitarian and resilience programming in the most food insecure countries of the world.
Science is beginning to catch up with and even ...
Detecting threats beyond the limits of human, sensor sight
2023-07-20
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Remember what it’s like to twirl a sparkler on a summer night? Hold it still and the fire crackles and sparks but twirl it around and the light blurs into a line tracing each whirl and jag you make.
A new patented software system developed at Sandia National Laboratories can find the curves of motion in streaming video and images from satellites, drones and far-range security cameras and turn them into signals to find and track moving objects as small as one pixel. The developers say this system can enhance the performance of any remote sensing application.
“Being able to track each pixel from a distance matters, ...
Nature inspires breakthrough achievement: hazard-free production of fluorochemicals
2023-07-20
For the first time, Oxford chemists have generated fluorochemicals – critical for many industries – without the use of hazardous hydrogen fluoride gas.
The innovative method was inspired by the biomineralization process that forms our teeth and bones.
The results are published today in the leading journal Science.
A team of chemists have developed an entirely new method for generating critically important fluorochemicals that bypasses the hazardous product hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas. ...
Could early induction of labor reduce inequities in pregnancy outcomes?
2023-07-20
Inducing labor at 39 weeks of pregnancy has the greatest benefit in risk reduction for women from more socioeconomically deprived areas, according to a new study published July 13th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Ipek Gurol-Urganci of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, UK, and colleagues. The findings suggest that increased uptake of induction of labor at 39 weeks may help reduce inequities in adverse perinatal outcomes.
Adverse perinatal outcomes— which include stillbirths, neonatal ...
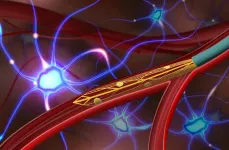
Ultra-flexible endovascular probe records deep-brain activity in rats, without surgery
2023-07-20
A new ultra-small and ultra-flexible electronic neural implant, delivered via blood vessels, can record single-neuron activity deep within the brains of rats, according to new study. “This technology could enable long-term, minimally invasive bioelectronic interfaces with deep-brain regions, writes Brian Timko in a related Perspective. Brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) enable direct electrical communication between the brain and external electronic systems. They allow brain activity to directly ...
[1] ... [1783]
[1784]
[1785]
[1786]
[1787]
[1788]
[1789]
[1790]
1791
[1792]
[1793]
[1794]
[1795]
[1796]
[1797]
[1798]
[1799]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.